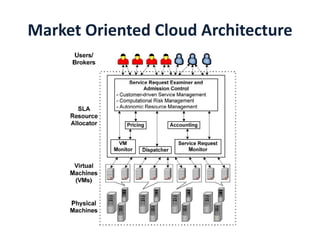
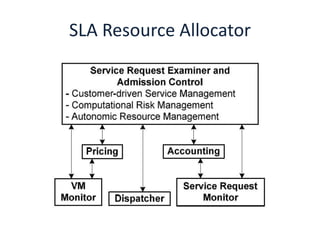
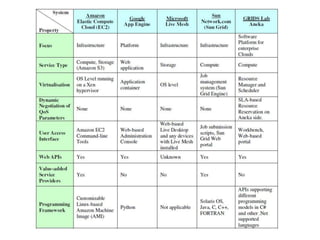
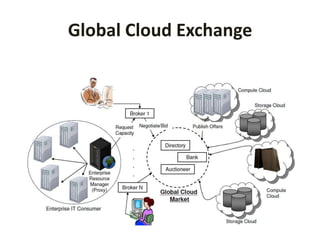
This document discusses the vision, hype and reality of delivering IT services as computing utilities. It outlines the need for a market oriented cloud architecture to regulate supply and demand of cloud resources. Emerging cloud platforms like Amazon EC2, Google App Engine, Microsoft Live Mesh and Sun Grid are presented. The limitations of present cloud service providers are discussed. Finally, the concept of a Global Cloud Exchange is proposed to address these limitations through features like a market directory, banking system, brokers and price setting mechanisms.