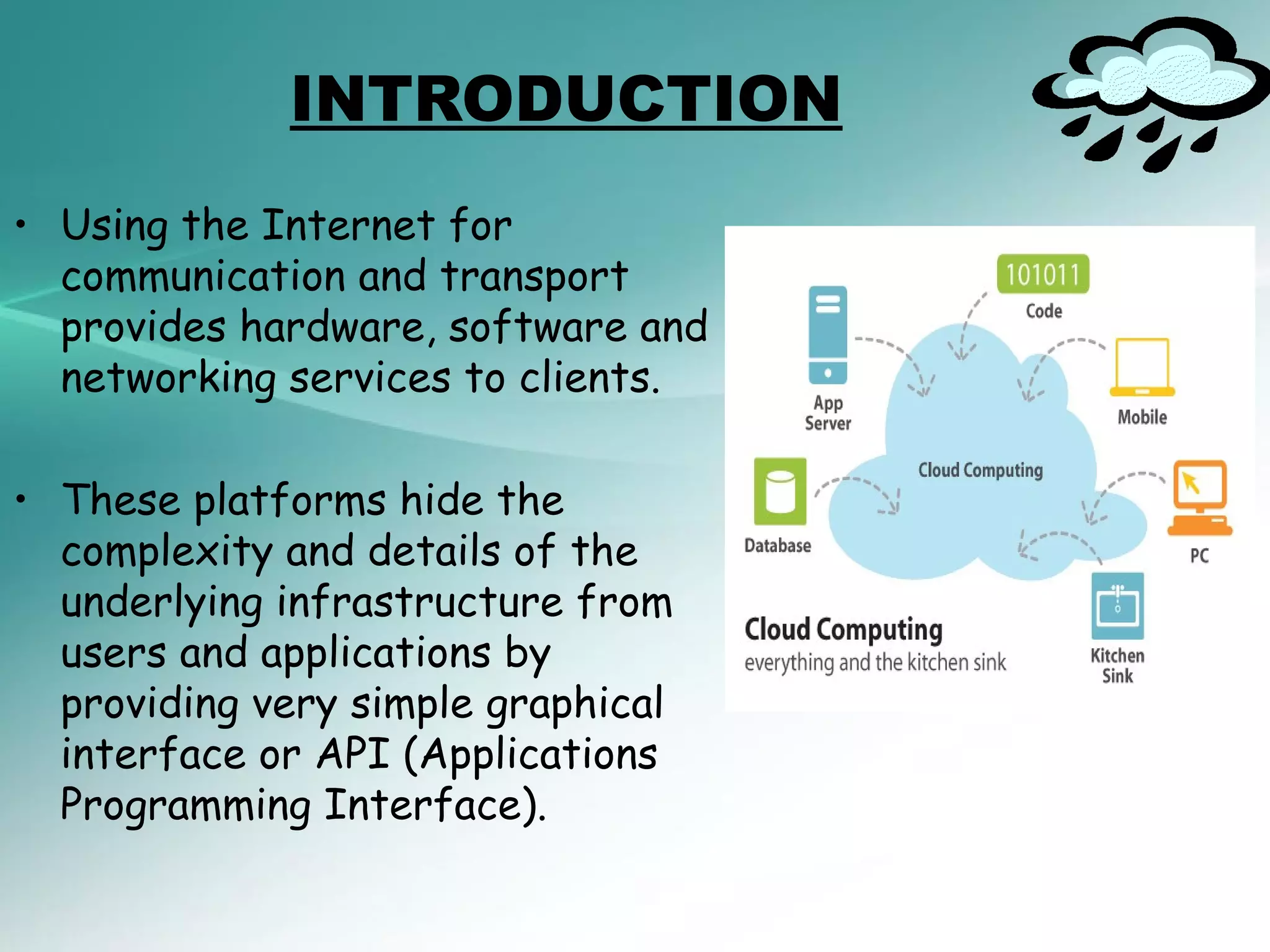
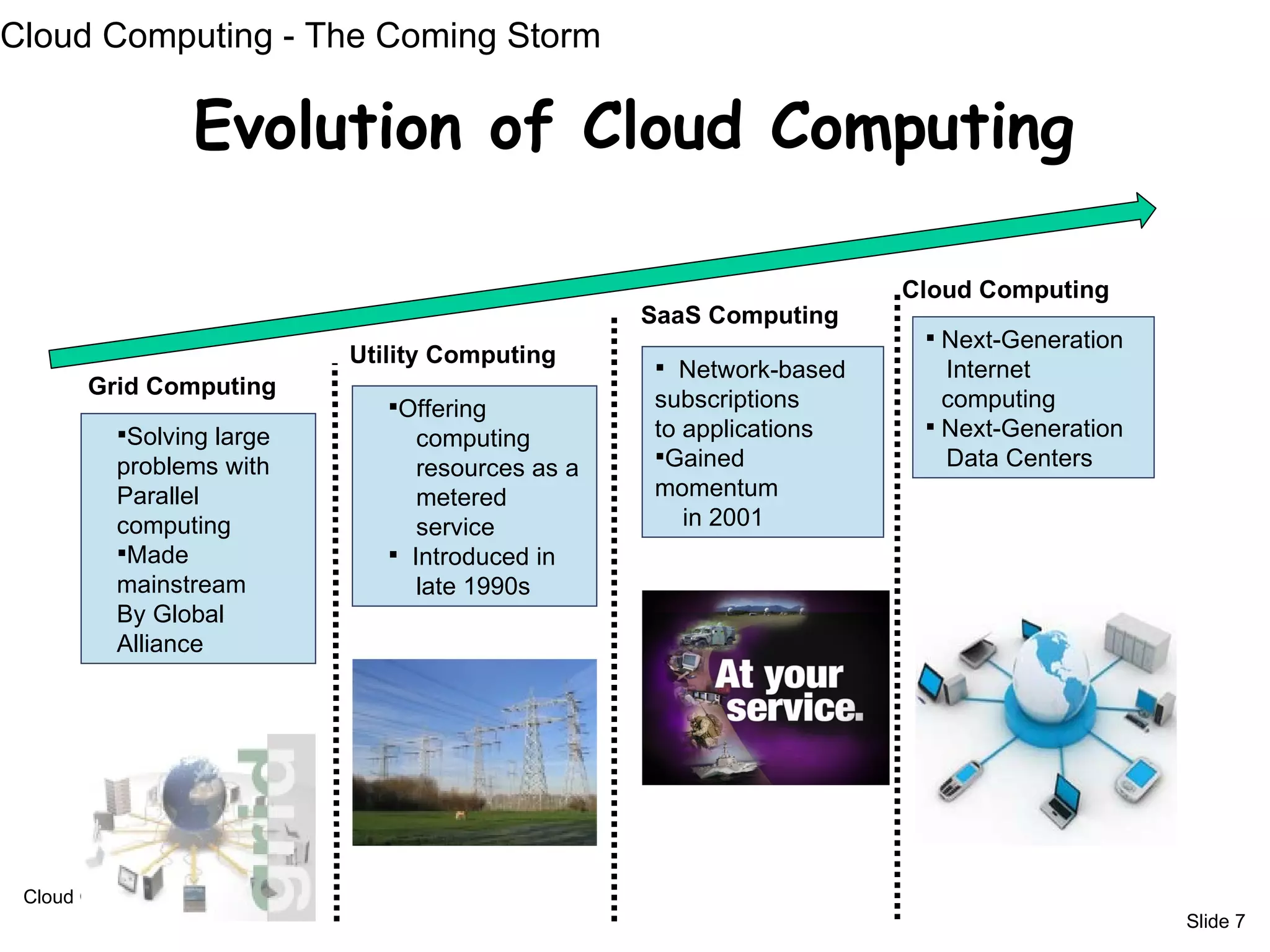
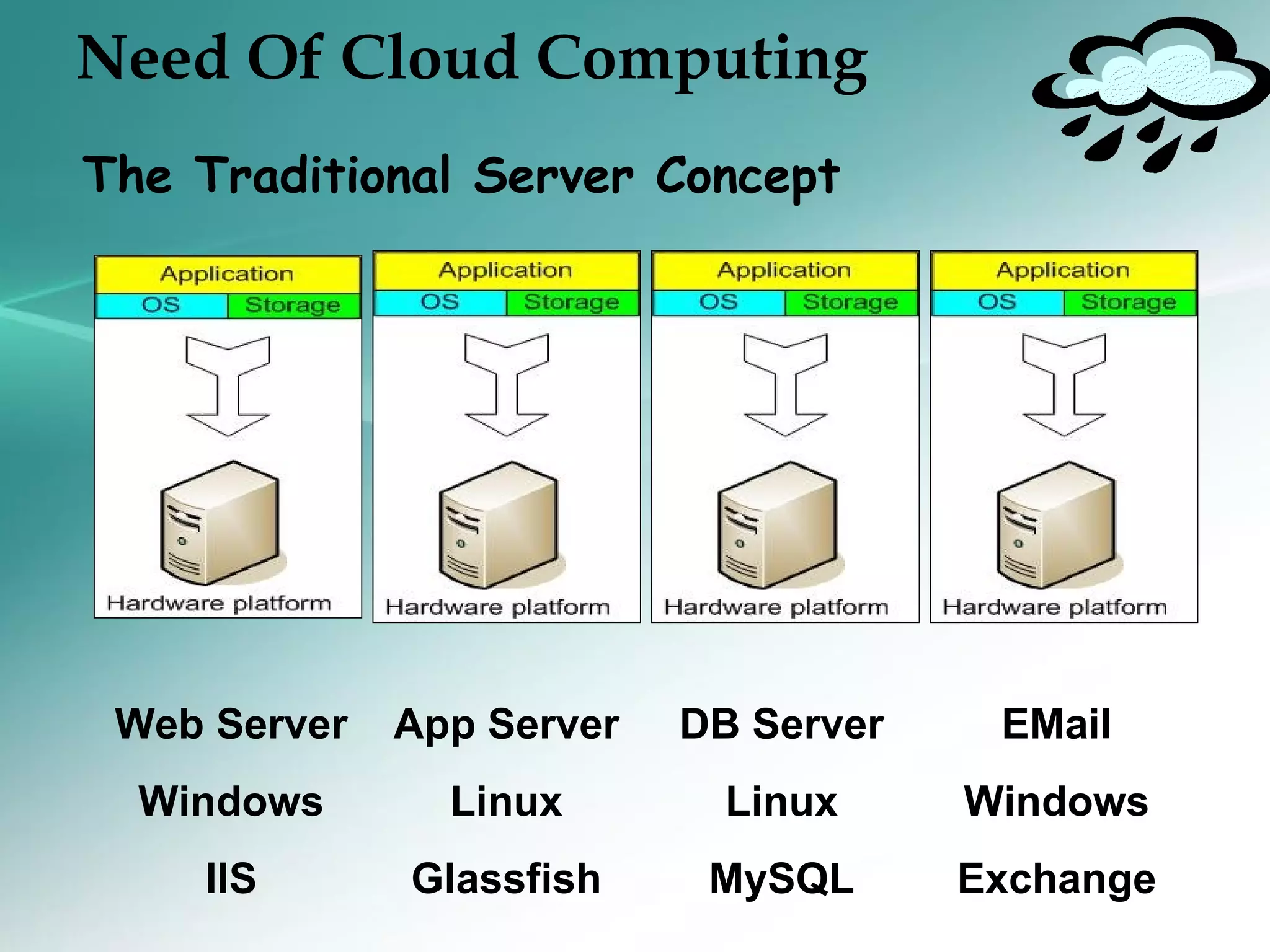
