Osteoporosis.pptx
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
0 likes•7 views
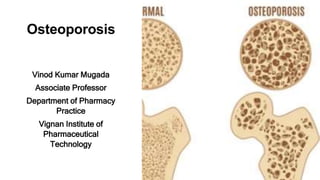
This disease is a long-term and gradually worsening condition that causes bones to become thinner, weaker, and more likely to break. Over time, the structure of the bones breaks down and their overall strength decreases, making them more fragile and prone to fractures. The FRAX® tool has been developed to evaluate fracture risk of patients. It is based on individual patient models that integrate the risks associated with clinical risk factors as well as bone mineral density (BMD) at the femoral neck.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Metabolic and genetic disorders of bone

This document provides an overview of metabolic and genetic disorders of bone. It begins with introducing bone anatomy, histology, and physiology. It then discusses bone metabolism and the role of bones in general metabolism. The document classifies bone disorders and discusses several metabolic bone diseases in depth, including osteoporosis, rickets, osteomalacia, and hyperparathyroidism. For each, it covers etiology, clinical features, oral manifestations, histopathology, and treatment. The document thus provides a comprehensive review of key metabolic and genetic bone disorders.
Osteoporosis and osteomalacia

Osteoporosis is a condition where bones become brittle and fragile due to loss of tissue, often as a result of hormonal changes or deficiencies in calcium or vitamin D. It is caused by lower bone density and loss of the internal supporting structure of bones. Risk factors include being female, older age, small frame size, family history, and low calcium intake. Symptoms may include back pain, loss of height, and fractures from minor injuries. Diagnosis involves bone density scans and lab tests. Treatment focuses on hormone therapy, medications, calcium/vitamin supplements, exercise, and nutrition.
Bone physiology, OSTEOPOROSIS, Pagets Disease, Hyperparathyoidism

A brief introduction to bone physiology, with more focus on Osteoporosis and its recent updates. Small tail topics include hyperparathyroidism and pagets disease.
Bone health and epilepsy

Medical management of epilepsy,
Seizures,
Epileptogenesis,
Anti-seizure medications,
Anti epileptic drugs,
status epilepticus,
management of seizures,
Management of status epilepticus
Osteoporosis

This presentation includes four major topics:
1- reviews the essentials of osteoporosis including definition, pathophysiology, etiology, epidemiology, and prognosis
2- talks about the presentation of osteoporosis, including risk factors, symptoms and signs, radiologic manifestations, and complications
3- reviews the workup process to diagnose and define the severity of osteoporosis, including the lab. and radiologic procedures
4- reviews management tools of osteoporosis, including pharmacologic and non pharmacologic methods, with brief description for each pharmacologic or non pharmacologic tool.
Finally, some statements about the education and prevention of osteoporosis.
OSTEOPOROSIS.pptx

little bone mineral density brought on by changed bone microstructure is known as osteoporosis, which ultimately predisposes individuals to fragility fractures with little force. The quality of life is significantly reduced as a result of osteoporotic fractures, which also increase morbidity, mortality, and disability.
Soon, a presentation on the management of osteoporosis with physical therapy will be made available.
Dont bend to Osteoporosis

This presentation was Shown on a community gathering in Gulshan Club Dhaka on the eve of the World Osteoporosis Day, 2010.
Prof. Shahiduzzaman was the key note speaker.
New zeland Dairy Milk was the organiser of this Seminar.
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by low bone mass and quality, leading to an increased risk of bone fractures. It is most common in postmenopausal women over age 50 and men over age 80. Risk factors include female gender, advancing age, family history, hypogonadism, glucocorticoid use, low body mass index, smoking, and nutritional deficiencies. Diagnosis is made through bone density scans and confirmed by fragility fractures. Treatment focuses on lifestyle modifications, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, bisphosphonates, estrogen therapy, selective estrogen receptor modulators, parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, and surgery for fractures. Monitoring involves repeat bone density scans and biochemical markers to assess response to
Recommended
Metabolic and genetic disorders of bone

This document provides an overview of metabolic and genetic disorders of bone. It begins with introducing bone anatomy, histology, and physiology. It then discusses bone metabolism and the role of bones in general metabolism. The document classifies bone disorders and discusses several metabolic bone diseases in depth, including osteoporosis, rickets, osteomalacia, and hyperparathyroidism. For each, it covers etiology, clinical features, oral manifestations, histopathology, and treatment. The document thus provides a comprehensive review of key metabolic and genetic bone disorders.
Osteoporosis and osteomalacia

Osteoporosis is a condition where bones become brittle and fragile due to loss of tissue, often as a result of hormonal changes or deficiencies in calcium or vitamin D. It is caused by lower bone density and loss of the internal supporting structure of bones. Risk factors include being female, older age, small frame size, family history, and low calcium intake. Symptoms may include back pain, loss of height, and fractures from minor injuries. Diagnosis involves bone density scans and lab tests. Treatment focuses on hormone therapy, medications, calcium/vitamin supplements, exercise, and nutrition.
Bone physiology, OSTEOPOROSIS, Pagets Disease, Hyperparathyoidism

A brief introduction to bone physiology, with more focus on Osteoporosis and its recent updates. Small tail topics include hyperparathyroidism and pagets disease.
Bone health and epilepsy

Medical management of epilepsy,
Seizures,
Epileptogenesis,
Anti-seizure medications,
Anti epileptic drugs,
status epilepticus,
management of seizures,
Management of status epilepticus
Osteoporosis

