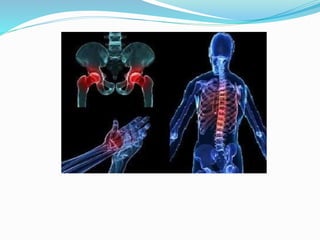
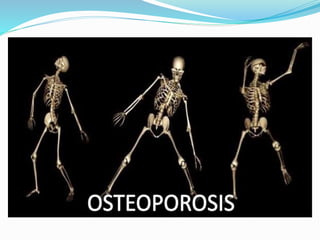
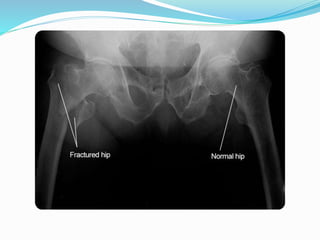
The document discusses osteoporosis, which is a disease characterized by low bone mass and fragile bones that break easily. It defines osteoporosis and describes that typical fractures occur in the vertebrae, ribs, hip and wrist. While it has no symptoms, its main consequence is an increased risk of bone fractures. The document outlines exams and tests used to diagnose osteoporosis, as well as lifestyle changes and medications used to treat and prevent the disease.