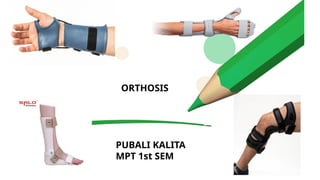
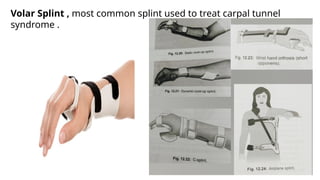
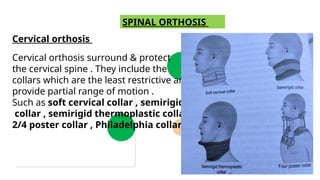
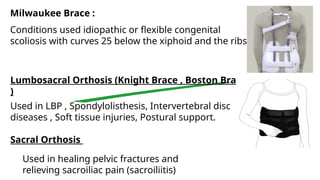
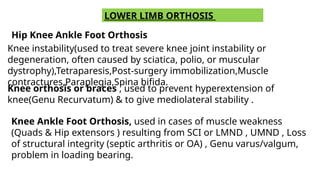
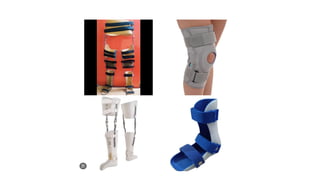
An orthosis is a customized device designed to maintain anatomical or functional positions of the body, with various classifications such as supportive, functional, corrective, and protective. Upper limb orthoses include static and dynamic splints for conditions like wrist drop and carpal tunnel syndrome, while lower limb orthoses treat issues like knee instability and muscle weakness. The document also discusses biomechanical principles and the advantages and disadvantages of using orthoses in rehabilitation.