This presentation includes four major topics:
1- reviews the essentials of osteoporosis including definition, pathophysiology, etiology, epidemiology, and prognosis
2- talks about the presentation of osteoporosis, including risk factors, symptoms and signs, radiologic manifestations, and complications
3- reviews the workup process to diagnose and define the severity of osteoporosis, including the lab. and radiologic procedures
4- reviews management tools of osteoporosis, including pharmacologic and non pharmacologic methods, with brief description for each pharmacologic or non pharmacologic tool.
Finally, some statements about the education and prevention of osteoporosis.
OSTEOPOROSIS.pptx

little bone mineral density brought on by changed bone microstructure is known as osteoporosis, which ultimately predisposes individuals to fragility fractures with little force. The quality of life is significantly reduced as a result of osteoporotic fractures, which also increase morbidity, mortality, and disability.
Soon, a presentation on the management of osteoporosis with physical therapy will be made available.
Dont bend to Osteoporosis

This presentation was Shown on a community gathering in Gulshan Club Dhaka on the eve of the World Osteoporosis Day, 2010.
Prof. Shahiduzzaman was the key note speaker.
New zeland Dairy Milk was the organiser of this Seminar.
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by low bone mass and quality, leading to an increased risk of bone fractures. It is most common in postmenopausal women over age 50 and men over age 80. Risk factors include female gender, advancing age, family history, hypogonadism, glucocorticoid use, low body mass index, smoking, and nutritional deficiencies. Diagnosis is made through bone density scans and confirmed by fragility fractures. Treatment focuses on lifestyle modifications, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, bisphosphonates, estrogen therapy, selective estrogen receptor modulators, parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, and surgery for fractures. Monitoring involves repeat bone density scans and biochemical markers to assess response to
osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a systemic bone disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to increased bone fragility and risk of fractures. It is most common in postmenopausal women. Risk factors include smoking, low body weight, steroid use, excess alcohol intake, and family history of fractures. Diagnosis involves measuring bone mineral density via DEXA scan. Treatment aims to prevent fractures and bone loss, and includes adequate calcium and vitamin D, weight-bearing exercise, falls prevention, pharmacologic agents like bisphosphonates, and surgery for fractures. Regular screening and monitoring of at-risk individuals is important.
Osteoporosis

This document discusses osteoporosis, including its definitions, epidemiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment options. Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to fragile bones and increased risk of fractures. It affects millions of people worldwide, especially postmenopausal women, and can be caused by aging, genetics, lifestyle factors, and certain medical conditions or medications. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications like diet, exercise and fall prevention as well as pharmacologic options like calcium, vitamin D, bisphosphonates, and drugs that modify bone metabolism.
osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a disease where bones become fragile and more likely to break. It occurs when the body loses more bone than it forms, reducing bone density and bone mass. Key risk factors include a family history of osteoporosis, being Caucasian or Asian, smoking, excessive alcohol use, and low body weight. Diagnosis relies on bone mineral density tests to determine a T-score. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes like exercise and nutrition, as well as medications to reduce bone loss and increase bone formation.
LECTURE 18; OSTEOPOROSIS &OSTEOMALACIA..pptx

Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by decreased bone mass and deterioration of bone structure, leading to fragile bones and increased risk of fractures from minor trauma. It is caused by an imbalance between bone resorption by osteoclasts and bone formation by osteoblasts, resulting in a net loss of bone. The most important risk factors for developing osteoporosis are loss of gonadal hormones during menopause and aging, as these lead to accelerated bone loss. Osteoporosis can be classified as primary (types 1 or 2) or secondary (type 3), with type 1 being postmenopausal osteoporosis resulting from estrogen deficiency after menopause.
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a disease where decreased bone strength increases the risk of broken bones, most commonly in the spine, forearm, and hip. It is often caused by lower than normal peak bone mass and increased bone loss after menopause due to lower estrogen levels. Symptoms do not usually appear until a fracture occurs. Prevention focuses on adequate calcium intake, exercise, avoiding risk factors like smoking and heavy drinking, and medication if fractures have already occurred.
Osteoporosis - Dr S L Yadav

This document provides information on osteoporosis, including its definition, prevalence, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and management. Some key points:
- Osteoporosis is a metabolic bone disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to increased bone fragility and fracture risk.
- It is a major public health problem worldwide due to its association with pain, disability, and loss of quality of life.
- Risk factors include age, gender, family history, smoking, excessive alcohol, low body weight, and certain medications like glucocorticoids.
- It is usually asymptomatic until a fracture occurs. Common fracture sites are the spine, hip, and wrist
Osteomyelitis, osteomalacia,osteoprosis, bne tumor

This document provides information about osteomyelitis, osteomalacia, osteoporosis, and bone tumors. It defines each condition, discusses causes and risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic tests, and medical and nursing management. Osteomyelitis is an acute bone infection that can be acute, subacute, or chronic. Osteomalacia is a disorder causing inadequate bone mineralization due to vitamin D or phosphate deficiencies. Osteoporosis is a disease where bone density decreases and fragility increases, causing higher fracture risk. Bone tumors can be benign or malignant, and types include osteosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, and chondrosarcoma.
Osteoporosis - Pharmacotherapy 

Osteoporosis is a bone disorder characterized by low bone density and compromised bone strength, predisposing individuals to fractures. It is most common in older adults and postmenopausal women. Risk factors include hormonal status, genetics, lifestyle factors like exercise and nutrition. Bone loss occurs when bone resorption exceeds bone formation, which can be caused by high bone turnover. Treatment goals are to prevent fractures, maintain or increase bone mineral density, and prevent secondary causes of bone loss. Medications like calcium, vitamin D, bisphosphonates, and raloxifene are used to reduce bone resorption and increase bone formation to achieve these goals.
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone density and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to fragile bones and increased fracture risk. It is diagnosed through bone mineral density tests and can be caused by many factors including older age, female sex, family history, and lifestyle factors. Management focuses on lifestyle modifications like calcium and vitamin D supplementation, exercise, and fall prevention, as well as pharmacological therapies to slow bone loss and increase bone density. Complications include fractures which can lead to disability, loss of independence, and even death in severe cases.
Osteoporosis

