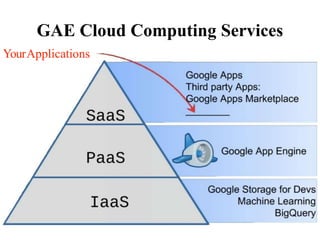
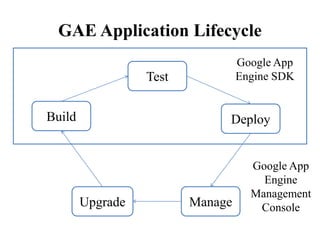
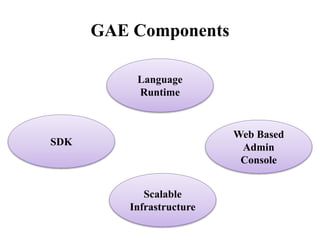
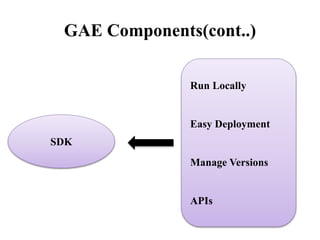
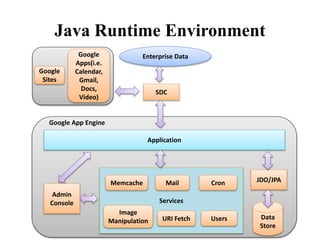
The document presents an overview of Google App Engine (GAE), a cloud computing platform that enables the hosting of web applications on Google's infrastructure. It discusses features such as automatic scaling, easy deployment, and the application lifecycle along with a comparison to Amazon Web Services. The conclusion highlights GAE's flexibility, security, and ease of use, while noting limitations like language restrictions and resource caps.