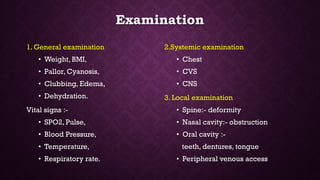
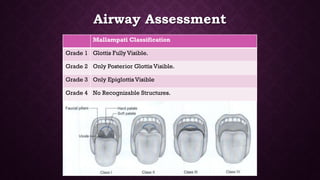
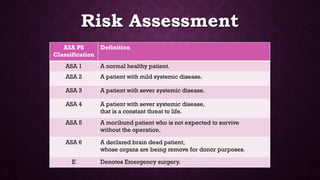
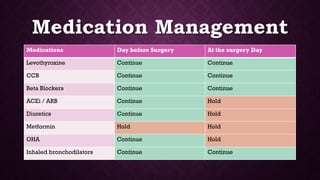
This document provides an overview of pre-anesthetic patient assessment. It discusses the goals of evaluating a patient's general health and anticipating complications. The pre-anesthetic checkup process involves collecting medical history, performing a physical exam, and ordering relevant medical investigations. This allows doctors to understand patient risk factors, create an anesthesia plan, and gain informed consent. The document outlines steps for history taking, examination, airway assessment, common investigations, risk classification, and medication management guidelines to safely prepare a patient for anesthesia and surgery.