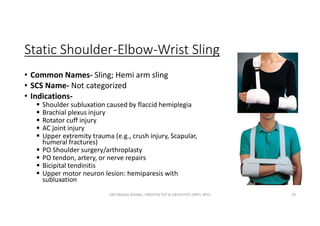
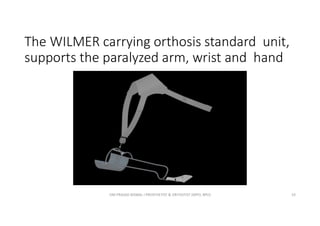
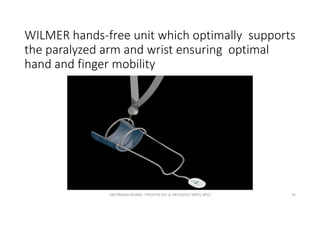
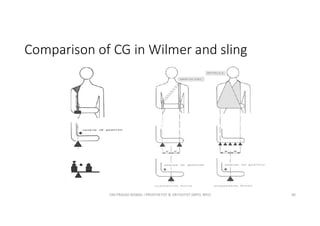
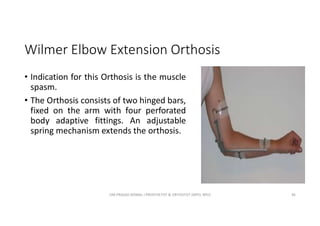
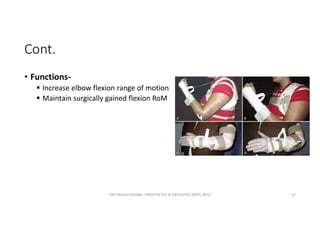
This document discusses various orthoses used for the shoulder, elbow, and forearm. It begins by outlining the main objectives of upper limb orthosis as protection, correction, and assistance. It then describes different types of orthoses categorized by joint covered, function provided, condition treated, appearance, and designer. Examples of specific orthoses are provided like figure-8 axilla orthosis, lateral trunk shoulder-elbow-wrist orthosis, and static shoulder-elbow-wrist sling. Design variations are also covered such as static, serial static, and dynamic. The document provides details on several orthosis like Wilmer carrying orthosis and its standard and hands-free units.
























![Lateral Trunk-Based Static Shoulder-Elbow-Wrist
Orthosis
• Common Names- Shoulder/Gunslinger Splint
• SCS Name-Shoulder adduction or abduction
immobilization; type 3[4]
• Functions-
To fully immobilize the shoulder (and sometimes the
elbow) to promote healing of surgically repaired
bony or soft tissues.
The elbow and wrist are immobilized to maintain full
control of the shoulder.
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-25-320.jpg)

![Lateral Trunk-Based Static (or Serial-Static)
Shoulder-Abduction (Elbow-Wrist) Orthosis
• Common Names- Axilla/Airplane
splint/Conformer/Arm abduction splint
• SCS Name- 120 degree shoulder abduction
immobilization/mobilization; type 3[4]
• Indications-
Axillary burns contractures
Post operative shoulder fusion
Post operative scar release
Shoulder dislocation
Burns –Shoulder adduction contractures
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-27-320.jpg)















![Posterior Static Elbow (Wrist) Orthosis
Posterior Static Elbow Flexion-Blocking Orthosis
• Common Names- (Posterior) Elbow Splint/Sugar-tong splint
• SCS Name-
90 degree flexion immobilization; type 0[1];
If the wrist is included, it ill be named 90 degree elbow flexion immobilization; type
1[1]
• Indications-
Rheumatoid arthritis
CTD
Forearm fractures
Post operative elbow arthroplasty
Elbow surgery
o Ulnar nerve transposition
o Tendon transfers
o Nerve repairs
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-48-320.jpg)

![Anterior Static Elbow Orthosis
Anterior Serial-Static Elbow Corrective-Extension Orthosis
Anterior Static Elbow Flexion-Blocking Orthosis
• Common Name- (Anterior) Elbow Splint
• SCS Name- Elbow extension immobilization or mobilization; type 0[1]
• Indications-
Burns
Ulnar nerve entrapment
Capsular tightness
Elbow injury or surgery
o Multiple trauma
o Intra-articular fractures
o Triceps rupture
o Tumor resection
o Total elbow arthroplasty
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-50-320.jpg)

