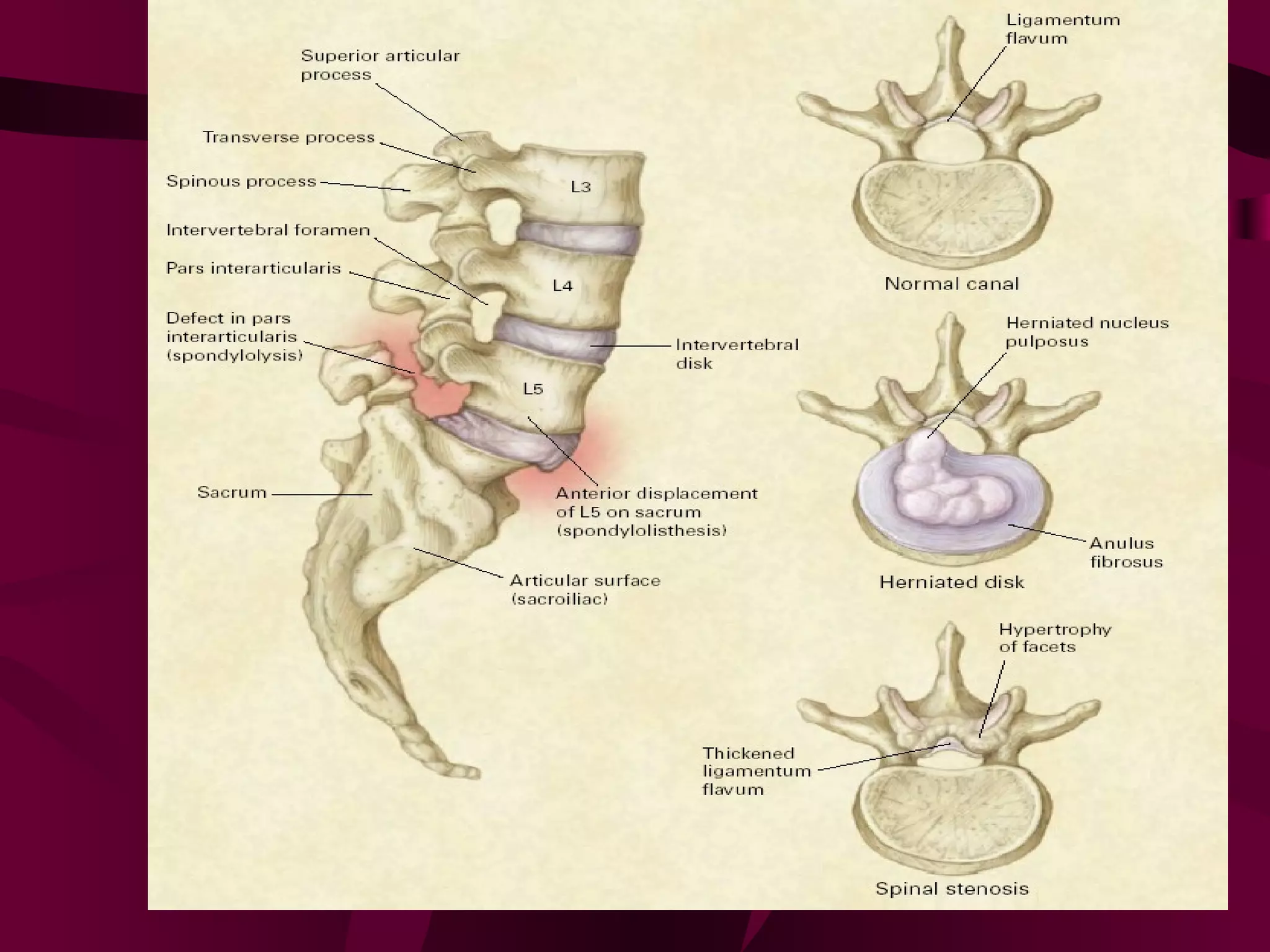
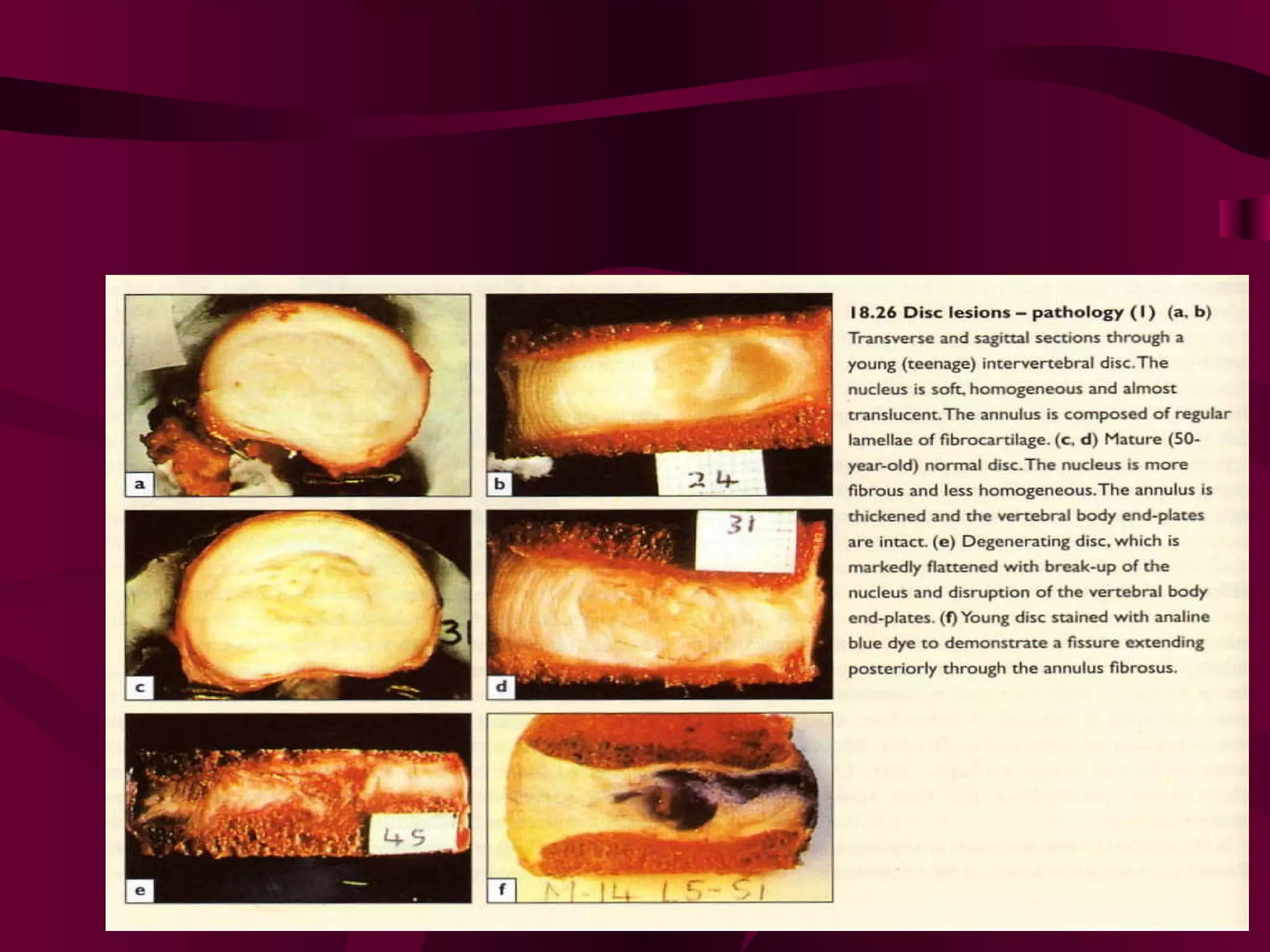
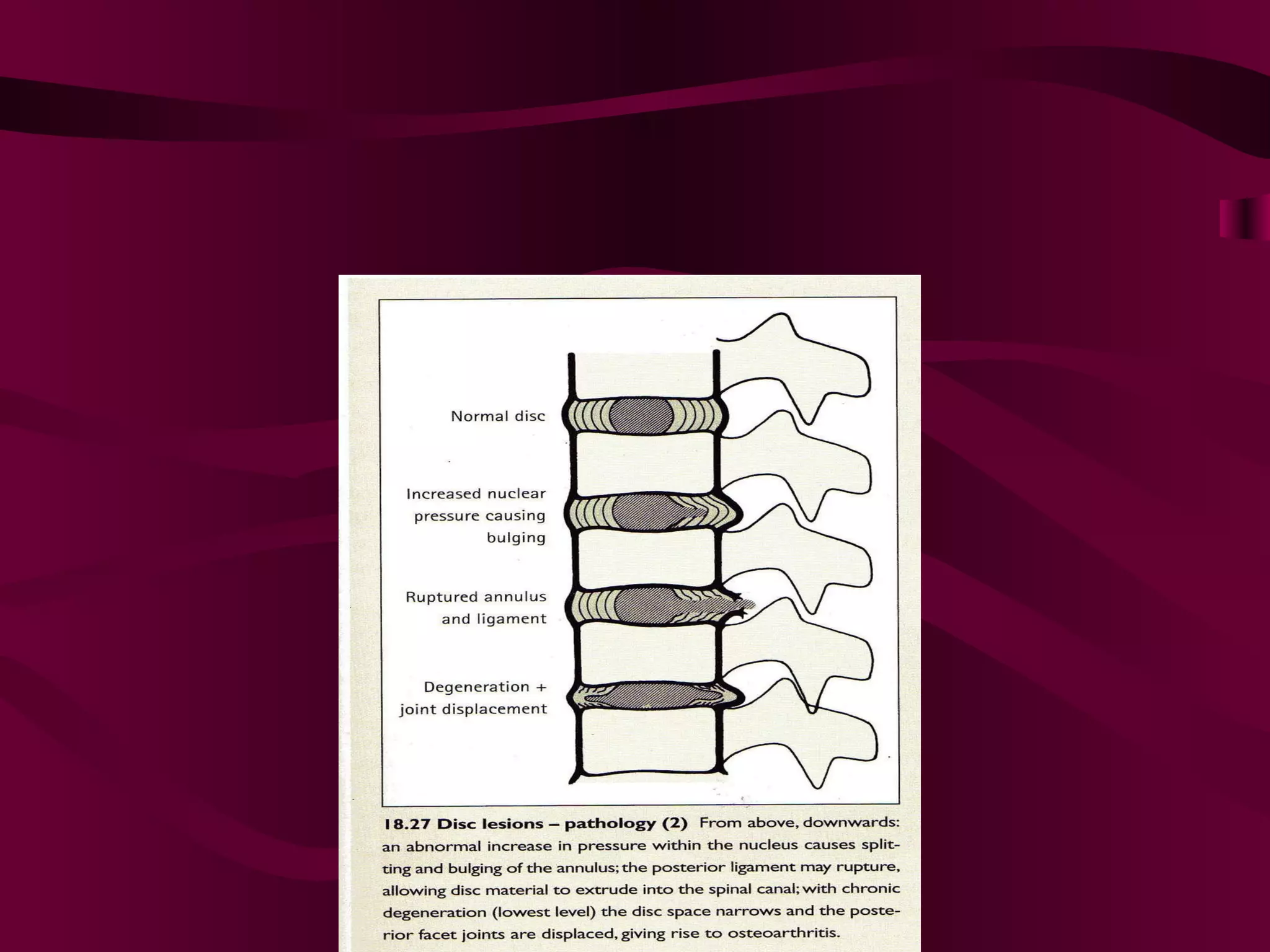