This document provides information on osteoporosis including its definition, pathophysiology, risk factors, diagnostic tools, treatment guidelines, and pharmacologic management options. Specifically, it defines osteoporosis as a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue leading to increased bone fragility and fracture risk. It notes that aging, loss of gonadal function, and estrogen deficiency are major risk factors and discusses tools like bone mineral density testing and FRAX for assessing fracture risk. Finally, it outlines treatment guidelines and FDA-approved pharmacologic options for prevention and management of osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by reduced bone mass and density, leading to fragile bones. It affects 35% of people over 50, with women four times more likely than men to have osteoporosis. It is classified as primary, including postmenopausal and senile osteoporosis, or secondary, caused by conditions like malnutrition, inflammatory diseases, corticosteroid use, and cancers. Postmenopausal osteoporosis is caused by accelerated bone loss following menopause. Risk factors include ethnicity, family history, and early menopause. Symptoms include back pain and fractures. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes, hormone replacement therapy, bisphosphonates, denosumab, and
Osteoporosis , causes , last update

Osteoporosis is a chronic disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to fragile bones that are more prone to fractures. It occurs due to an imbalance between bone resorption by osteoclasts and bone formation by osteoblasts. Key factors that contribute to osteoporosis include estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal women, aging, calcium deficiency, use of corticosteroids, and lack of exercise. Preventive measures include maintaining a diet with adequate calcium and vitamin D, engaging in weight-bearing exercise, not smoking, and taking measures to prevent falls in older adults.
Osteoporesis and Gout _RDP

Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by reduced bone density and strength, increasing the risk of fractures. It results from an imbalance between bone resorption and formation, with resorption exceeding formation. This can be due to age-related changes that reduce osteoblast function and bone quality over time, as well as other factors like reduced physical activity, nutritional deficiencies, genetics, and hormonal changes in women after menopause. Symptoms include fractures of the vertebrae, hips, and wrists. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes and medications to reduce bone resorption and promote formation.
OSTEOPOROSIS.pptx

This document provides an overview of osteoporosis, including its definition, epidemiology, pathophysiology, classification, clinical features, risk factors, investigations, and management. Osteoporosis is defined by reduced bone density and deterioration of bone tissue, increasing the risk of fractures. It most commonly causes fractures of the forearm, spine, and hip. Risk factors include low bone mass, hormonal changes, smoking, low body weight, and nutritional deficiencies. Diagnosis involves bone mineral density tests and laboratory tests. Treatment includes lifestyle modifications, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, exercise, and pharmacological therapies.
1933864184

This document discusses osteoporosis and provides information about its characteristics, risk factors, epidemiology, and classification. Some key points:
- Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone structure, leading to an increased risk of fractures. It is caused by an imbalance between bone formation and resorption.
- Risk factors include being Caucasian or Asian, female sex, advanced age, family history, smoking, excess alcohol, low body weight, and loss of sex hormones.
- It affects many older adults, especially women past menopause. Hip fractures from osteoporosis can significantly increase mortality and disability.
- Osteoporosis is
Osteoporosis

osteoprosis
• Definition
• Pathophysiology
• Risk Factor • Causes
• Signs and Symptoms
• Diagnostic procedure
• Prevention and medical management
• Nursing Process
Calsi soya ppt

This document discusses bone health and osteoporosis. It defines osteoporosis as a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and increased fracture risk. Key factors discussed include bone composition, homeostasis and remodeling, risk factors for osteoporosis like age and hormones, methods of diagnosis like DXA scans, complications of fractures, and principles of management including lifestyle modifications and medications to prevent bone loss.
Osteoporosis.ppt

This document discusses risk factors for osteoporosis. It defines osteoporosis as a disease causing reduction in bone mass and strength. Some key risk factors include estrogen deficiency, mechanical factors like lack of exercise, tobacco use, and steroid use. It also discusses evaluation of bone mineral density, pathophysiology of different osteoporosis types, and consequences of osteoporotic fractures including significant morbidity and increased mortality rates.
Osteoporosis seminar final.pptx

Osteoporosis is a progressive bone disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, making bones brittle and prone to fracture. It is defined as a T-score of -2.5 or below as measured by dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scanning. Key risk factors include older age, female sex, family history, smoking, low body weight and lack of exercise. Treatment focuses on lifestyle modifications like calcium and vitamin D supplementation, exercise and fall prevention, as well as pharmacologic therapies like bisphosphonates.
DIABETES.pptx

Essential elements of the management plan
Glycemic control,
Medical nutrition therapy (MNT),
Diabetes self-management education,
Physical activity, and
Psychosocial assessment and care
The target A1C goal is
6.5% or less
<7% for most nonpregnant adults and
<7.5% for pediatric patient
AUTOMATED DATABASES INTRO.docx

Post marketing studies of drug effects must then generally include at least 10,000 exposed persons in a cohort study, or enroll diseased patients from a population of equivalent size for a case–control study. A study of this size would be 95% certain of observing at least one case of any adverse effect that occurs with an incidence of 3 per 10 000 or greater (see Chapter 3). However, studies this large are expensive and difficult to perform. Yet, these studies often need to be conducted quickly, to address acute and serious regulatory, commercial, and/or public health crises. For all of these reasons, the past two decades have seen a growing use of computerized databases containing medical care data, so called “automated databases,” as potential data sources for pharmacoepidemiology studies.
More Related Content
Similar to Osteoporosis.pptx
osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a systemic bone disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to increased bone fragility and risk of fractures. It is most common in postmenopausal women. Risk factors include smoking, low body weight, steroid use, excess alcohol intake, and family history of fractures. Diagnosis involves measuring bone mineral density via DEXA scan. Treatment aims to prevent fractures and bone loss, and includes adequate calcium and vitamin D, weight-bearing exercise, falls prevention, pharmacologic agents like bisphosphonates, and surgery for fractures. Regular screening and monitoring of at-risk individuals is important.
Osteoporosis

