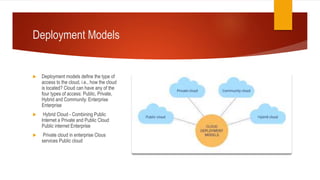
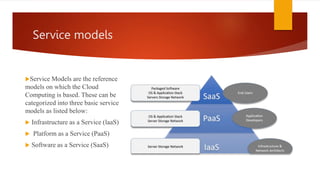
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to shared computing resources like networks, servers, storage, applications and services over the internet. There are different deployment models for cloud computing including public, private, hybrid and community clouds. The main service models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides fundamental computing resources, PaaS provides platforms for developing and delivering applications, and SaaS provides access to software applications. While cloud computing provides benefits like reduced costs and infrastructure independence, there are also challenges regarding data security, access control and reliability.