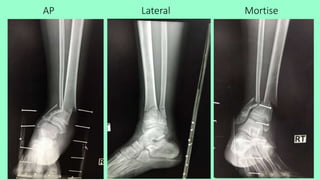
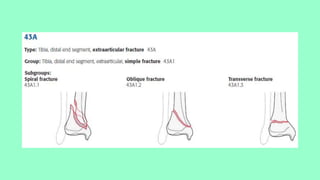
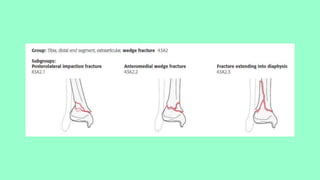
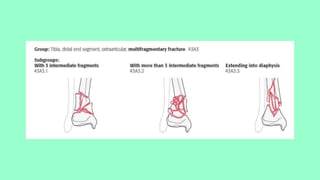
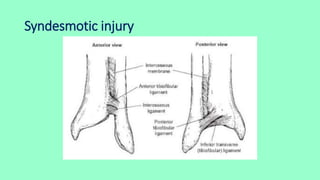
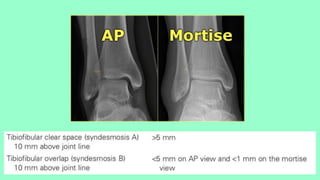
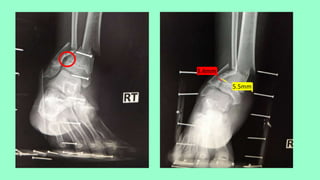
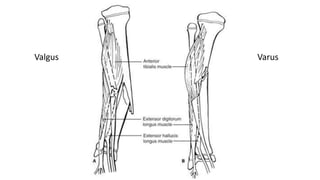
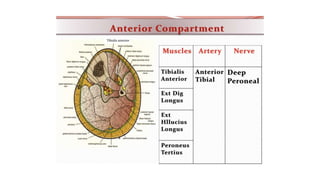
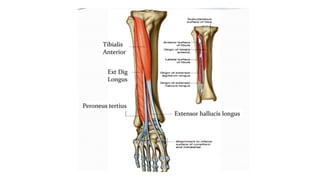
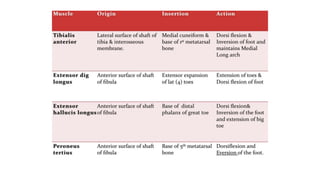
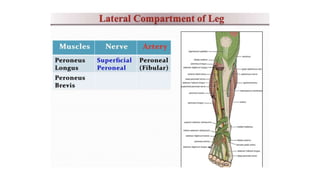
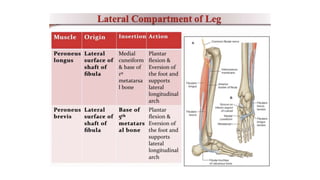
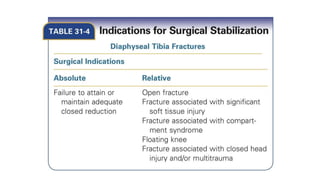
This document summarizes a case of a 9 year old female who presented with right leg pain for 2 hours after a bicycle accident. On examination, she had deformity, swelling and tenderness of the right ankle with limited range of motion due to pain. X-rays showed close transverse fractures of the right distal tibia and fibula with minimal displacement. The diagnosis was close fractures of both bones of the right leg. Management included pain control, possible closed reduction, application of a long leg posterior splint, and monitoring for compartment syndrome. The document then reviews general knowledge of tibia and fibula fractures including mechanisms of injury, signs and symptoms, radiological findings, and treatment options such as cast immobilization or surgery.