This document discusses osteoporosis, including its definitions, epidemiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment options. Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to fragile bones and increased risk of fractures. It affects millions of people worldwide, especially postmenopausal women, and can be caused by aging, genetics, lifestyle factors, and certain medical conditions or medications. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications like diet, exercise and fall prevention as well as pharmacologic options like calcium, vitamin D, bisphosphonates, and drugs that modify bone metabolism.
osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a disease where bones become fragile and more likely to break. It occurs when the body loses more bone than it forms, reducing bone density and bone mass. Key risk factors include a family history of osteoporosis, being Caucasian or Asian, smoking, excessive alcohol use, and low body weight. Diagnosis relies on bone mineral density tests to determine a T-score. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes like exercise and nutrition, as well as medications to reduce bone loss and increase bone formation.
LECTURE 18; OSTEOPOROSIS &OSTEOMALACIA..pptx

Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by decreased bone mass and deterioration of bone structure, leading to fragile bones and increased risk of fractures from minor trauma. It is caused by an imbalance between bone resorption by osteoclasts and bone formation by osteoblasts, resulting in a net loss of bone. The most important risk factors for developing osteoporosis are loss of gonadal hormones during menopause and aging, as these lead to accelerated bone loss. Osteoporosis can be classified as primary (types 1 or 2) or secondary (type 3), with type 1 being postmenopausal osteoporosis resulting from estrogen deficiency after menopause.
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a disease where decreased bone strength increases the risk of broken bones, most commonly in the spine, forearm, and hip. It is often caused by lower than normal peak bone mass and increased bone loss after menopause due to lower estrogen levels. Symptoms do not usually appear until a fracture occurs. Prevention focuses on adequate calcium intake, exercise, avoiding risk factors like smoking and heavy drinking, and medication if fractures have already occurred.
Osteoporosis - Dr S L Yadav

This document provides information on osteoporosis, including its definition, prevalence, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and management. Some key points:
- Osteoporosis is a metabolic bone disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to increased bone fragility and fracture risk.
- It is a major public health problem worldwide due to its association with pain, disability, and loss of quality of life.
- Risk factors include age, gender, family history, smoking, excessive alcohol, low body weight, and certain medications like glucocorticoids.
- It is usually asymptomatic until a fracture occurs. Common fracture sites are the spine, hip, and wrist
Osteomyelitis, osteomalacia,osteoprosis, bne tumor

This document provides information about osteomyelitis, osteomalacia, osteoporosis, and bone tumors. It defines each condition, discusses causes and risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic tests, and medical and nursing management. Osteomyelitis is an acute bone infection that can be acute, subacute, or chronic. Osteomalacia is a disorder causing inadequate bone mineralization due to vitamin D or phosphate deficiencies. Osteoporosis is a disease where bone density decreases and fragility increases, causing higher fracture risk. Bone tumors can be benign or malignant, and types include osteosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, and chondrosarcoma.
Osteoporosis - Pharmacotherapy 

Osteoporosis is a bone disorder characterized by low bone density and compromised bone strength, predisposing individuals to fractures. It is most common in older adults and postmenopausal women. Risk factors include hormonal status, genetics, lifestyle factors like exercise and nutrition. Bone loss occurs when bone resorption exceeds bone formation, which can be caused by high bone turnover. Treatment goals are to prevent fractures, maintain or increase bone mineral density, and prevent secondary causes of bone loss. Medications like calcium, vitamin D, bisphosphonates, and raloxifene are used to reduce bone resorption and increase bone formation to achieve these goals.
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone density and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to fragile bones and increased fracture risk. It is diagnosed through bone mineral density tests and can be caused by many factors including older age, female sex, family history, and lifestyle factors. Management focuses on lifestyle modifications like calcium and vitamin D supplementation, exercise, and fall prevention, as well as pharmacological therapies to slow bone loss and increase bone density. Complications include fractures which can lead to disability, loss of independence, and even death in severe cases.
Osteoporosis

This document provides information on osteoporosis including its definition, pathophysiology, risk factors, diagnostic tools, treatment guidelines, and pharmacologic management options. Specifically, it defines osteoporosis as a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue leading to increased bone fragility and fracture risk. It notes that aging, loss of gonadal function, and estrogen deficiency are major risk factors and discusses tools like bone mineral density testing and FRAX for assessing fracture risk. Finally, it outlines treatment guidelines and FDA-approved pharmacologic options for prevention and management of osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by reduced bone mass and density, leading to fragile bones. It affects 35% of people over 50, with women four times more likely than men to have osteoporosis. It is classified as primary, including postmenopausal and senile osteoporosis, or secondary, caused by conditions like malnutrition, inflammatory diseases, corticosteroid use, and cancers. Postmenopausal osteoporosis is caused by accelerated bone loss following menopause. Risk factors include ethnicity, family history, and early menopause. Symptoms include back pain and fractures. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes, hormone replacement therapy, bisphosphonates, denosumab, and
Osteoporosis , causes , last update

Osteoporosis is a chronic disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to fragile bones that are more prone to fractures. It occurs due to an imbalance between bone resorption by osteoclasts and bone formation by osteoblasts. Key factors that contribute to osteoporosis include estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal women, aging, calcium deficiency, use of corticosteroids, and lack of exercise. Preventive measures include maintaining a diet with adequate calcium and vitamin D, engaging in weight-bearing exercise, not smoking, and taking measures to prevent falls in older adults.
Osteoporesis and Gout _RDP

Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by reduced bone density and strength, increasing the risk of fractures. It results from an imbalance between bone resorption and formation, with resorption exceeding formation. This can be due to age-related changes that reduce osteoblast function and bone quality over time, as well as other factors like reduced physical activity, nutritional deficiencies, genetics, and hormonal changes in women after menopause. Symptoms include fractures of the vertebrae, hips, and wrists. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes and medications to reduce bone resorption and promote formation.
OSTEOPOROSIS.pptx

