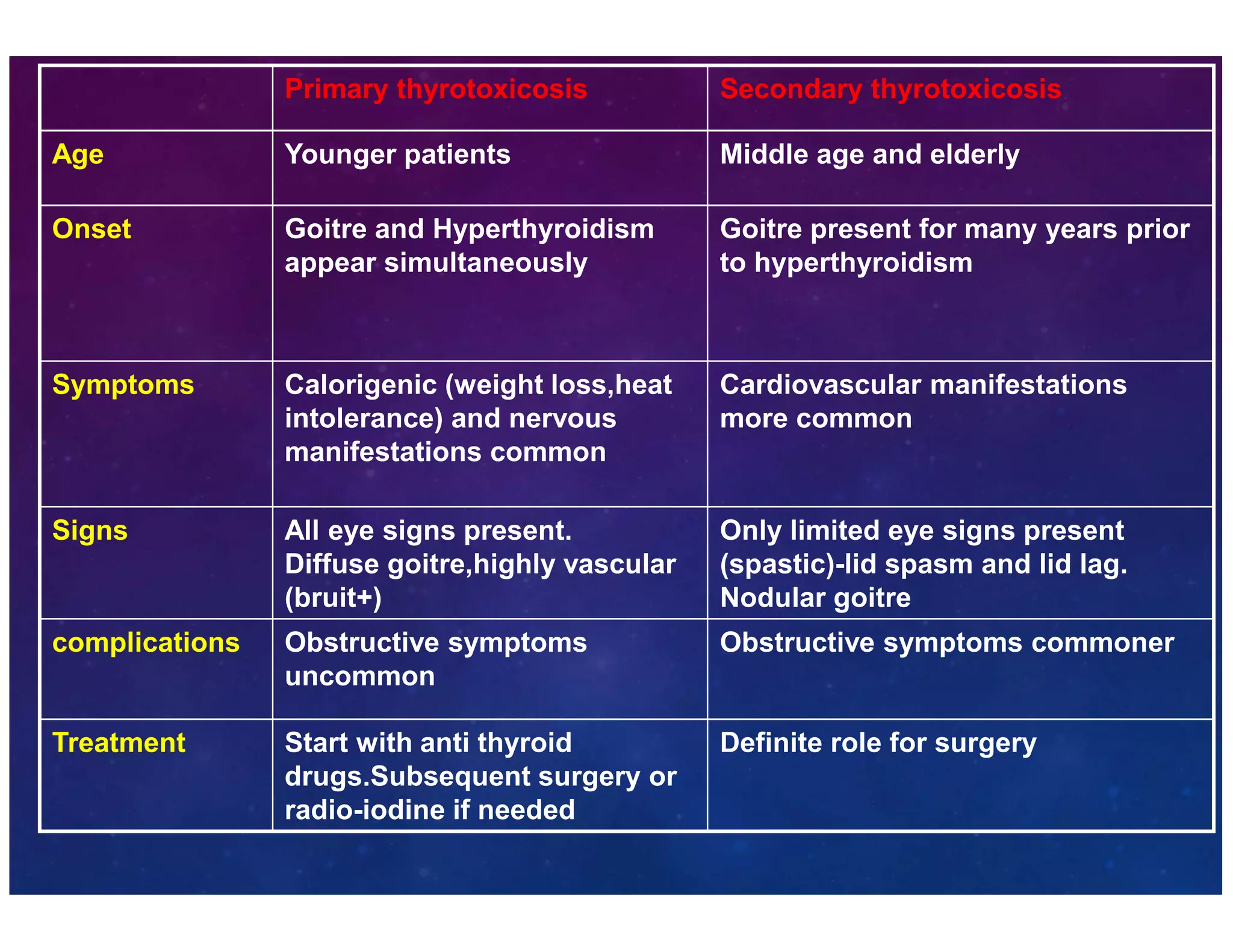
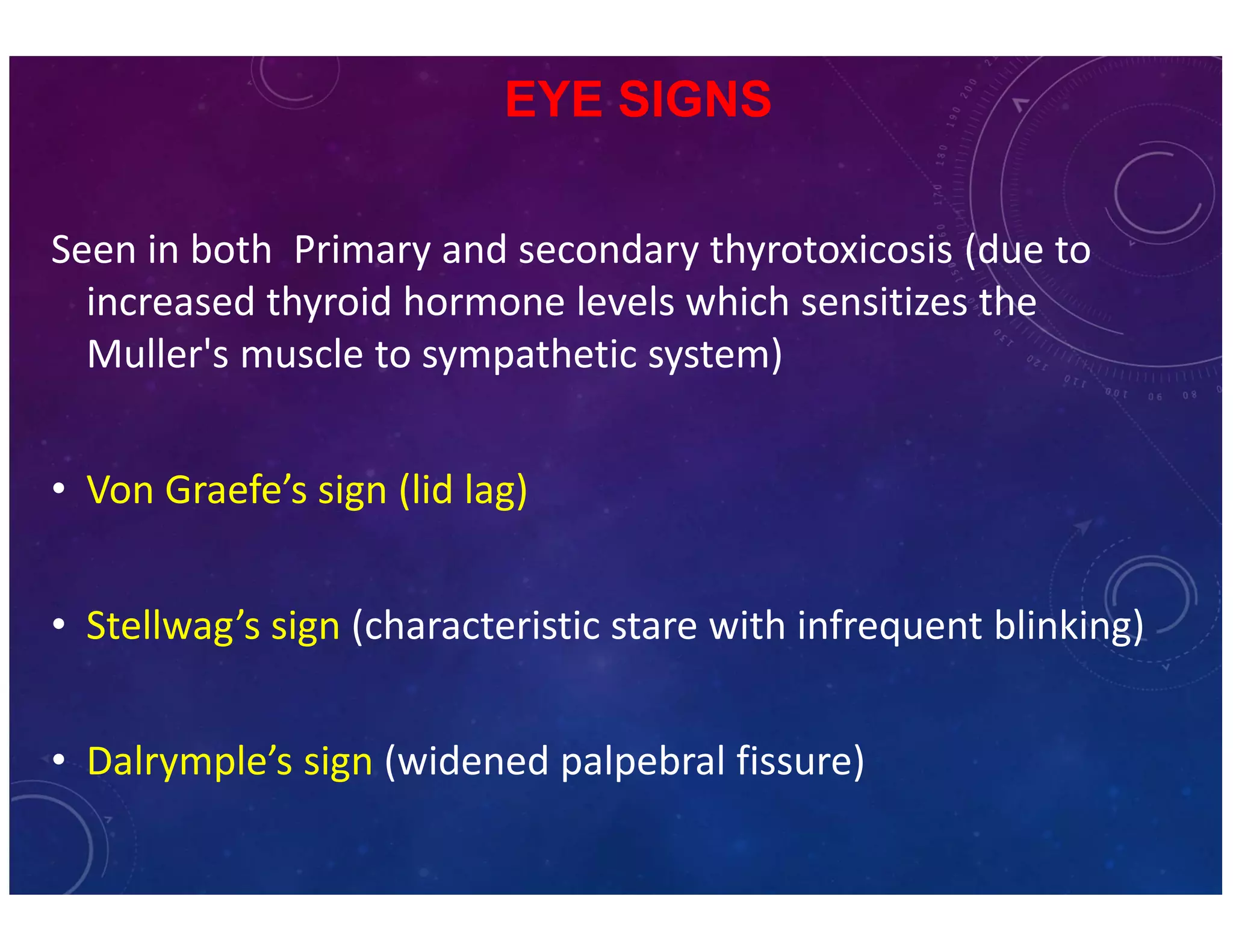
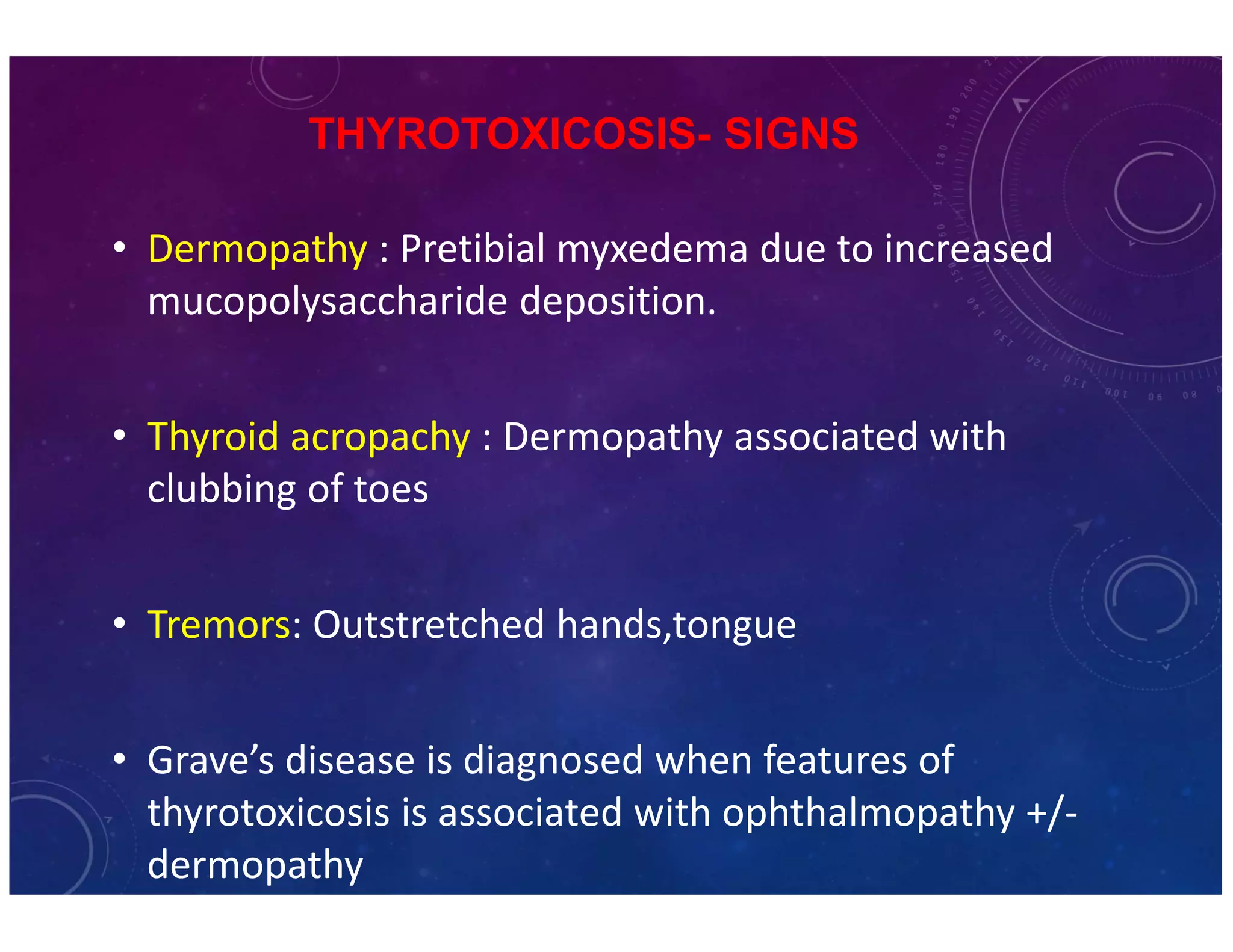
