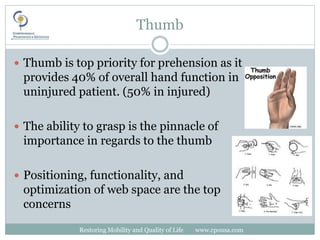
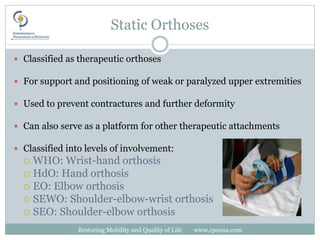
This document discusses upper extremity orthotics for restoring mobility and quality of life. It covers common orthotic components for the shoulder, elbow, wrist, fingers and thumb. Static orthoses are used for positioning and prevention of deformities while functional orthoses provide assistance for tasks using internal or external power sources. Fracture/post-operative orthoses provide compression and positioning for proper healing. The document reviews specific orthotic designs for various conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.