This document provides an overview of osteoporosis, including its definition, epidemiology, pathophysiology, classification, clinical features, risk factors, investigations, and management. Osteoporosis is defined by reduced bone density and deterioration of bone tissue, increasing the risk of fractures. It most commonly causes fractures of the forearm, spine, and hip. Risk factors include low bone mass, hormonal changes, smoking, low body weight, and nutritional deficiencies. Diagnosis involves bone mineral density tests and laboratory tests. Treatment includes lifestyle modifications, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, exercise, and pharmacological therapies.
1933864184

This document discusses osteoporosis and provides information about its characteristics, risk factors, epidemiology, and classification. Some key points:
- Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone structure, leading to an increased risk of fractures. It is caused by an imbalance between bone formation and resorption.
- Risk factors include being Caucasian or Asian, female sex, advanced age, family history, smoking, excess alcohol, low body weight, and loss of sex hormones.
- It affects many older adults, especially women past menopause. Hip fractures from osteoporosis can significantly increase mortality and disability.
- Osteoporosis is
Osteoporosis

osteoprosis
• Definition
• Pathophysiology
• Risk Factor • Causes
• Signs and Symptoms
• Diagnostic procedure
• Prevention and medical management
• Nursing Process
Calsi soya ppt

This document discusses bone health and osteoporosis. It defines osteoporosis as a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and increased fracture risk. Key factors discussed include bone composition, homeostasis and remodeling, risk factors for osteoporosis like age and hormones, methods of diagnosis like DXA scans, complications of fractures, and principles of management including lifestyle modifications and medications to prevent bone loss.
Osteoporosis.ppt

This document discusses risk factors for osteoporosis. It defines osteoporosis as a disease causing reduction in bone mass and strength. Some key risk factors include estrogen deficiency, mechanical factors like lack of exercise, tobacco use, and steroid use. It also discusses evaluation of bone mineral density, pathophysiology of different osteoporosis types, and consequences of osteoporotic fractures including significant morbidity and increased mortality rates.
Osteoporosis seminar final.pptx

Osteoporosis is a progressive bone disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, making bones brittle and prone to fracture. It is defined as a T-score of -2.5 or below as measured by dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scanning. Key risk factors include older age, female sex, family history, smoking, low body weight and lack of exercise. Treatment focuses on lifestyle modifications like calcium and vitamin D supplementation, exercise and fall prevention, as well as pharmacologic therapies like bisphosphonates.
Similar to Osteoporosis.pptx (20)
Osteomyelitis, osteomalacia,osteoprosis, bne tumor

Osteomyelitis, osteomalacia,osteoprosis, bne tumor
More from VinodkumarMugada1
DIABETES.pptx

Essential elements of the management plan
Glycemic control,
Medical nutrition therapy (MNT),
Diabetes self-management education,
Physical activity, and
Psychosocial assessment and care
The target A1C goal is
6.5% or less
<7% for most nonpregnant adults and
<7.5% for pediatric patient
AUTOMATED DATABASES INTRO.docx

Post marketing studies of drug effects must then generally include at least 10,000 exposed persons in a cohort study, or enroll diseased patients from a population of equivalent size for a case–control study. A study of this size would be 95% certain of observing at least one case of any adverse effect that occurs with an incidence of 3 per 10 000 or greater (see Chapter 3). However, studies this large are expensive and difficult to perform. Yet, these studies often need to be conducted quickly, to address acute and serious regulatory, commercial, and/or public health crises. For all of these reasons, the past two decades have seen a growing use of computerized databases containing medical care data, so called “automated databases,” as potential data sources for pharmacoepidemiology studies.
Osteoporosis.pptx

Osteoporosis therapy contains bisphosphonares and anabolic agents. Lifestyle measures should be corrected. Initiating therapy with bisphosphonates due to efficacy, favorable cost, and long-term safety is considered.
ELECTROCARDIOGRAM.pptx

The electrical impulses from the SA node can be detected through electrodes placed on the skin, usually on the chest, arms, and legs. The ECG provides a graphical representation of the electrical impulses generated by the heart's muscle cells.
Viral Conjunctivitis.pptx

Viral conjunctivitis is acquired by direct contact with fingers, towels, washcloths, contaminated ophthalmic instruments, contaminated swimming pools, other infected eye, infected person, or other viral infection elsewhere in the body. The most common viruses are adenovirus, herpes simplex virus, enterovirus. Except for herpes, most viral infections are self-limited.Topical corticosteroids are not recommended for the treatment of HSV, as they may exacerbate the condition
Conjunctivitis.pptx

Bacterial conjunctivitis is inflammation of the bulbar and tarsal conjunctiva arising from a broad group of bacterial pathogens. It is also known as "pink eye".
Lymphatic System.pptx

The lymphatic system helps fight infection, remove waste, maintain fluid balance, and absorb fats. It consists of lymph, lymphatic vessels, lymphatic tissue, and red bone marrow. Lymphatic vessels begin as capillaries that absorb fluid and transport it through larger vessels and lymph nodes. The spleen filters blood and stores blood cells. Disorders of the lymphatic system include lymphedema, lymphangitis, and lymphadenopathy.
Glaucoma.pptx

Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that cause damage to the optic nerve and vision loss. Open-angle glaucoma is the most common type, where fluid drainage is impaired but the drainage angle remains open. Elevated intraocular pressure damages the optic nerve over time. Main treatments are eye drop medications that lower pressure by increasing outflow or decreasing fluid production, including prostaglandin analogs, beta-blockers, alpha-2 agonists, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Combination therapy is often used if single drugs do not adequately lower pressure and prevent further vision loss.
Hematopoietic System.pptx