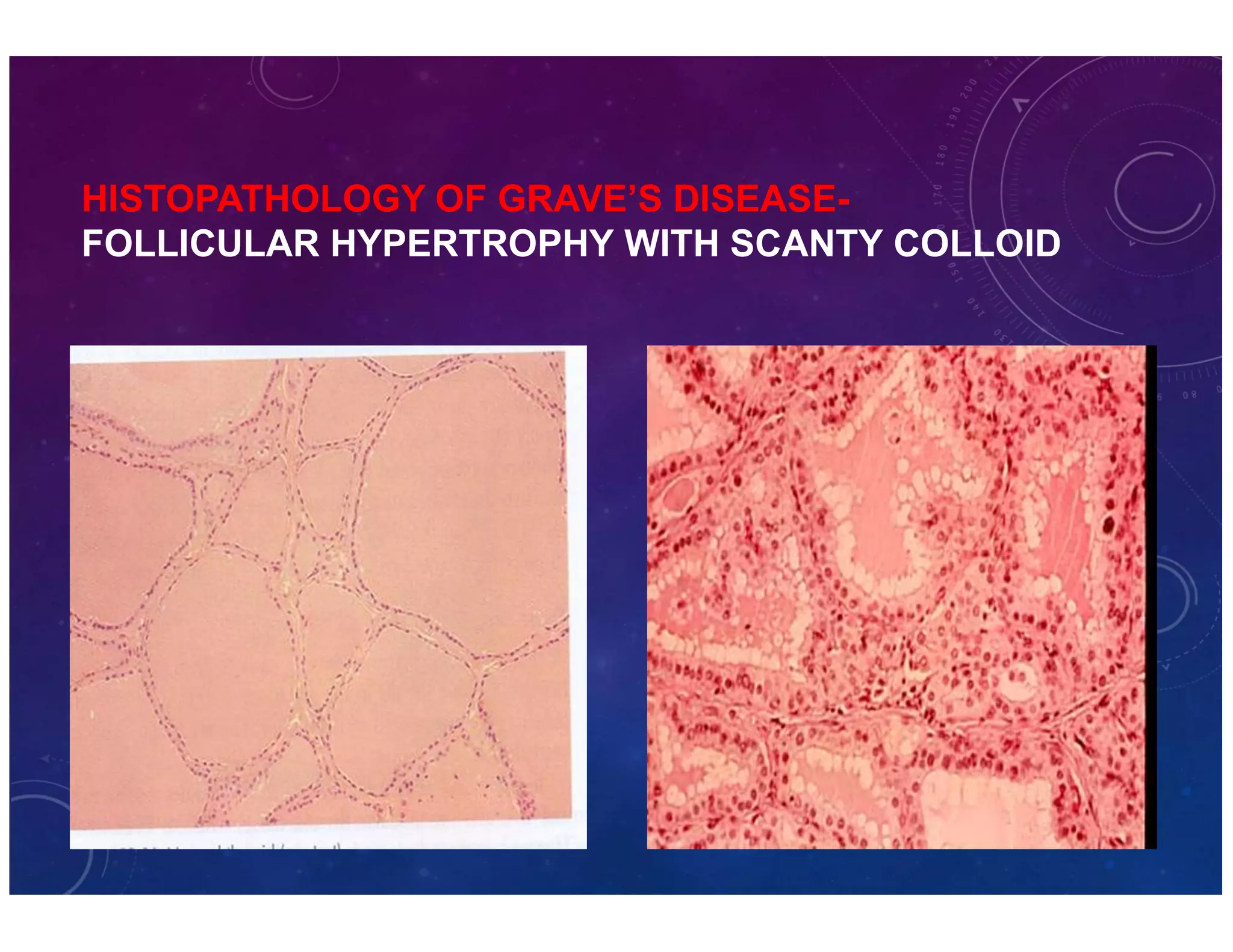
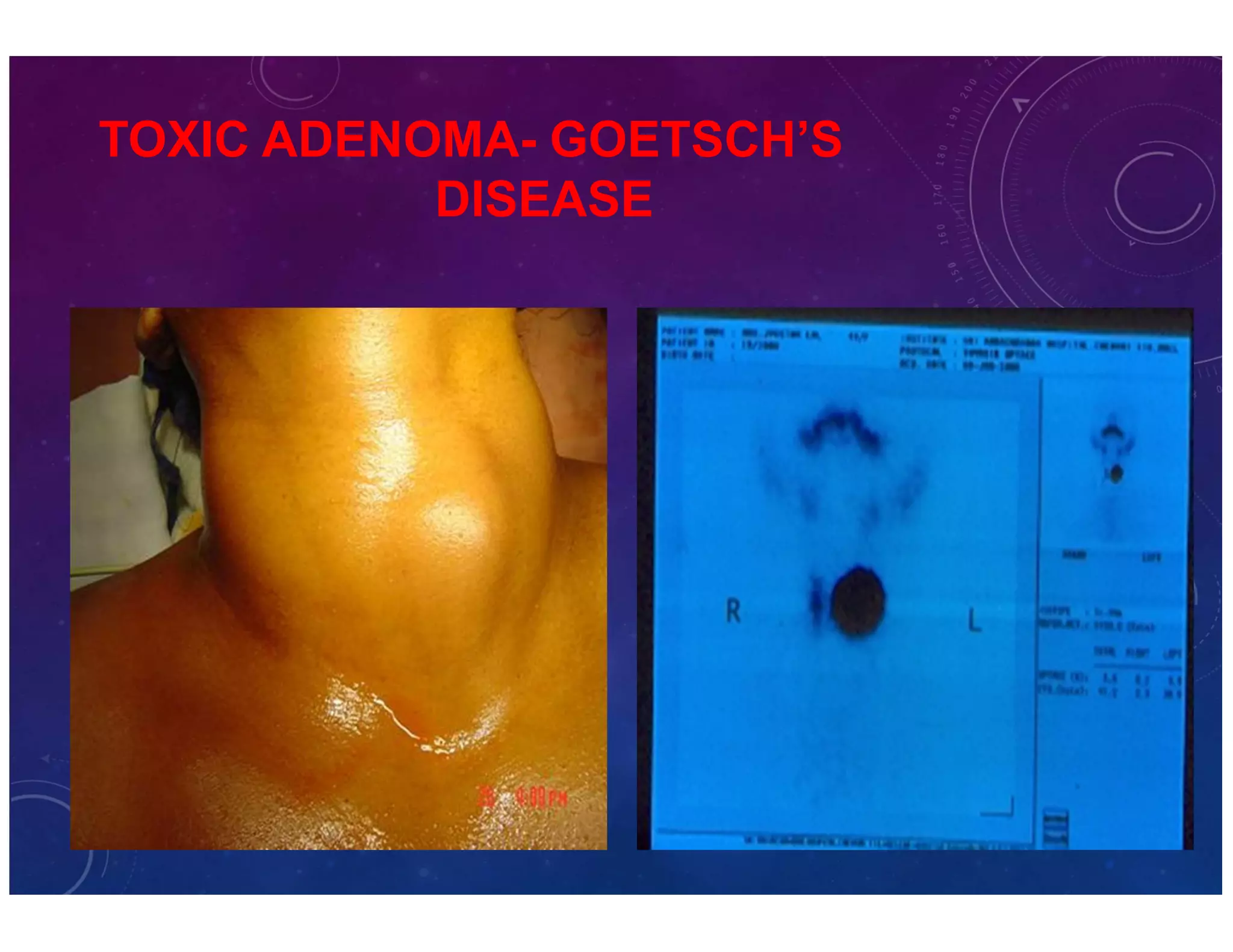
