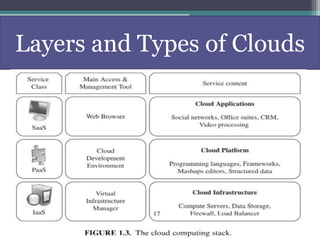
The document provides an overview of cloud computing principles, technologies, architecture, and applications, aimed at educating students on this subject. It includes definitions, historical context, service models (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS), and challenges within cloud environments. Key features and security considerations are also discussed to illustrate the operational intricacies of cloud computing.