The hematopoietic system, also known as the blood-forming system, is a complex network of organs, tissues, and cells responsible for the production and circulation of blood cells throughout the body. The primary function of the hematopoietic system is to maintain a constant supply of healthy blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
More from VinodkumarMugada1 (9)
Recently uploaded
5 Effective Homeopathic Medicines for Irregular Periods

Discover the benefits of homeopathic medicine for irregular periods with our guide on 5 common remedies. Learn how these natural treatments can help regulate menstrual cycles and improve overall menstrual health.
Visit Us: https://drdeepikashomeopathy.com/service/irregular-periods-treatment/
Microbiology & Parasitology Exercises Parts of the Microscope

Exercise 1 of Microbiology and Parasitology which is the parts of the microscope and their uses
Pharmacology of Prostaglandins, Thromboxanes and Leukotrienes

This presentation gives information on the pharmacology of Prostaglandins, Thromboxanes and Leukotrienes i.e. Eicosanoids. Eicosanoids are signaling molecules derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids like arachidonic acid. They are involved in complex control over inflammation, immunity, and the central nervous system. Eicosanoids are synthesized through the enzymatic oxidation of fatty acids by cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase enzymes. They have short half-lives and act locally through autocrine and paracrine signaling.
Patellar Instability: Diagnosis Management

Pictorial and detailed description of patellar instability with sign and symptoms and how to diagnose , what investigations you should go with and how to approach with treatment options . I have presented this slide in my 2nd year junior residency in orthopedics at LLRM medical college Meerut and got good reviews for it
After getting it read you will definitely understand the topic.
Public Health Lecture 4 Social Sciences and Public Health

Sociology, Anthropology and Psychology as applied to Public Health
Nutritional deficiency disorder in Child

Nutritional deficiency Disorder are problems in india.
It is very important to learn about Indian child's nutritional parameters as well the Disease related to alteration in their Nutrition.
Call Girls Lucknow 9024918724 Vip Call Girls Lucknow

Call Girls Lucknow 9024918724 Vip Call Girls Lucknow
biomechanics of running. Dr.dhwani.pptx

The biomechanics of running involves the study of the mechanical principles underlying running movements. It includes the analysis of the running gait cycle, which consists of the stance phase (foot contact to push-off) and the swing phase (foot lift-off to next contact). Key aspects include kinematics (joint angles and movements, stride length and frequency) and kinetics (forces involved in running, including ground reaction and muscle forces). Understanding these factors helps in improving running performance, optimizing technique, and preventing injuries.
Full Handwritten notes of RA by Ayush Kumar M pharm - Al ameen college of pha...

Full Handwritten notes of RA by Ayush Kumar M pharm - Al ameen college of pha...ayushrajshrivastava7
Regulatory Affairs
Full hand written notes
M.pharm - 1st year .NARCOTICS- POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR ITS USE

This document outlines policies and procedures for handling narcotic and controlled drugs in NABH accredited hospitals.
Medical Quiz ( Online Quiz for API Meet 2024 ).pdf

This quiz was conducted as a promotional event for the 2024 Annual Meet of Kerala Chapter of API.
More than 20 participants took part everyday !
Osvaldo Bernardo Muchanga-GASTROINTESTINAL INFECTIONS AND GASTRITIS-2024.pdf

Osvaldo Bernardo Muchanga-GASTROINTESTINAL INFECTIONS AND GASTRITIS-2024.pdfOsvaldo Bernardo Muchanga
GASTROINTESTINAL INFECTIONS AND GASTRITIS
Osvaldo Bernardo Muchanga
Gastrointestinal Infections
GASTROINTESTINAL INFECTIONS result from the ingestion of pathogens that cause infections at the level of this tract, generally being transmitted by food, water and hands contaminated by microorganisms such as E. coli, Salmonella, Shigella, Vibrio cholerae, Campylobacter, Staphylococcus, Rotavirus among others that are generally contained in feces, thus configuring a FECAL-ORAL type of transmission.
Among the factors that lead to the occurrence of gastrointestinal infections are the hygienic and sanitary deficiencies that characterize our markets and other places where raw or cooked food is sold, poor environmental sanitation in communities, deficiencies in water treatment (or in the process of its plumbing), risky hygienic-sanitary habits (not washing hands after major and/or minor needs), among others.
These are generally consequences (signs and symptoms) resulting from gastrointestinal infections: diarrhea, vomiting, fever and malaise, among others.
The treatment consists of replacing lost liquids and electrolytes (drinking drinking water and other recommended liquids, including consumption of juicy fruits such as papayas, apples, pears, among others that contain water in their composition).
To prevent this, it is necessary to promote health education, improve the hygienic-sanitary conditions of markets and communities in general as a way of promoting, preserving and prolonging PUBLIC HEALTH.
Gastritis and Gastric Health
Gastric Health is one of the most relevant concerns in human health, with gastrointestinal infections being among the main illnesses that affect humans.
Among gastric problems, we have GASTRITIS AND GASTRIC ULCERS as the main public health problems. Gastritis and gastric ulcers normally result from inflammation and corrosion of the walls of the stomach (gastric mucosa) and are generally associated (caused) by the bacterium Helicobacter pylor, which, according to the literature, this bacterium settles on these walls (of the stomach) and starts to release urease that ends up altering the normal pH of the stomach (acid), which leads to inflammation and corrosion of the mucous membranes and consequent gastritis or ulcers, respectively.
In addition to bacterial infections, gastritis and gastric ulcers are associated with several factors, with emphasis on prolonged fasting, chemical substances including drugs, alcohol, foods with strong seasonings including chilli, which ends up causing inflammation of the stomach walls and/or corrosion. of the same, resulting in the appearance of wounds and consequent gastritis or ulcers, respectively.
Among patients with gastritis and/or ulcers, one of the dilemmas is associated with the foods to consume in order to minimize the sensation of pain and discomfort. RESPIRATORY DISEASES by bhavya kelavadiya

