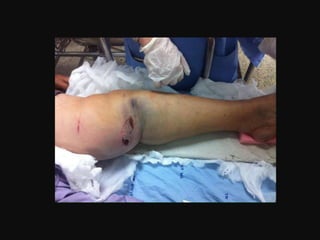
- The patient is a 54-year-old female who was in a motorcycle accident 4 hours prior where her motorcycle was hit on the side causing her to fall and injure her left leg.
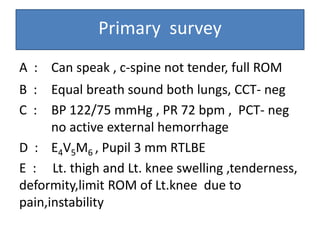
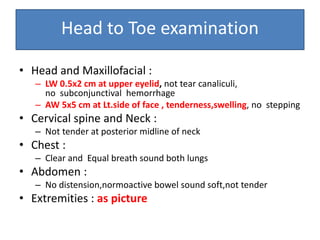
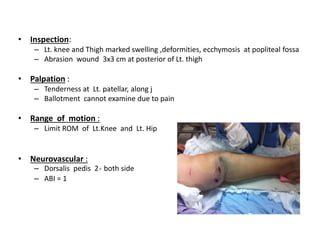
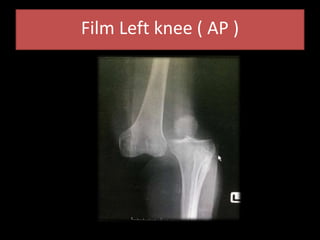
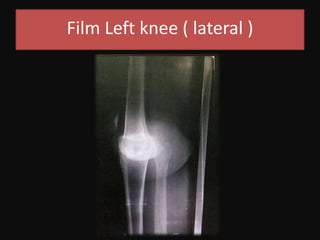
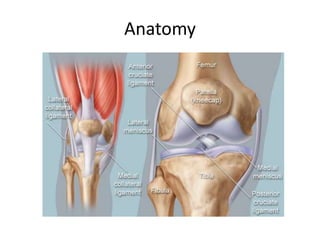
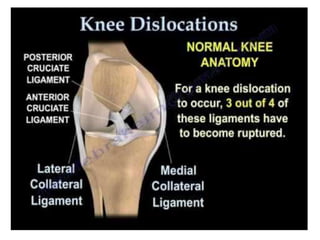
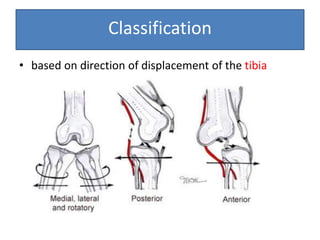
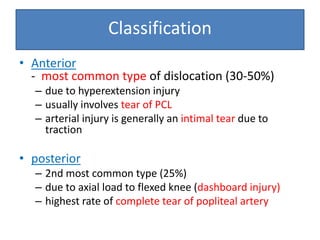
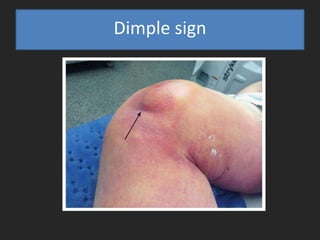
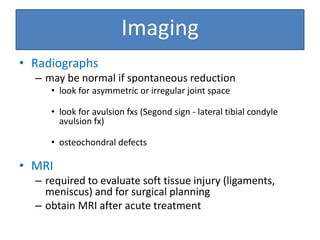
- On examination, she had swelling and deformity of her left knee and thigh with tenderness and limited range of motion. X-rays showed a posterolateral dislocation of the left knee.
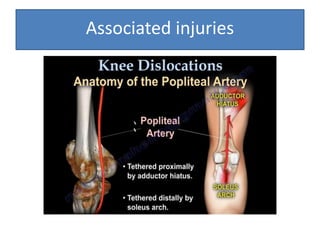
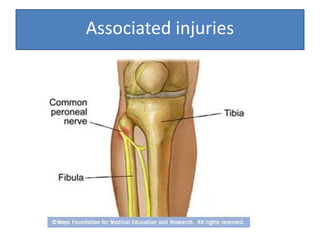
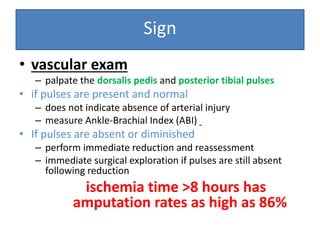
- She underwent closed reduction of the knee dislocation. A CTA showed no evidence of vascular injury. She was diagnosed with a posterolateral left knee dislocation and given splinting and pain management.