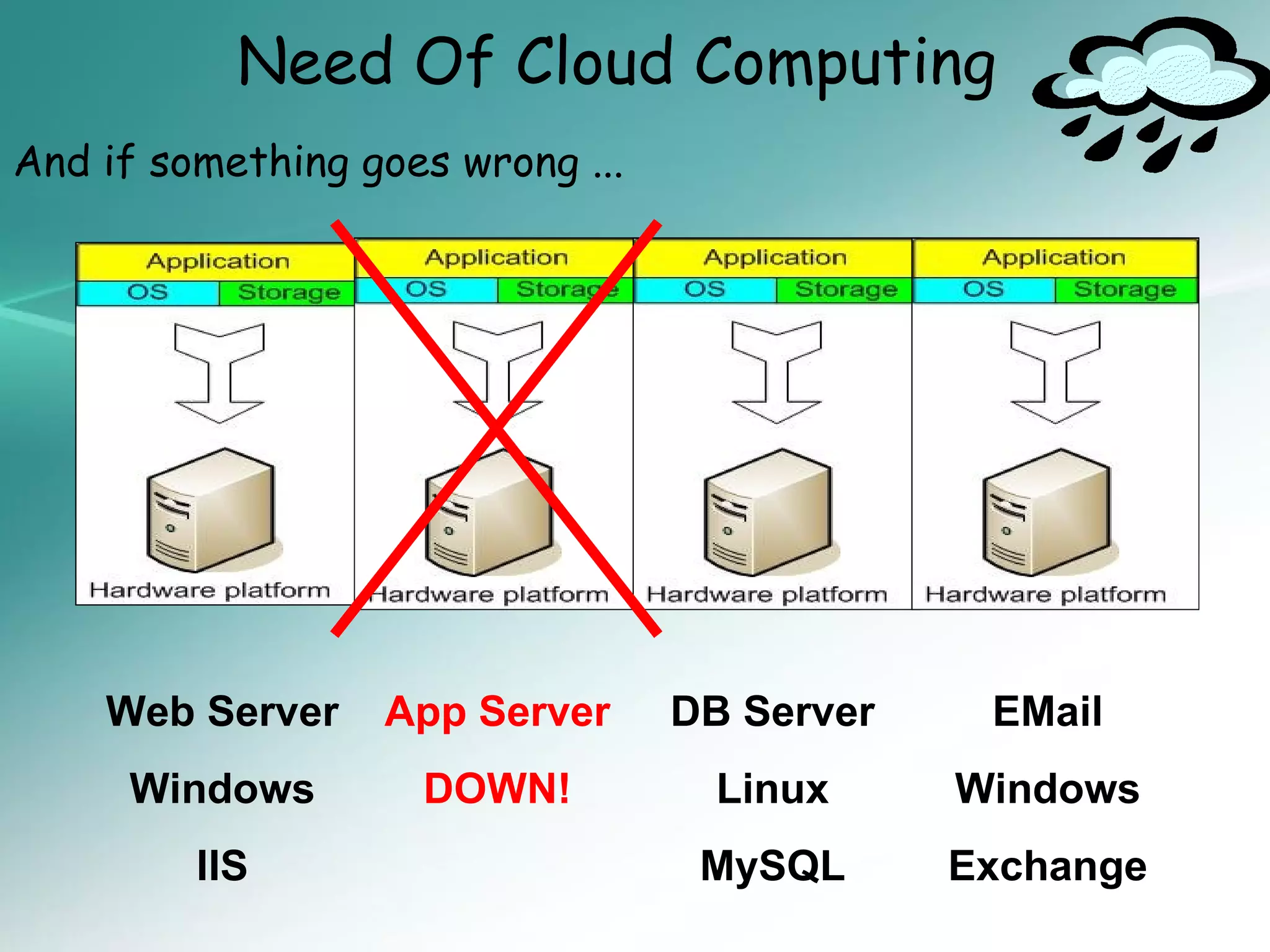
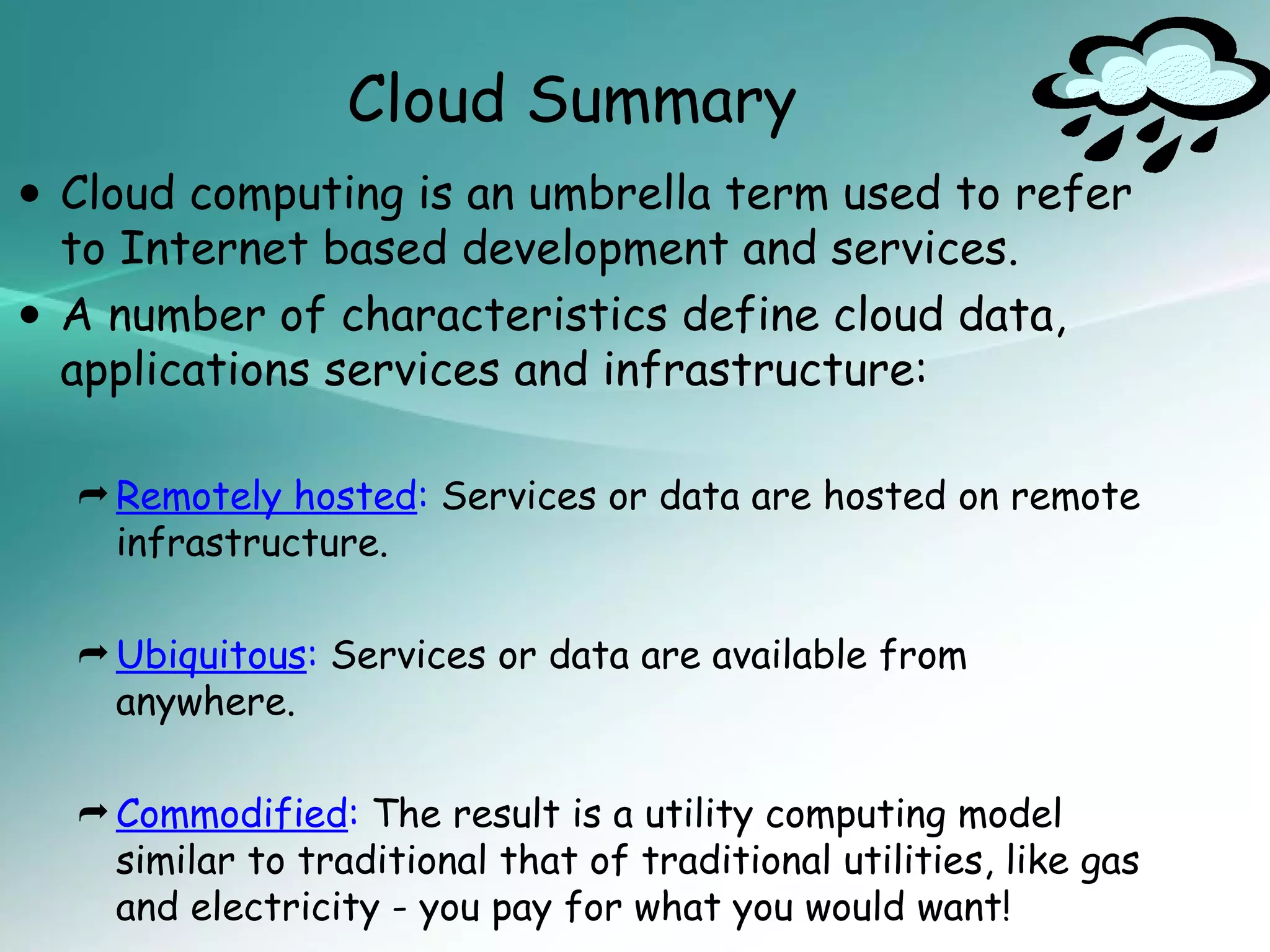
