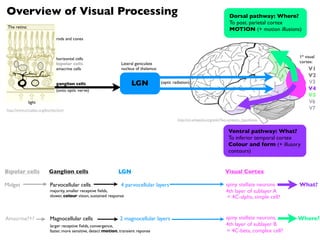
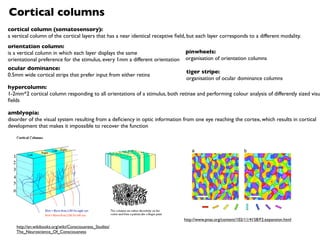
The document provides an overview of visual processing in the brain. It describes the two major visual pathways - the dorsal pathway which processes motion and travels to the parietal cortex, and the ventral pathway which processes colour and form and travels to the temporal cortex. It outlines the key stages of visual processing from the retina through the lateral geniculate nucleus and into the primary and higher-level visual cortices.