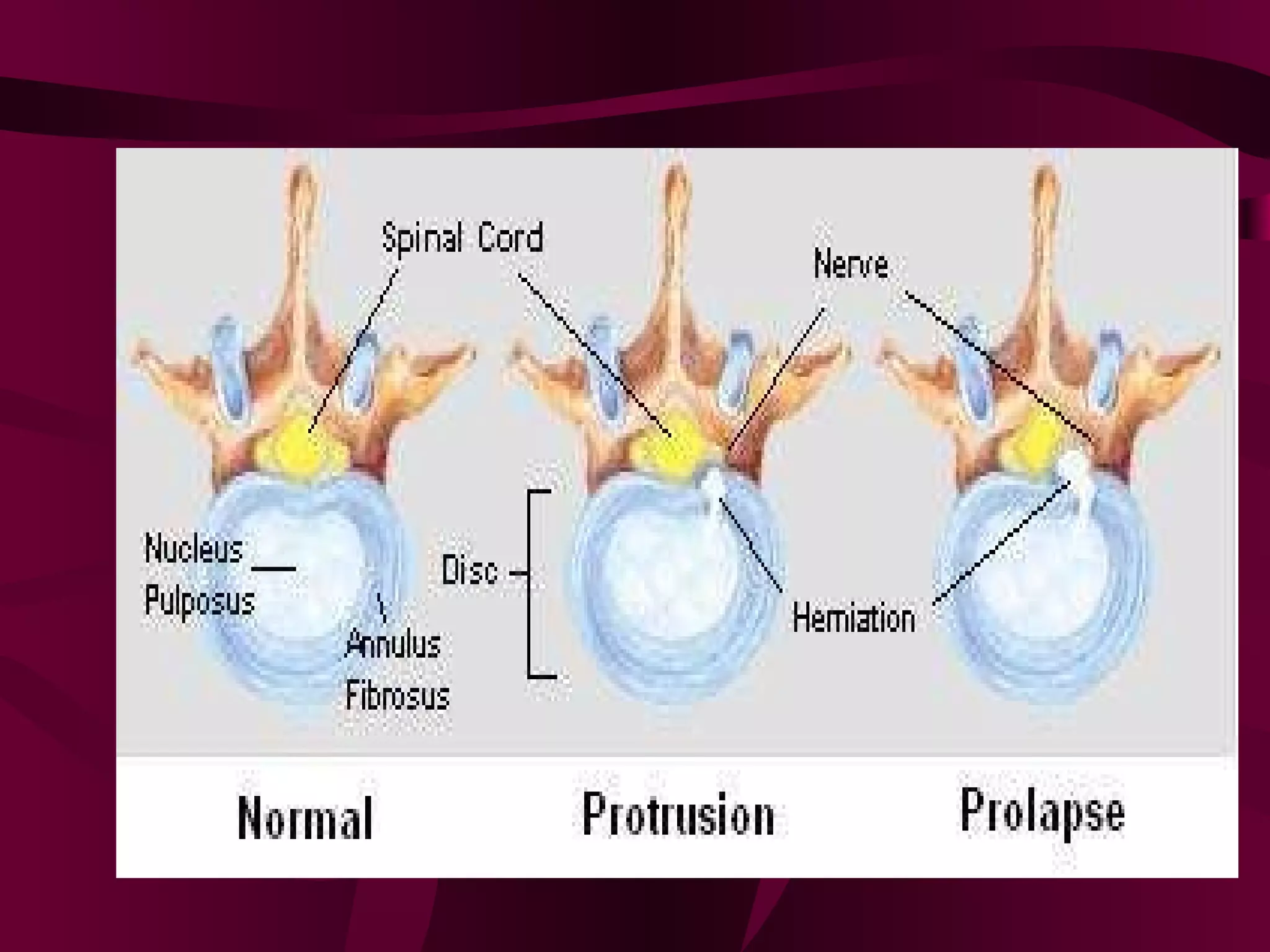
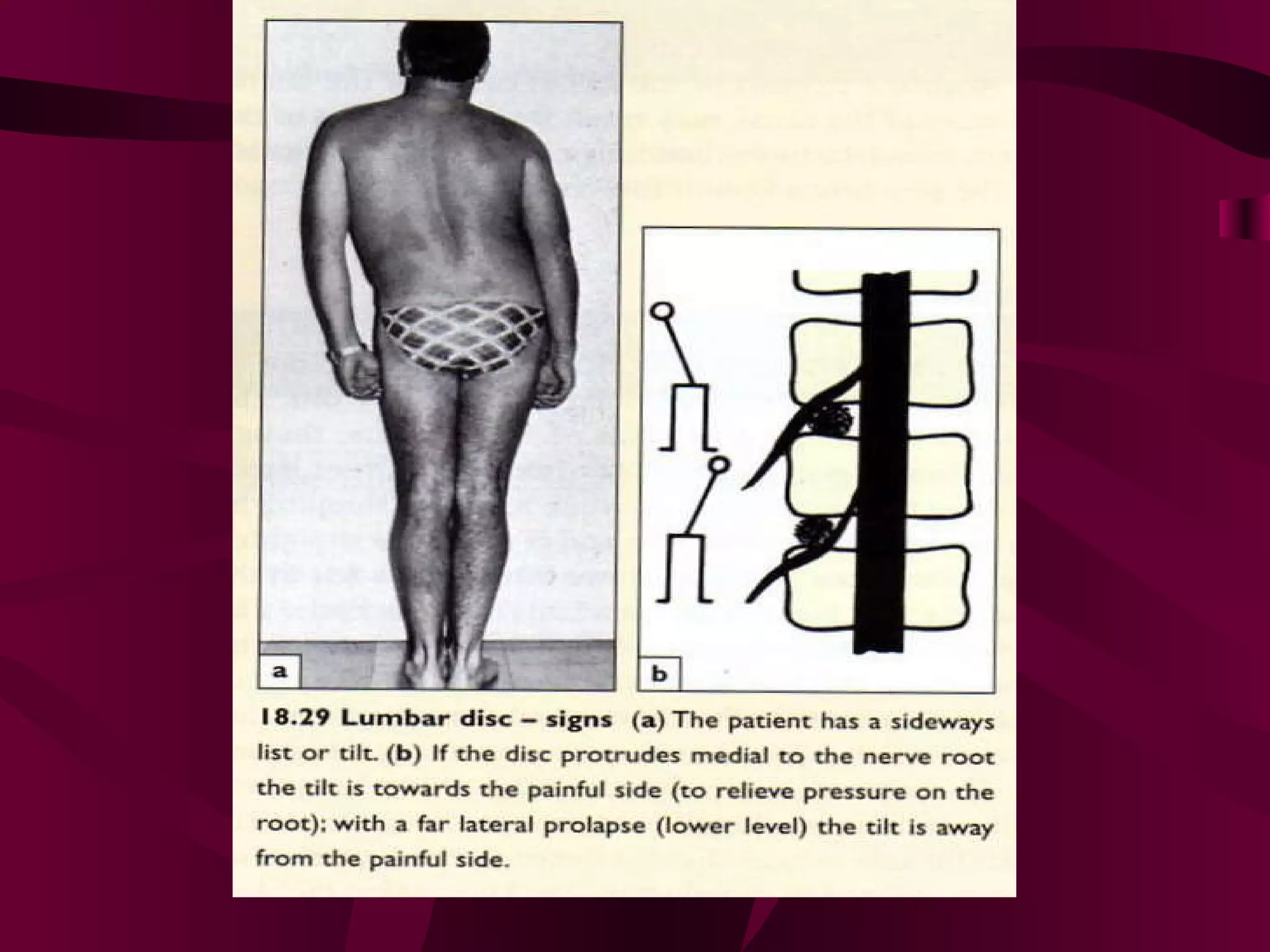
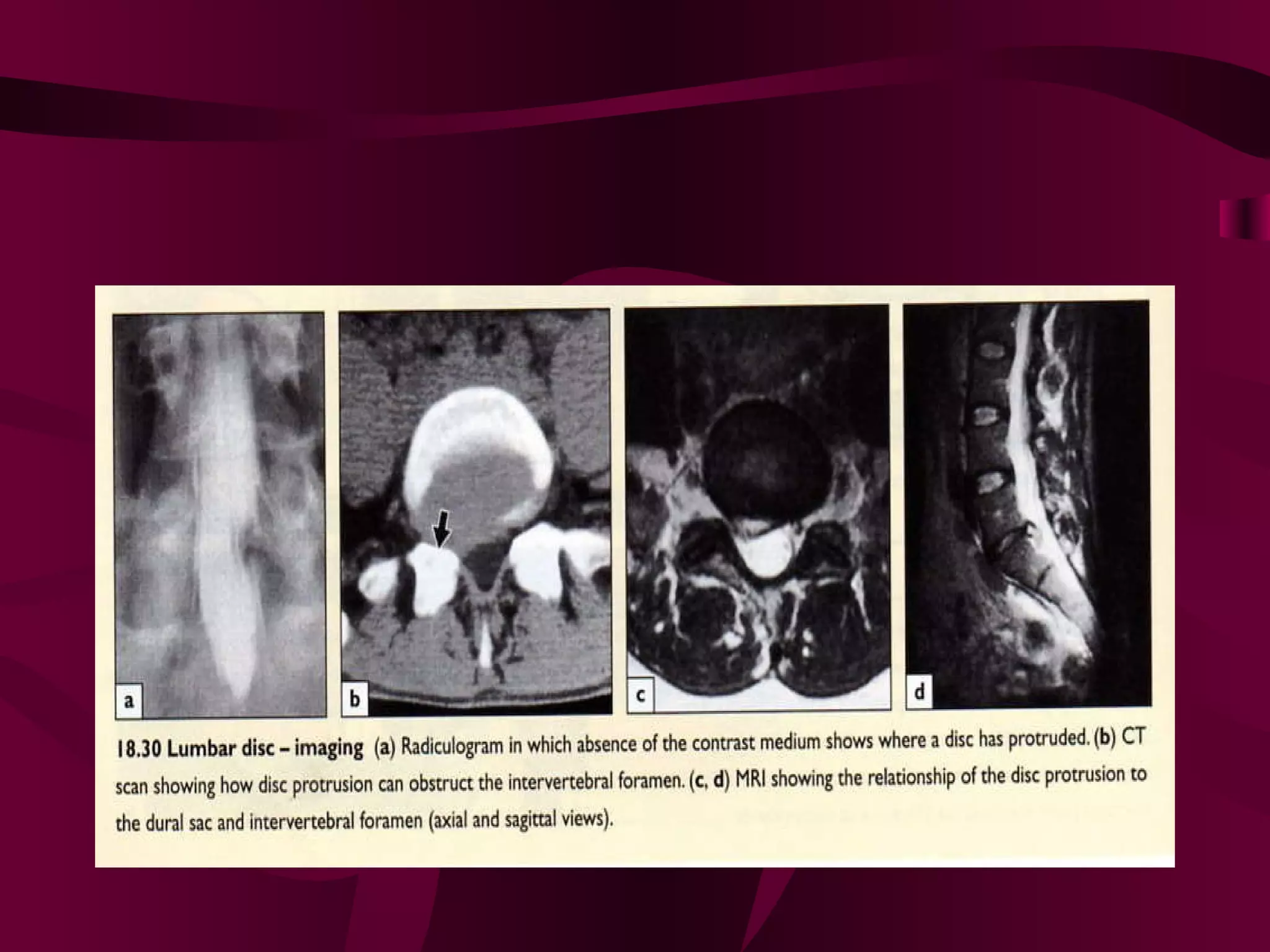