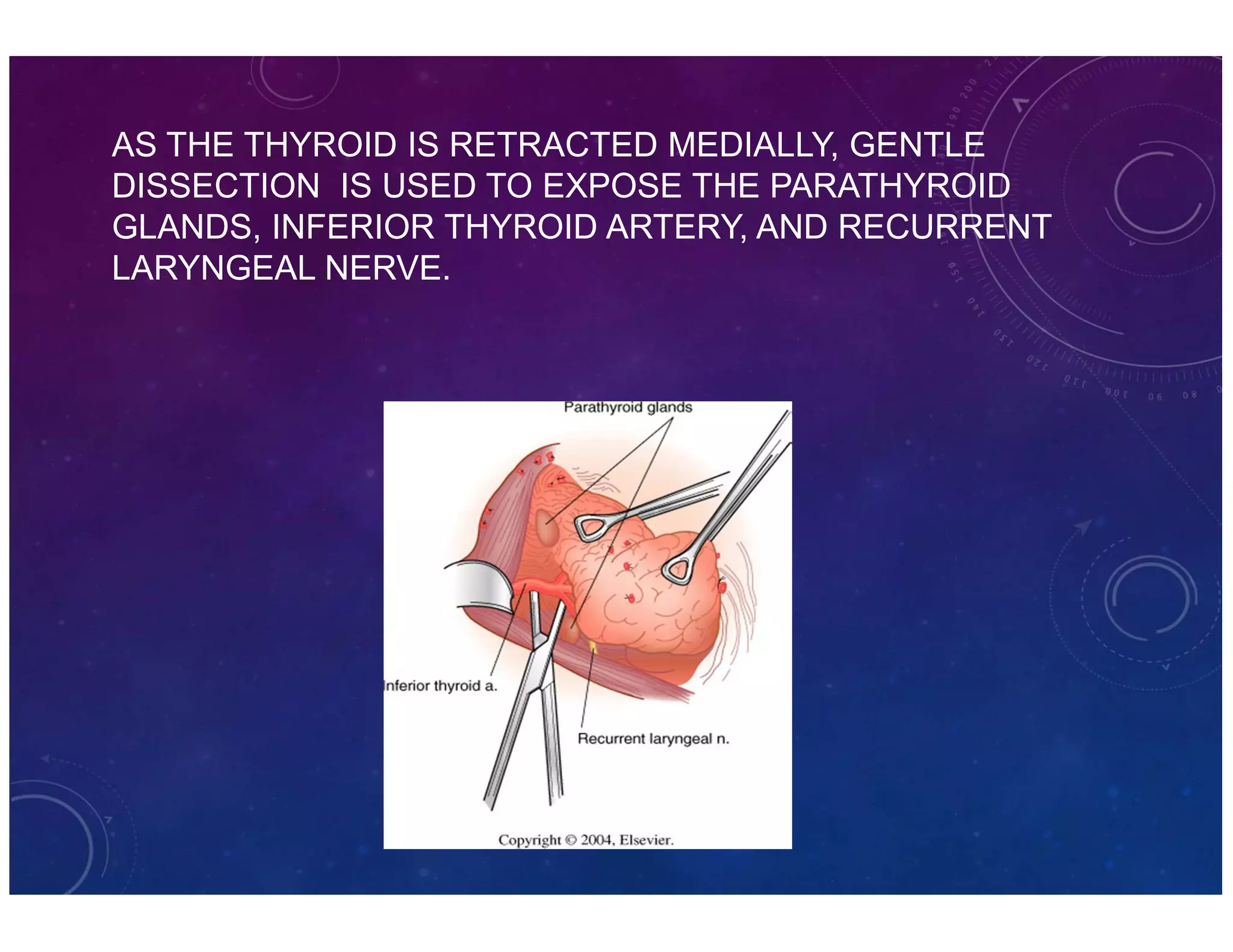
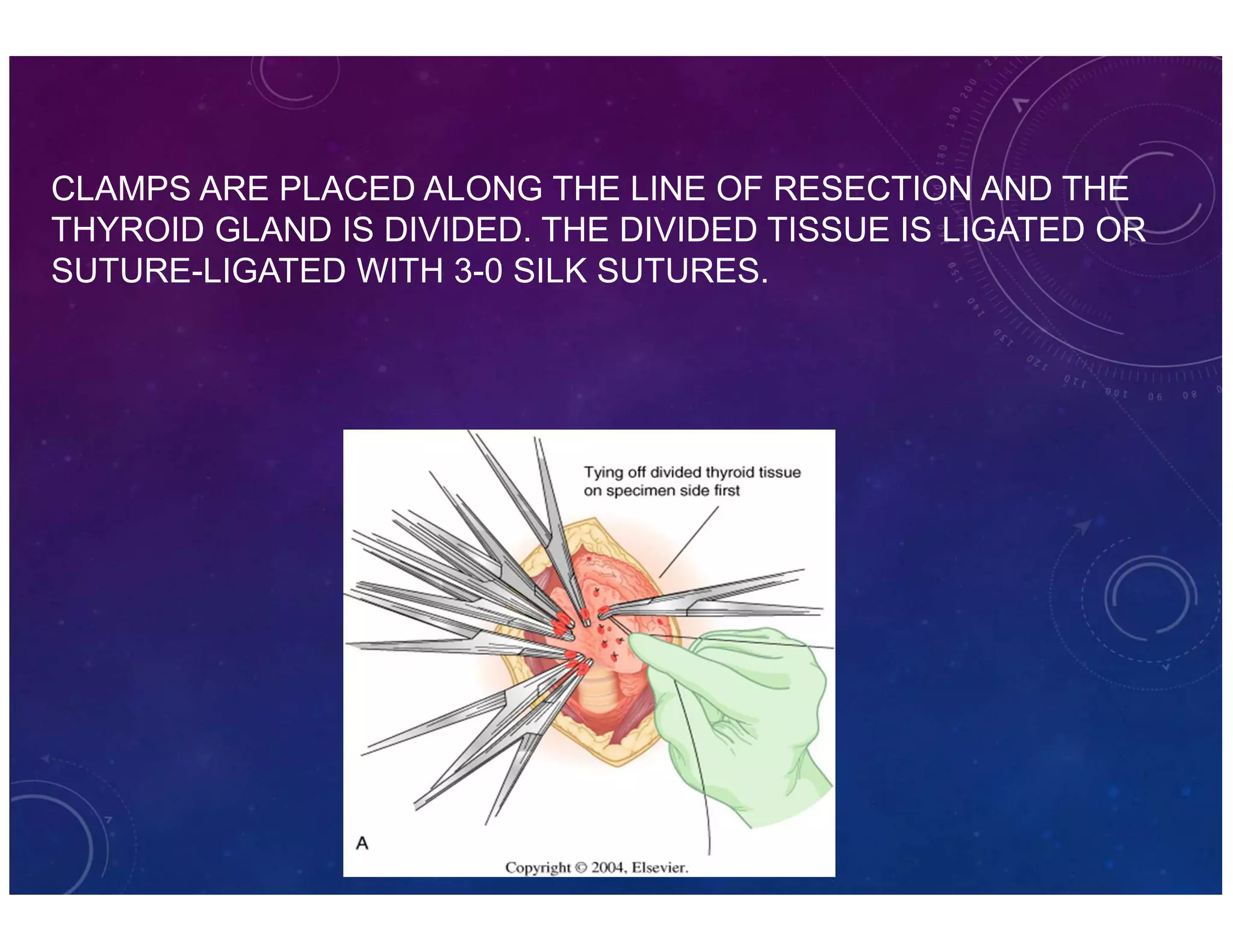
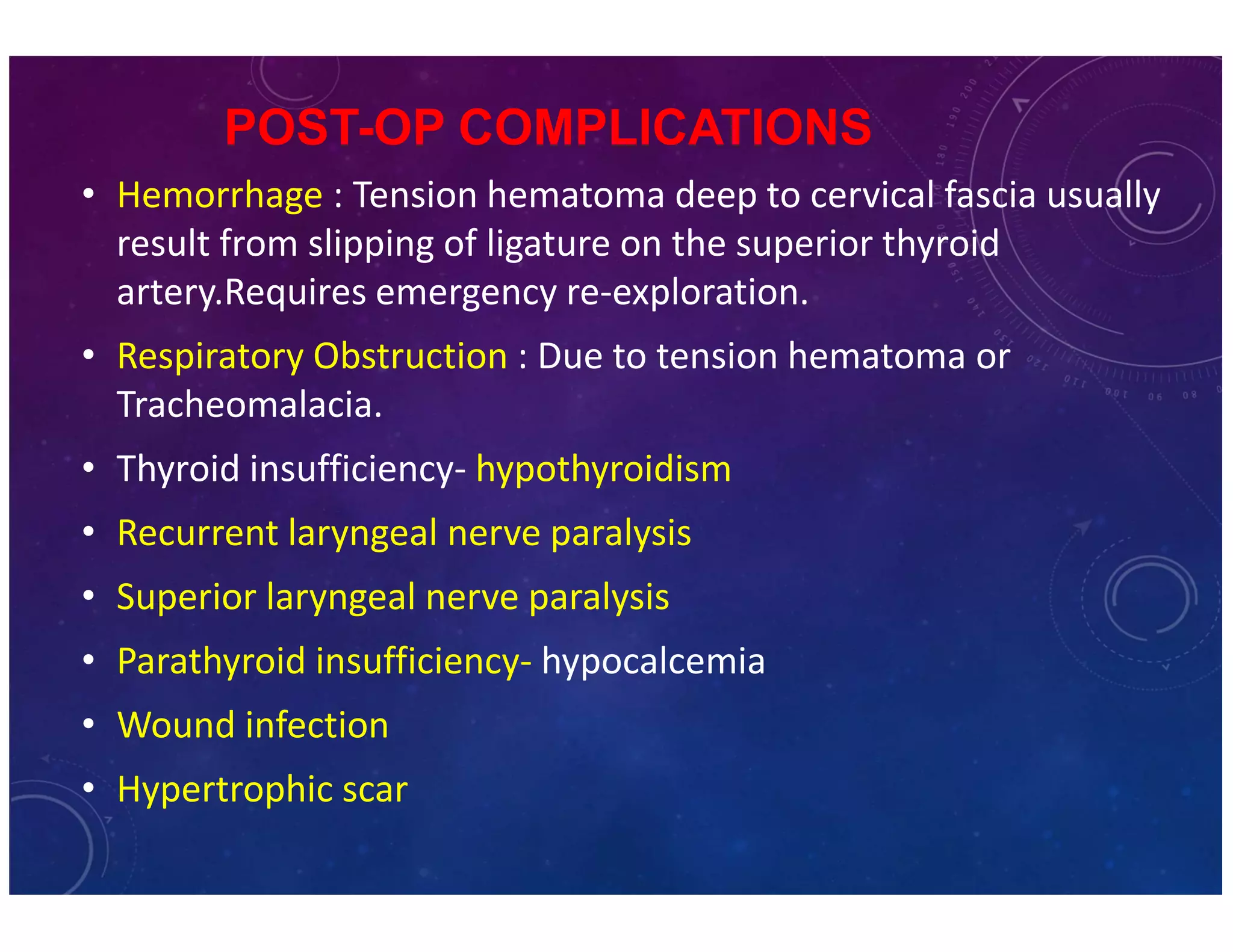
The document discusses various thyroid conditions, particularly focusing on thyrotoxicosis, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options including Graves' disease, toxic nodular goiter, and toxic adenoma. Treatments such as anti-thyroid drugs, radioactive iodine ablation, and surgical interventions are outlined, alongside their indications, mechanisms, and potential complications. It emphasizes the necessity of careful management in cases such as thyroid storm and during pregnancy.