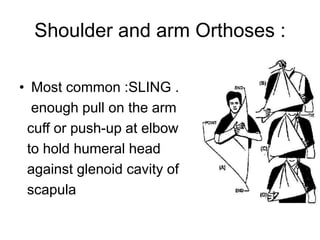
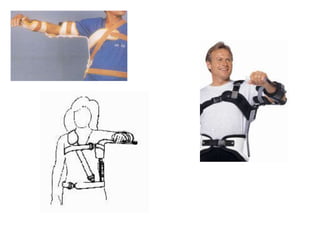
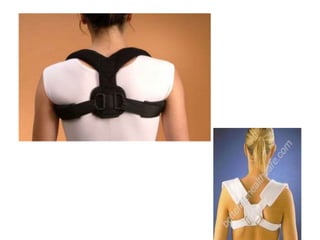
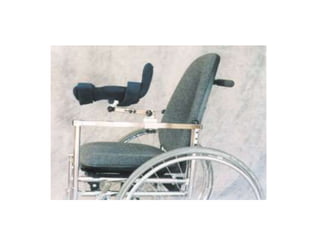
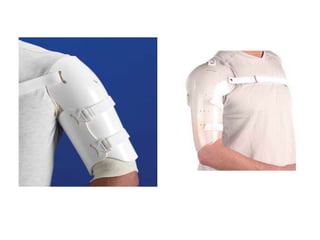
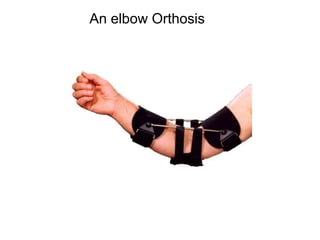
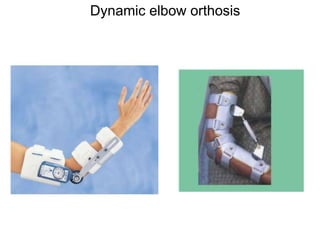
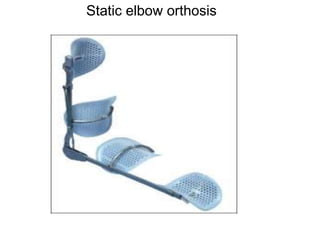
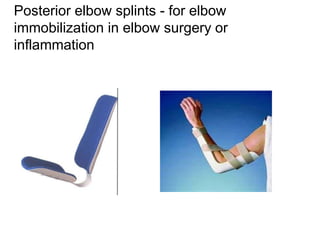
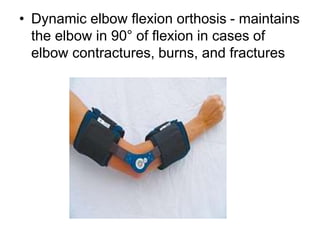
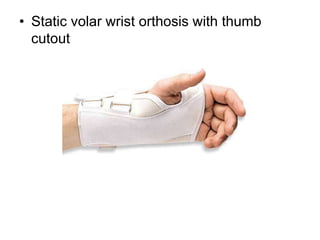
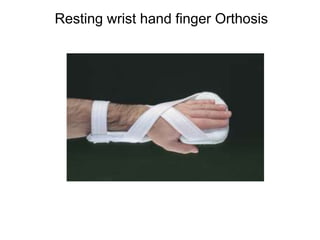
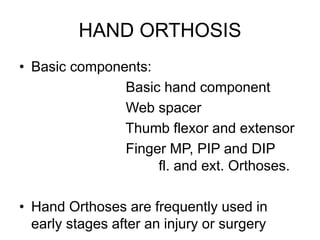
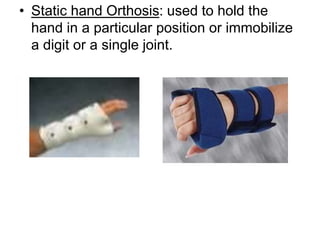
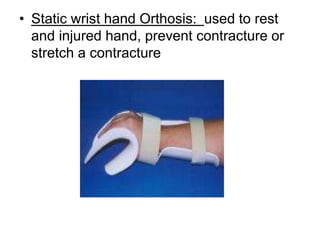
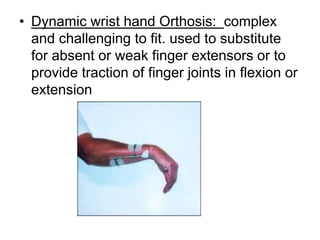
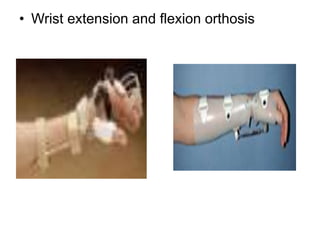
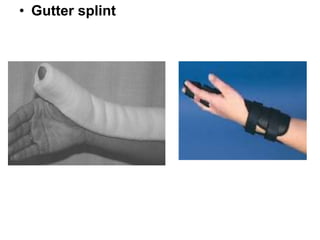
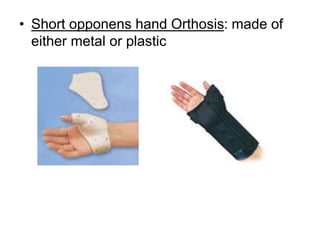
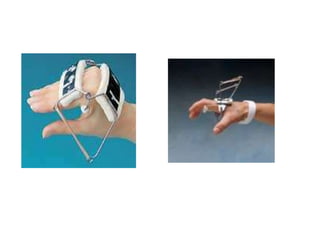
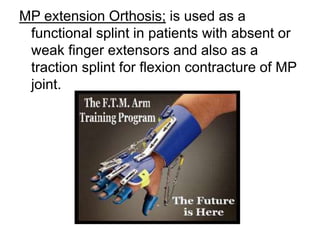
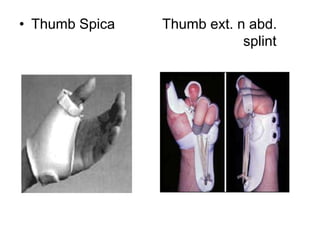
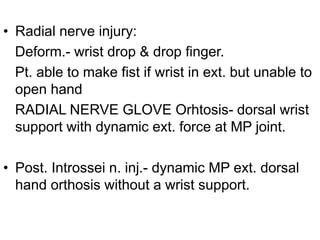
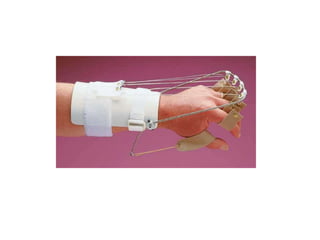
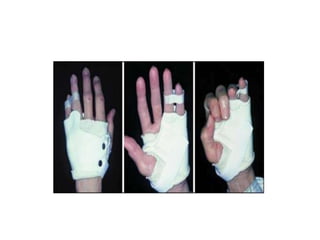
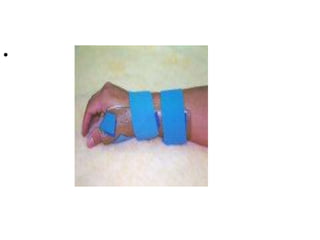
