This document provides information on spinal disc herniation, including:
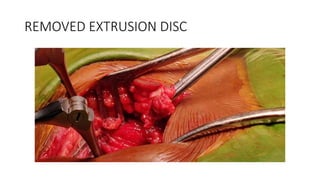
- Disc herniation occurs when the nucleus pulposus is pushed through tears in the annulus fibrosus into the spinal canal.
- Common causes are age-related degeneration, trauma, and straining. It progresses from internal disruption to instability.
- Diagnosis is typically made using MRI, which can identify protrusions, extrusions, and sequestrations.
- Treatment involves initial conservative measures like rest, ice, and NSAIDs. Surgery such as discectomy or microdiscectomy may be required for persistent or severe cases.
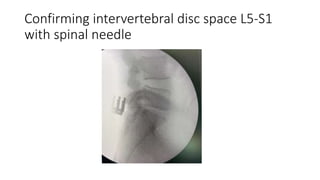
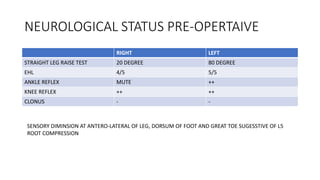
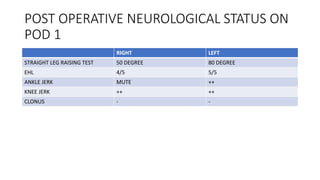
- A case study describes the successful surgical treatment of a 29-year