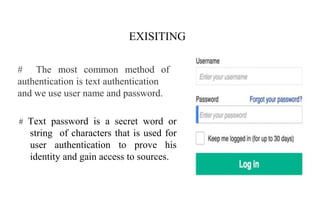
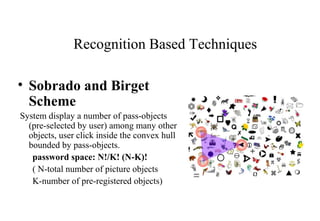
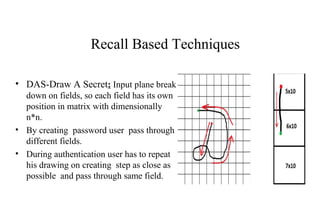
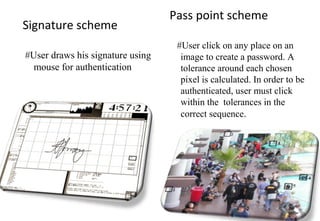
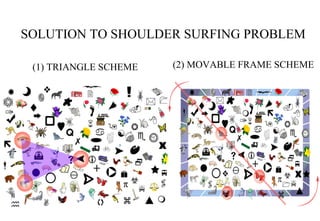
Graphical passwords provide an alternative authentication method to alphanumeric passwords. They involve selecting images or points on images to create a password. This survey paper categorizes existing graphical password techniques as either recognition-based, where the user identifies previously selected images, or recall-based, where the user reproduces a previous creation like a drawing. While graphical passwords can be more memorable and secure, challenges include longer registration/login times and vulnerability to shoulder surfing. Proposed solutions to shoulder surfing involve using movable frames or geometric configurations like triangles.