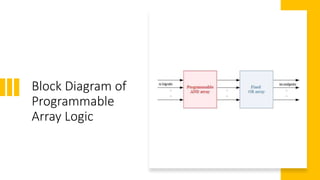
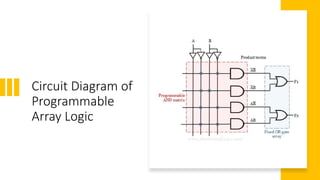
This document provides an overview of Programmable Array Logic (PAL). It defines PAL as a commonly used programmable logic device with a programmable AND array and fixed OR array, making it easier to use but less flexible than a PLA. The document includes a block diagram of PAL, compares it to other programmable logic devices like PLA and ROM, provides an example of implementing Boolean functions with a PAL, and lists advantages such as being highly efficient, low cost, secure, reliable, and flexible.