The Children are very vulnerable to get affected with respiratory disease.
In our country, the respiratory Disease conditions are consider as major cause for mortality and Morbidity in Child.
PGx Analysis in VarSeq: A User’s Perspective

Since our release of the PGx capabilities in VarSeq, we’ve had a few months to gather some insights from various use cases. Some users approach PGx workflows by means of array genotyping or what seems to be a growing trend of adding the star allele calling to the existing NGS pipeline for whole genome data. Luckily, both approaches are supported with the VarSeq software platform. The genotyping method being used will also dictate what the scope of the tertiary analysis will be. For example, are your PGx reports a standalone pipeline or would your lab’s goal be to handle a dual-purpose workflow and report on PGx + Diagnostic findings.
The purpose of this webcast is to:
Discuss and demonstrate the approaches with array and NGS genotyping methods for star allele calling to prep for downstream analysis.
Following genotyping, explore alternative tertiary workflow concepts in VarSeq to handle PGx reporting.
Moreover, we will include insights users will need to consider when validating their PGx workflow for all possible star alleles and options you have for automating your PGx analysis for large number of samples. Please join us for a session dedicated to the application of star allele genotyping and subsequent PGx workflows in our VarSeq software.
Dr. Tan's Balance Method.pdf (From Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin)

Home
Organization
Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin
Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin
Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin
About AOMA: The Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin offers a masters-level graduate program in acupuncture and Oriental medicine, preparing its students for careers as skilled, professional practitioners. AOMA is known for its internationally recognized faculty, award-winning student clinical internship program, and herbal medicine program. Since its founding in 1993, AOMA has grown rapidly in size and reputation, drawing students from around the nation and faculty from around the world. AOMA also conducts more than 20,000 patient visits annually in its student and professional clinics. AOMA collaborates with Western healthcare institutions including the Seton Family of Hospitals, and gives back to the community through partnerships with nonprofit organizations and by providing free and reduced price treatments to people who cannot afford them. The Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin is located at 2700 West Anderson Lane. AOMA also serves patients and retail customers at its south Austin location, 4701 West Gate Blvd. For more information see www.aoma.edu or call 512-492-303434.
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis - Pathogenesis , Clinical Features & Manage...

In this presentation , SBP ( spontaneous bacterial peritonitis ) , which is a common complication in patients with cirrhosis and ascites is described in detail.
The reference for this presentation is Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease Textbook ( 11th edition ).
Hemodialysis: Chapter 5, Dialyzers Overview - Dr.Gawad

- Video recording of this lecture in English language: https://youtu.be/Pt1nA32sdHQ
- Video recording of this lecture in Arabic language: https://youtu.be/uFdc9F0rlP0
- Link to download the book free: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/nephrotube-nephrology-books.html
- Link to NephroTube website: www.NephroTube.com
- Link to NephroTube social media accounts: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/join-nephrotube-on-social-media.html
Recently uploaded (20)
5 Effective Homeopathic Medicines for Irregular Periods

5 Effective Homeopathic Medicines for Irregular Periods
Tele Optometry (kunj'sppt) / Basics of tele optometry.

Tele Optometry (kunj'sppt) / Basics of tele optometry.
Microbiology & Parasitology Exercises Parts of the Microscope

Microbiology & Parasitology Exercises Parts of the Microscope
Pharmacology of Prostaglandins, Thromboxanes and Leukotrienes

Pharmacology of Prostaglandins, Thromboxanes and Leukotrienes
pharmacy exam preparation for undergradute students.pptx

pharmacy exam preparation for undergradute students.pptx
Public Health Lecture 4 Social Sciences and Public Health

Public Health Lecture 4 Social Sciences and Public Health
Call Girls Lucknow 9024918724 Vip Call Girls Lucknow

Call Girls Lucknow 9024918724 Vip Call Girls Lucknow
Full Handwritten notes of RA by Ayush Kumar M pharm - Al ameen college of pha...

Full Handwritten notes of RA by Ayush Kumar M pharm - Al ameen college of pha...
Medical Quiz ( Online Quiz for API Meet 2024 ).pdf

Medical Quiz ( Online Quiz for API Meet 2024 ).pdf
Osvaldo Bernardo Muchanga-GASTROINTESTINAL INFECTIONS AND GASTRITIS-2024.pdf

Osvaldo Bernardo Muchanga-GASTROINTESTINAL INFECTIONS AND GASTRITIS-2024.pdf
Dr. Tan's Balance Method.pdf (From Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin)

Dr. Tan's Balance Method.pdf (From Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin)
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis - Pathogenesis , Clinical Features & Manage...

Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis - Pathogenesis , Clinical Features & Manage...
Hemodialysis: Chapter 5, Dialyzers Overview - Dr.Gawad

