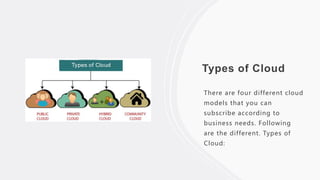
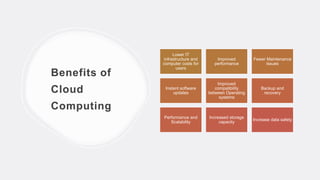
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, defining it as the online storage and access of data and computing services, allowing users to utilize resources without managing physical infrastructure. It describes different cloud models, such as private, community, and hybrid clouds, along with the benefits of cloud computing, including cost savings and improved performance. Additionally, the text highlights challenges such as security risks and lack of expertise, while discussing various cloud computing services and their characteristics.