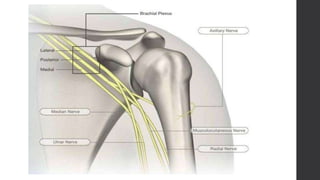
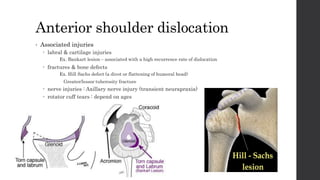
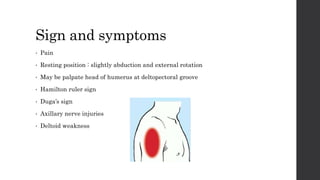
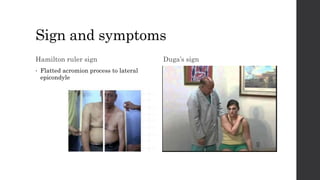
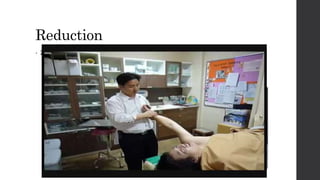
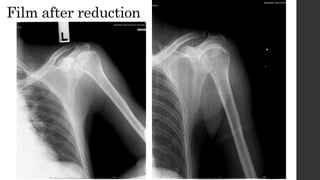
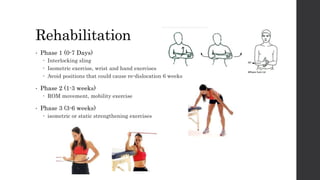
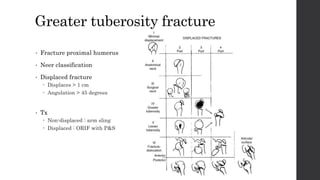
This document summarizes an orthopedic case of a 42-year-old Thai male who presented to the emergency room with left shoulder pain after hearing a popping sound while lifting roof tiles. On examination, he was found to have deformity and tenderness of the left shoulder with the humeral head palpable in the anterior shoulder, indicating an anterior shoulder dislocation. X-rays confirmed an anterior shoulder dislocation with an associated greater tuberosity fracture. The patient was taken to the operating room for closed reduction of the dislocation and rehabilitation.