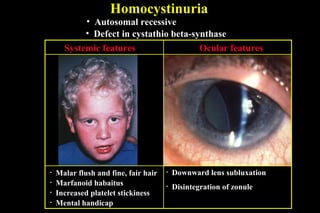
Ectopia lentis refers to displacement of the lens from its normal position. It can be acquired through trauma or tumors, or inherited through isolated familial forms or associated with systemic syndromes like Marfan syndrome, Weill-Marchesani syndrome, and Homocystinuria. Treatment options depend on the cause and symptoms but may include spectacle correction, laser zonulysis to displace the lens, or surgical removal of the lens.