![Bi-surfaced Static Elbow Orthosis
Bi-surfaced Serial-Static Elbow Corrective-Flexion/Extension Orthosis
Bi-surfaced Static Elbow Flexion-Blocking Orthosis
• Common Name- Elbow splint
• SCS Name- Elbow extension immobilization splint; type 0[1]
• Indications-
Burns
Ulnar nerve entrapment
Capsular tightness
Rheumatoid arthritis
Forearm fractures
Post operative elbow arthroplasty
Elbow surgery
o Ulnar nerve transposition
o Tendon transfers
o Nerve repairs
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 52](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-52-320.jpg)

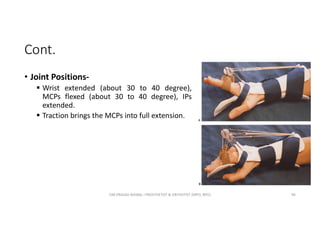
![Static-Progressive Elbow-Flexion Harness
• Common Name- Elbow flexion splint
• SCS Name- Elbow flexion mobilization; type 1[2]
• Indications-
Flexion contractures caused by
o Intra-articular fractures
o Multiple trauma
o Capsular tightness
o Supracondylar fracture
o Radial head fracture
Post-operatively: total elbow arthroplasty
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 54](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-54-320.jpg)




![Spiral Dynamic Forearm-Rotation Thumb-Abduction
Strap
• Common Name- Thumb abduction supination splint; Prefabricated Rolyan Upper
extremity Tone and Positioning (TAP) Splint
• SCS Name- Forearm pronation/supination mobilization, thumb abduction
mobilization; type 1[3]- i.e., thumb MCP is the secondary joints; primary joints are
forearm and thumb CMC; total joints=3
• Indications-
Hypertonicity/hypotonicity associated with-
o Head injury
o Cerebral palsy
o Multiple sclerosis
o Cerebrovascular accident
Peripheral or central nerve lesions
Distal radio-ulnar joint stiffness
Forearm stiffness secondary to cast immobilization for a wrist fracture
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 61](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-61-320.jpg)




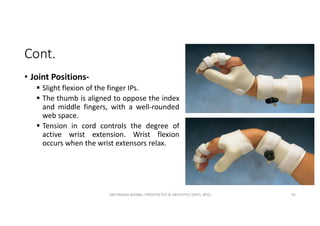
![Cont.
• SCS Name- Wrist extension immobilization; type 0[1]
• Design Considerations-
Volar: Provides optimal support to the carpal bones; recommended for joint
inflammation or instability; cane be used to mount flexion outriggers.
Dorsal: Blocks sensation less than other designs; can be used to mount
extension outriggers; has integrated palmar bar.
Ulnar: Can be used to mount flexion or extension outriggers.
Radial: Restricts wrist motion less than other designs, permitting wrist ulnar
deviation and some flexion; can be used to mount flexion or extension
outriggers.
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 67](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-67-320.jpg)

![Circumferential Forearm-Based Static Wrist
Orthosis (with Ulnar opening)
• Common Name- Circumferential
work(ing) splint; Gauntlet immobilization
splint; CTS Splint; Radial fracture brace
• SCS Name- Wrist extension
immobilization; type 0[1]
• Indications-
Carpal tunnel syndrome (full circumferential)
Fracture of the radius or base of the
metacarpal (with ulnar opening)
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 70](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-70-320.jpg)

![Dorsal Forearm-Based Dynamic Joint-Aligned
Coil-Spring Wrist Assistive-Extension Orthosis
• Common Name- Dynamic wrist extension splint
• SCS Name- Wrist extension immobilization; type
0[1]
• Indications-
Weak or paralyzed wrist extensors (e.g., radial nerve
palsy)
• Functions-
Passively extend the wrist while allowing active wrist
flexion.
Prevent contracture of unopposed, innervated wrist
flexors.
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 72](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-72-320.jpg)
![Dorsal-Volar Forearm-Based Static Wrist Writing/Painting
Orthosis
• Common Name- Writing splint
• SCS Name- Wrist extension immobilization; type
0[1]
• Indications-
Spinal cord injury at level C5 or above i.e. wrist
extensors are paralyzed.
• Functions-
Enable writing, drawing, or painting by positioning
the wrist in functional extension and providing an
attachment for a pen, pencil, or paintbrush.
Enable erasing of pencil marks or turning of pages
with the mounted eraser.
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 73](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-73-320.jpg)
![Radial Forearm-Based Static Wrist-Thumb Orthosis
• Common Names-
De Quervain’s splint
Wrist and thumb static splint
Long thumb CMC immobilization splint
Long opponens splint
Radial thumb gutter splint
Wrist-thumb orthosis for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis
• SCS Name- Thumb MP extension immobilization;
type 2[3]
• Indications-
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 74](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-74-320.jpg)