Hemodialysis: Chapter 5, Dialyzers Overview - Dr.Gawad
Osteoporosis.pptx
- 1. Osteoporosis Vinod Kumar Mugada Associate Professor Department of Pharmacy Practice Vignan Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology
- 2. Definition This disease is a long-term and gradually worsening condition that causes bones to become thinner, weaker, and more likely to break. Over time, the structure of the bones breaks down and their overall strength decreases, making them more fragile and prone to fractures.
- 3. Pathophysiology- Primary Osteoporosis • Primary osteoporosis chiefly afflicts the geriatric population • Etiology: progressive bone loss and microarchitectural deterioration • Alternatively denominated as age-related osteoporosis • Idiopathic primary osteoporosis: atypical manifestation in juveniles and young adults • Obscure etiology for idiopathic primary osteoporosis • Potential causes: reduced bone genesis, augmented bone resorption, or both • Underlying factor: primary defect in osteocyte functional regulation
- 4. Pathophysiology- Secondary Osteoporosis • Genetic disorders: cystic fibrosis, idiopathic hypercalciuria, hemochromatosis, osteogenesis imperfecta • Hypogonadal states: anorexia nervosa, athletic amenorrhea, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, premature ovarian failure • Endocrine disorders: Cushing syndrome, adrenal insufficiency, type 1 diabetes mellitus, hyperparathyroidism, thyrotoxicosis • Gastrointestinal diseases: malabsorption, inflammatory bowel disease, gastrectomy, primary biliary cirrhosis
- 5. Pathophysiology- Secondary Osteoporosis • Secondary osteoporosis results from a variety of specific clinical conditions, diseases, or medications, all of which can accelerate bone loss • Hematologic disorders: sickle cell disease, multiple myeloma, hemophilia, leukemias, lymphomas • Rheumatic and autoimmune diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, ankylosing spondylitis • Medications: heparin, glucocorticoids, anticonvulsants, lithium, methotrexate, thyroxine, parenteral nutrition, gonadotropin- releasing hormone agonists, cyclosporine A, tacrolimus
- 6. Mechanism of Age-Related Osteoporosis •Age-related osteoporosis: most prevalent form of the condition •Affects both genders; 2-3 times more common in females •Women's bone loss: biphasic (rapid menopausal phase lasting 4-8 years, followed by slower phase) •Men's bone loss: monophasic, slow, and continuous •Rapid phase in women: 5-10% cortical bone loss; 20-30% trabecular bone loss •Osteoporotic fractures: predominantly in trabecular bone (proximal/distal limb bones, vertebral bodies)
- 7. Mechanism of Age-Related Osteoporosis •Slower phase: 20-25% of cortical and trabecular bone loss for both genders •Rapid phase cause: estrogen deficiency, increased bone resorption, decreased bone formation •Slower phase factors: impaired bone formation, reduced calcium/vitamin D intake, decreased physical activity •Men's hormone conversion: testosterone transformed to estrogen by aromatase enzyme •Deficiency in men: primarily due to increased sex hormone- binding globulin, reducing bioavailability of testosterone and estrogen
- 8. Mechanism of Age-Related Osteoporosis •99% of bodily calcium reserves: sequestered within the skeleton •Calcium: vital for robust skeletal support structure •Calcium requirements: stable for women pre-menopause; increase during menopause •Menopausal calcium demand: driven by estrogen-related alterations in renal calcium conservation and intestinal calcium absorption •Age-related decrease in calcium absorption efficiency: contributing factor •By age 65: intestinal calcium absorption efficiency declines to 50% below adolescent peak absorption levels
- 9. History and Physical + The FRAX® tool has been developed to evaluate fracture risk of patients. It is based on individual patient models that integrate the risks associated with clinical risk factors as well as bone mineral density (BMD) at the femoral neck.
- 11. History and Physical • Fall risk assessment: crucial during patient evaluation • Risk factors to consider: • History of falls, loss of consciousness, or fainting • Balance, dizziness, or coordination issues • Muscle weakness • Lower extremity arthritis • Difficulty standing or walking • Impaired vision • Lower extremity neuropathy • Medication history: potential impact on coordination and balance • 4 or more risk factors: 80% increased likelihood of a fall • Home assessment: may be necessary for comprehensive fall
- 12. Medical History • Female gender: nonmodifiable risk factor; 2-3 times more common than in men • Adult, geriatric (>65 years): increased risk with age • White ethnicity: higher risk for white and Asian women • Family history of osteoporosis: significant genetic influence • Past medical history of bone fracture: increased future fracture risk • Weight <70 kg: higher osteoporosis risk • Smoking: direct toxic effects on osteoblasts; decreases bone mineral density
- 13. Medical History • Adrenal glucocorticoid use: major risk factor for bone loss and fractures • Hypogonadism: secondary osteoporosis cause in both genders • Menopause: rapid bone loss post-menopause • Amenorrhea: risk factor for osteoporosis • Delayed puberty: nonmodifiable risk factor • Lactation: associated with mild BMD decreases • Dietary calcium deficiency: decreases bone mineral density
- 14. Medical History • Vitamin D deficiency: contributes to osteoporosis • Alcohol abuse: detrimental effects on BMD, increased fall and fracture risk • Sedentary lifestyle: significant and rapid bone loss • Hyperthyroidism: associated with decreased bone mass and osteopenia • Hypervitaminosis A: secondary osteoporosis cause • Anticonvulsant use: increased fracture risk; secondary osteoporosis cause • Heparin use: associated with bone loss; increased osteoporosis risk • Proton pump inhibitor use: independent risk factor for osteoporotic fracture in older adults, especially postmenopausal women
- 15. Treatment Summary • Goals of therapy: prevent fractures, stabilize/increase bone mass, relieve symptoms, maximize physical function • Fracture prevention: primary goal for confirmed diagnosis or increased osteoporosis risk • Strategies: maintain bone health, prevent bone injury, dietary measures, lifestyle modifications • Individual treatment recommendations: based on risk assessment, fracture history, BMD measurements • Pharmacologic therapy: for men and women with osteoporosis or fragility fractures • National Osteoporosis Foundation: drug therapy recommendations based on BMD T-scores and fracture probability
- 16. Treatment Summary • American Association of Endocrinology: drug therapy recommendations based on BMD T-scores and fracture history • North American Menopause Society: osteoporosis pharmacotherapy recommendations • FDA-approved agents: antiresorptive agents and anabolic agent (teriparatide) • Tailoring treatment: consider severity of bone loss and comorbidities • United States Surgeon General's office: encourage prevention of bone loss in young and middle-aged adults • Treatment for specific populations: FDA-approved Prescribing Information recommendations • Acute symptomatic vertebral compression fracture: calcitonin therapy, surgical treatment considerations, avoid vertebroplasty