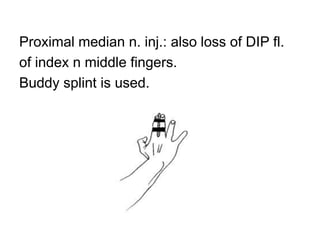
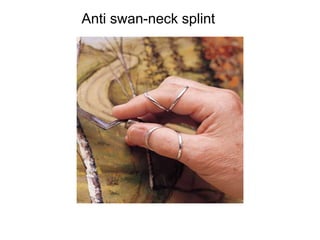
Orthoses are externally applied devices that modify the structural characteristics and function of the neuro-musculoskeletal system. They are used to immobilize, support, correct deformities, assist weak muscles, and substitute for absent motor function. The document discusses various types of orthoses for the upper limb including static/dynamic orthoses for the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hand, and fingers. It provides examples of orthoses used to treat conditions like nerve injuries, burns, rheumatoid arthritis, and spinal cord injuries. The principles and goals of orthosis prescription for different parts of the body and medical conditions are explained.

![Introduction
• The term “Orthosis” adopted by the American
Orthotics and Prosthetics Association (AOPA)
in 1960
• In Greek, Orthosis- “making straight”
[Simon K. M. Wong. Hand Surgery, Vol. 7, No. 2 (
December 2002) 209–213]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthoses-230423130605-dd957a3d/85/ORTHOSES-ppt-2-320.jpg)