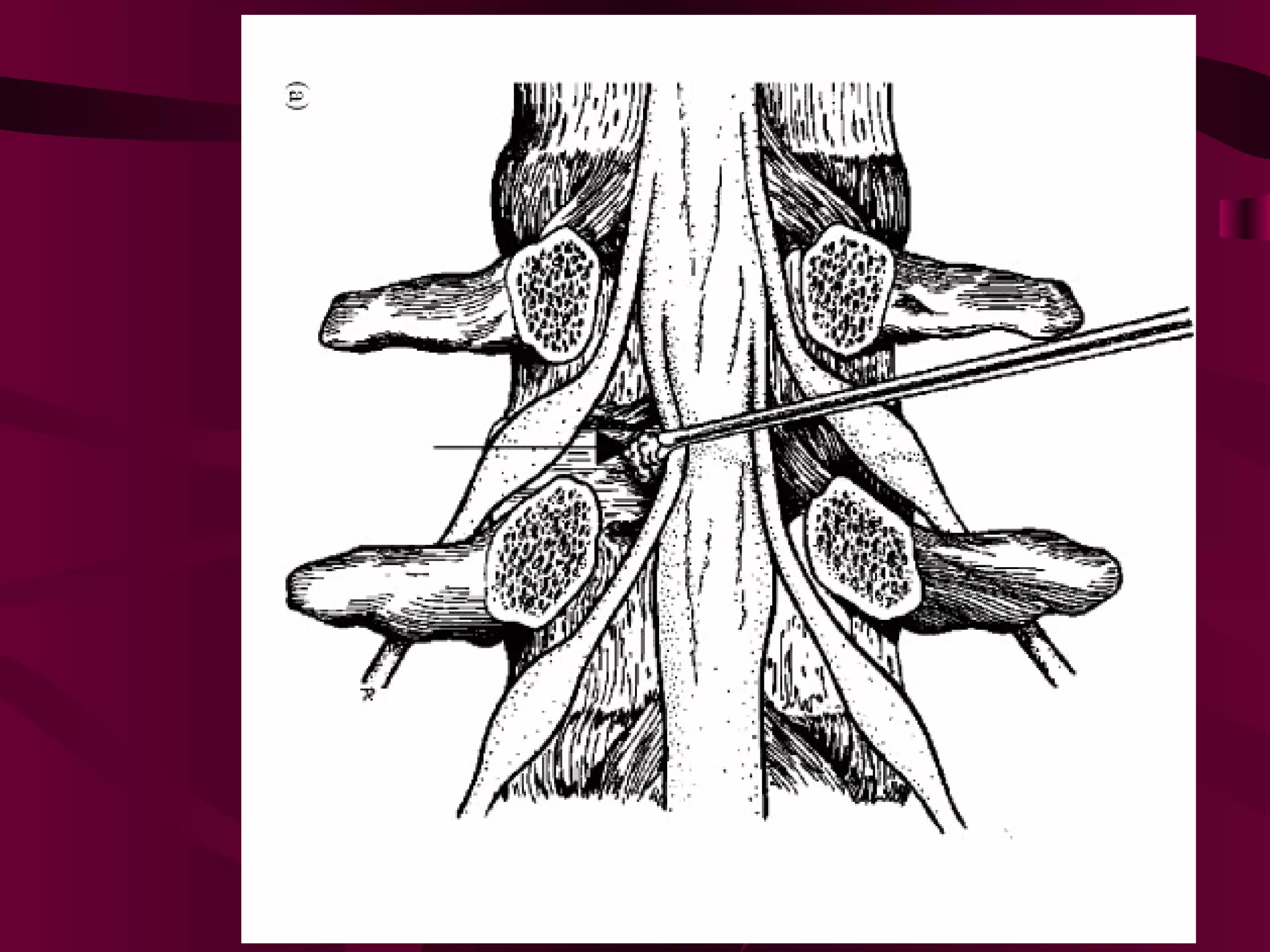
Prolapsed Intervertebral Discs can be caused by chronic degeneration from normal aging or acute disc herniation which causes pain and compression effects on the nerve root. Imaging like x-rays, MRI, and CT scans are used to diagnose the condition. Treatment options include rest, gentle massage, bracing, anti-inflammatory medications, epidural blocks, and surgery like microdiscectomy if conservative treatments fail. Surgical treatment aims to decompress the nerve root while avoiding excessive scarring and early mobilization is emphasized.