![Volar Forearm-Based Static Wrist-Thumb Orthosis
• Common Names-
Scaphoid fracture splint
Radial thumb gutter splint
Thumb spica
De Quervain’s static splint
• SCS Name- Thumb MC extension immobilization; type
2[3]
• Indications-
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis
Scaphoid fracture
Bennett’s fracture-dislocation-at the base of the first MC
Instability or joint inflammation of the wrist and thumb
CMC/MCP (e.g., RA)
Quadriplegia
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 76](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-76-320.jpg)

![Volar Forearm-Based Static Wrist and D2-5 MCP-
Stabilizing Orthosis
• Common Name- Wrist MCP splint
• SCS Name- Wrist and index through small finger
MP extension immobilization; type 0[5]
• Indications-
Joint inflammation (e.g., RA with or without CTS)
• Functions-
Immobilize the wrist and finger MCPs.
Relieve pain and inflammation.
Prevent or correct joint deformity (e.g., wrist radial
deviation and volar subluxation; MCP ulnar drift and
volar subluxation)
Unload lax joint capsules and ligaments or promote
resorption and correct joint instability.
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 78](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-78-320.jpg)
![Dorsal Forearm-Based Dynamic Arching Spring-
Wire D1-5 MCP Assistive-Extension Orthosis
• Common Names-
Radial nerve splint
MCP extension-assist splint
MCP arthroplasty splint
Dynamic cock-up
• SCS Name- Index through small finger MP
extension mobilization; type 1[5]
• Indications-
Weak wrist, finger MCPs, and thumb extensors; radial
nerve lesion
MCP arthroplasty-angle the wires to pull the MCPs
radially
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 79](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-79-320.jpg)

![Dorsal Forearm-Based Dynamic Arching Spring-Wire
Wrist and D1-5 MCP Assistive-Extension Orthosis
• Common Names- Radial nerve splint;
MCP extension assist splint; Dynamic
cock-up splint.
• SCS Name- Wrist and MP extension
mobilization; type 0[5]
• Indications-
Weak wrist, finger MCPs, and thumb
extensors; radial nerve lesion
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 81](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-81-320.jpg)

![Volar Forearm-Based Dynamic D2-5 MCP Corrective-
Flexion Orthosis
• Common Names- Dynamic MCP flexion splint
• SCS Name- Index through small finger MP
flexion mobilization; type 1[5]
• Indications-
Extension contracture of the MCPs caused by
shortened collateral ligaments
• Functions-
Gently stress the MCP collateral ligaments to
promote desired growth and increase flexion
range.
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 83](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-83-320.jpg)
![Volar Forearm-Based Static (or Serial-Static) C-Bar
Wrist-Hand Orthosis
• Common Name- Resting Hand Splint
• SCS Name- Wrist extension, index through small finger MCP and IP extension,
thumb CMC palmar abduction immobilization/mobilization; type 0[16]
• Indications-
Dupuytren’s release
Boxer’s fracture (neck of fifth MC)
Crush injury
Inflammatory joint disease
Flaccid paralysis
Burns
Replantation
Skin graft
Scleroderma
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 84](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-84-320.jpg)


![Bisurfaced Forearm-Based Static (or Serial-Static)
Wrist-Hand Orthosis
• Common Name- Anti-spasticity splint; dorsal volar hand splint
• SCS Name- Wrist extension, index through small finger MCP and IP extension,
thumb CMC palmar abduction immobilization/mobilization; type 0[16]
• Indications-
Dupuytren’s release (when it’s desirable for the proximal palm or volar surface
of the forearm to be uncovered)
Boxer’s fracture (neck of fifth MC)
Crush injury
High tone associated with-
o Head injury
o Cerebral palsy
o Multiple sclerosis
o Cerebrovascular accident
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 87](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-87-320.jpg)

![Ulnar Forearm-Based Static Wrist-Hand Cone-Style
Tone-Reducing Orthosis
• Common Name- Anti-spasticity cone splint
• SCS Name- Wrist extension, index through
small finger MCP and IP extension, thumb
CMC palmar abduction immobilization
/mobilization; type 0[16]
• Indications- High tone associated with-
Head injury
Cerebral palsy
Multiple sclerosis
Cerebrovascular accident
OM PRASAD BISWAL I PROSTHETIST & ORTHOTIST (MPO, BPO) 89](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orthosesforshoulderelbowandforearm-210507073302/85/Orthoses-for-shoulder-elbow-and-forearm-89-320.jpg)