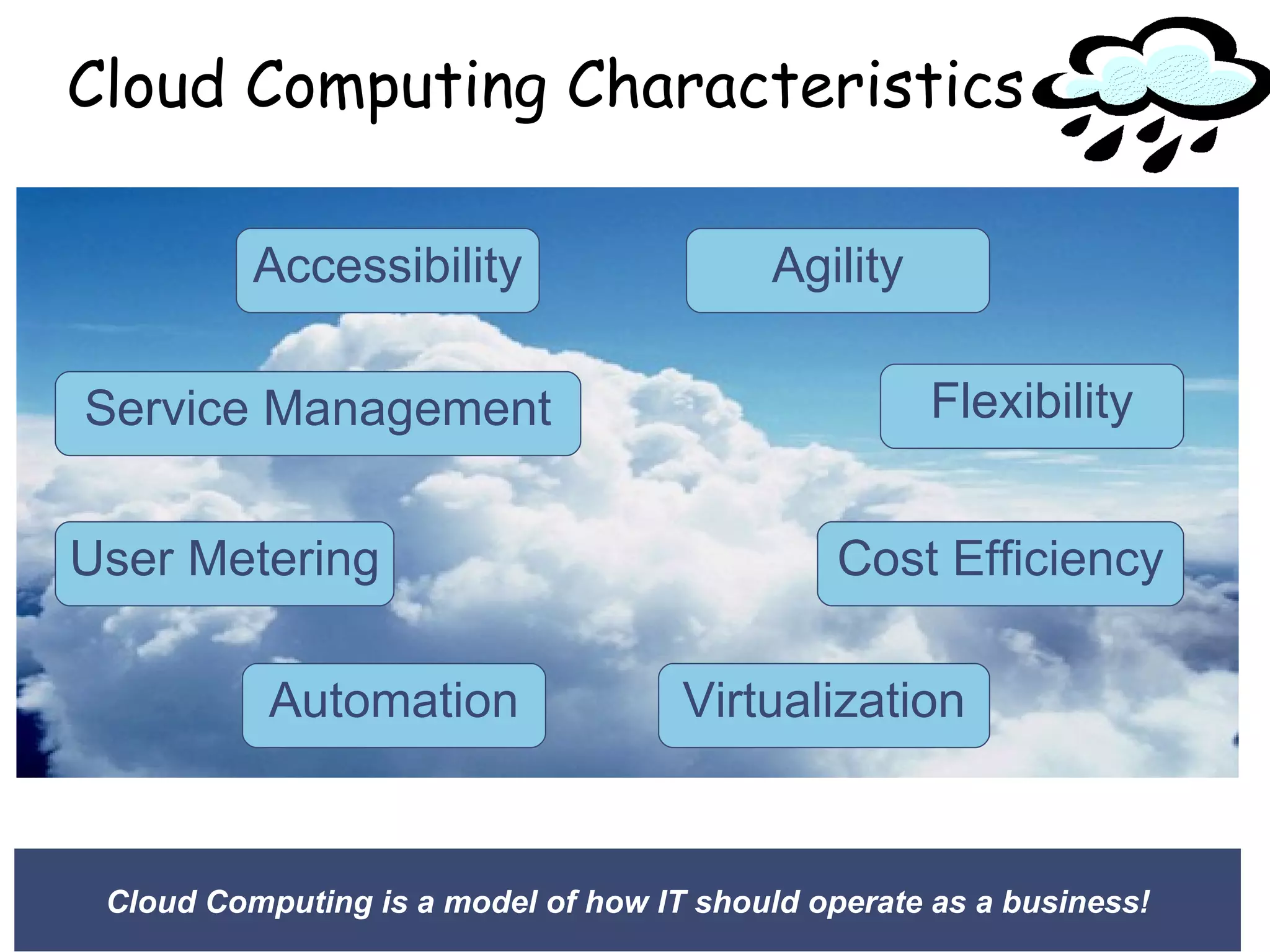
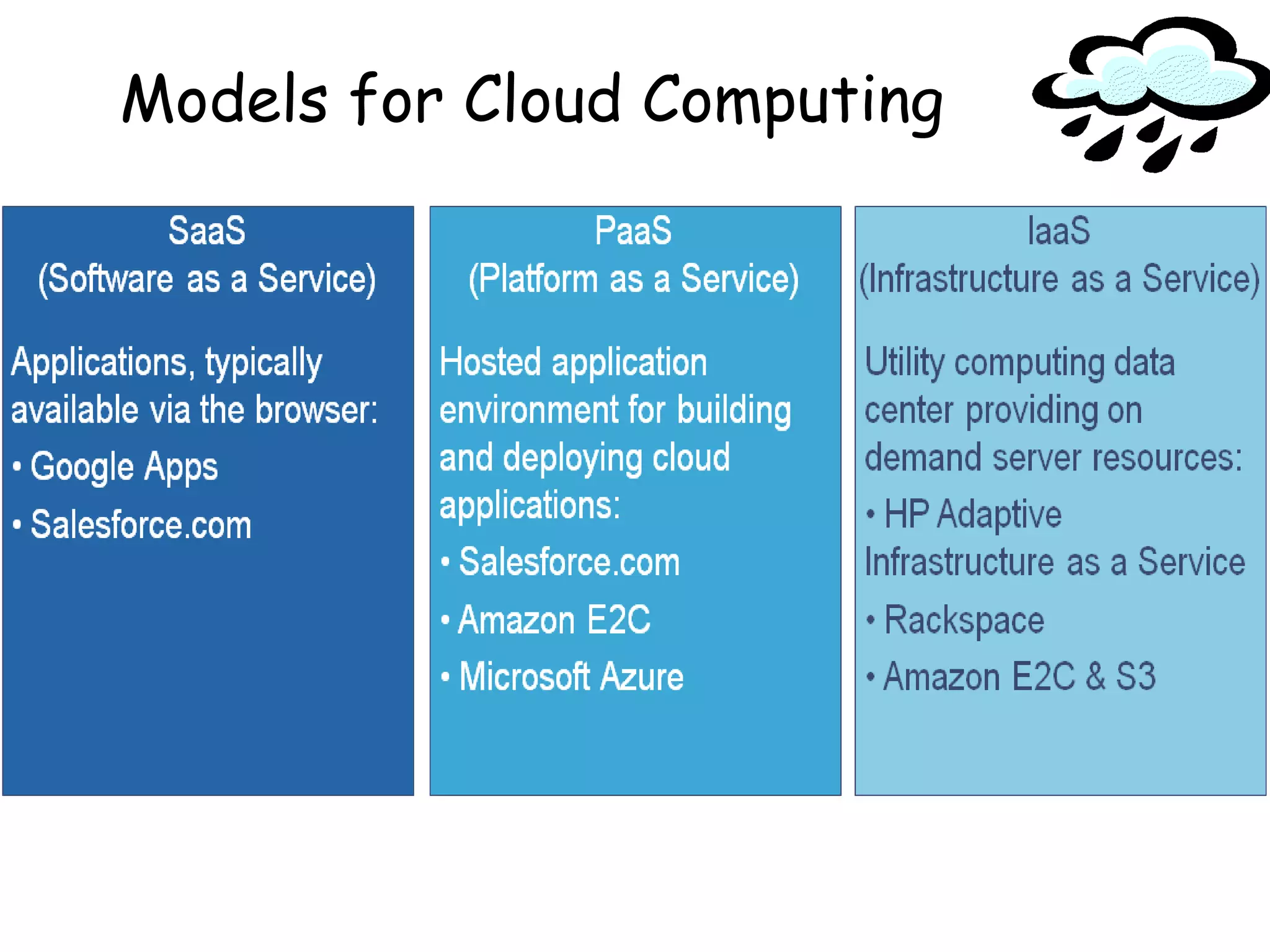
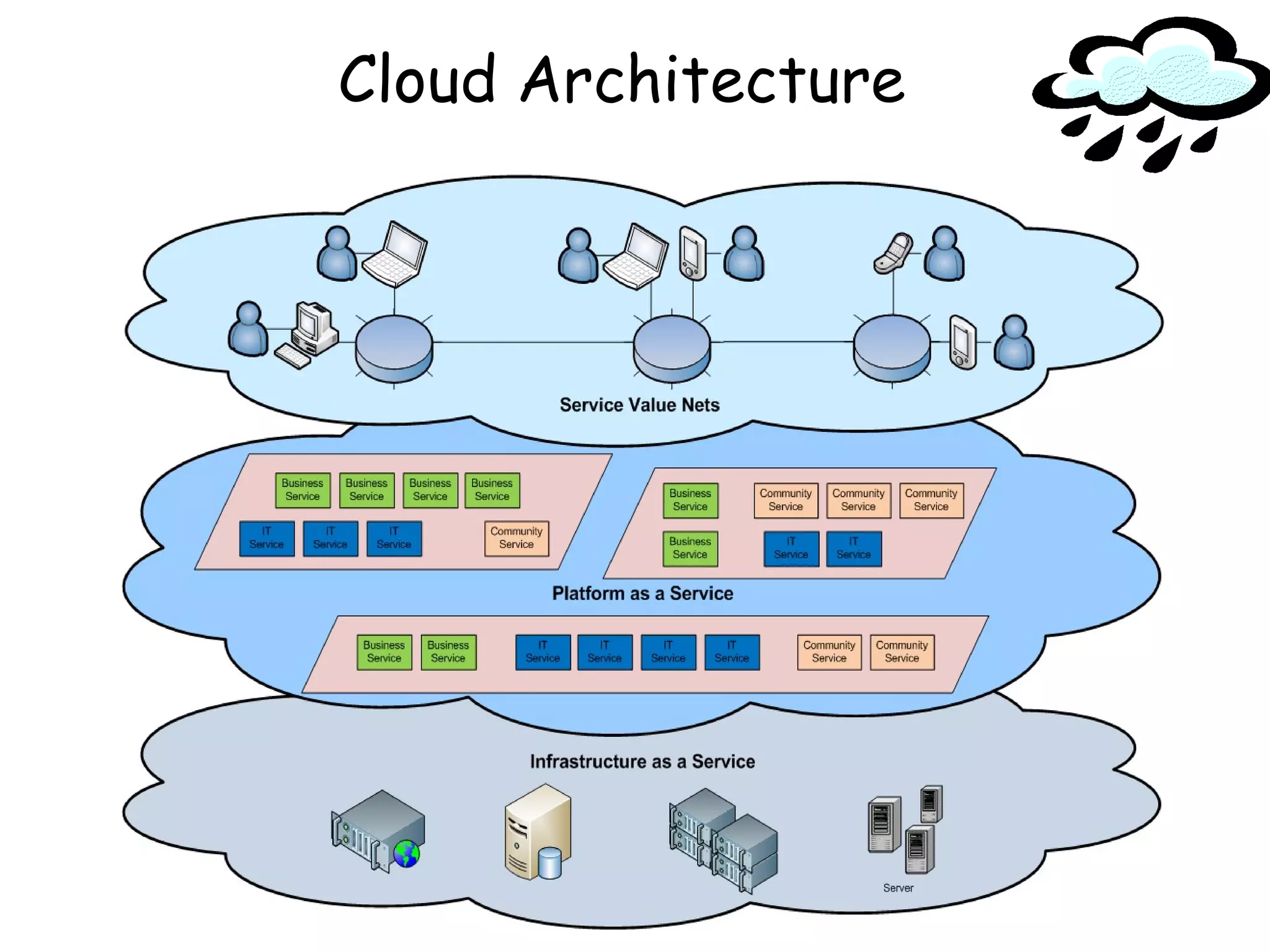
The document provides an introduction to cloud computing, including definitions and concepts. It discusses the evolution of cloud computing from earlier technologies like grid computing and utility computing. It also outlines some key characteristics of cloud computing models including software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). Additionally, it covers basic cloud architecture, characteristics, purposes and benefits, as well as opportunities and challenges of cloud computing.