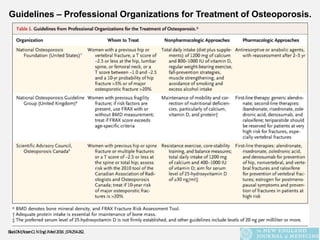
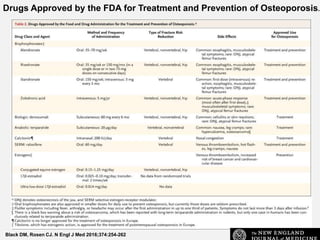
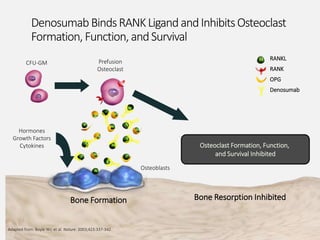
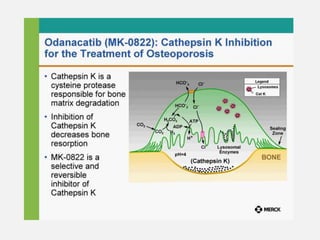
This document provides an overview of osteoporosis including its definition, epidemiology, pathophysiology, causes, clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment. Some key points include:
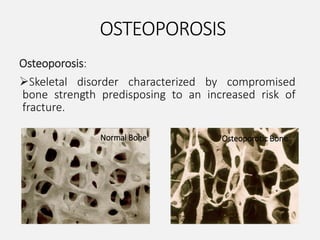
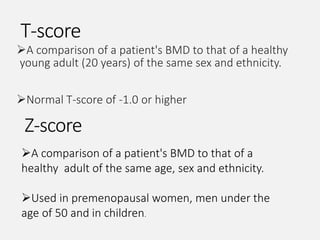
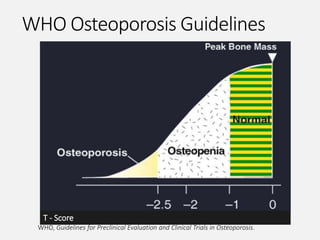
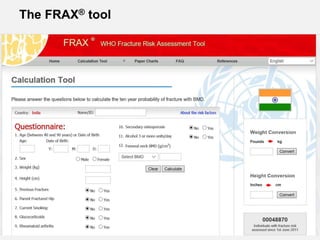
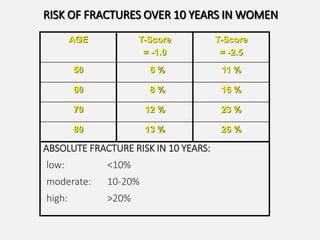
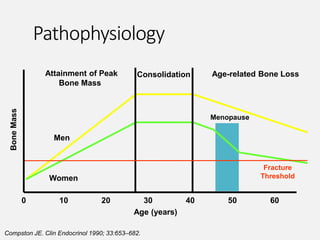
- Osteoporosis is a skeletal disorder characterized by compromised bone strength and increased risk of fracture. It is defined by the WHO as a bone density 2.5 standard deviations below the mean.
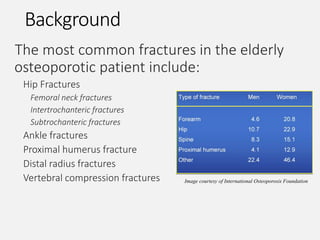
- It is a major global health problem, particularly affecting post-menopausal women and the elderly. Lifetime risk of osteoporotic fractures is 30-50% in females and 15-30% in males.
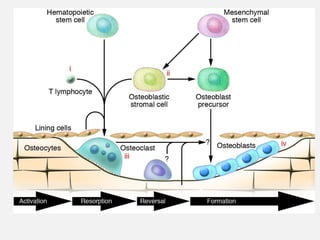
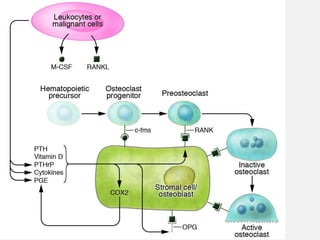
- Causes include failure to achieve peak bone mass, increased bone resorption, and inadequate bone formation