1. The patient is a 70-year-old Thai man who fell at his home 1 day ago and was brought to the hospital.
2. On examination, he had a sutured head wound and swelling and pain in his right ankle that prevented walking.
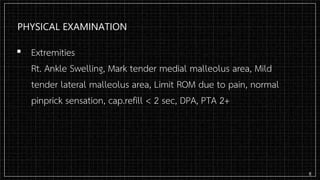
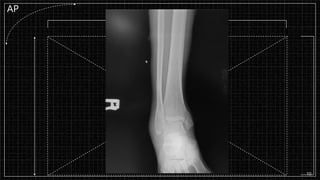
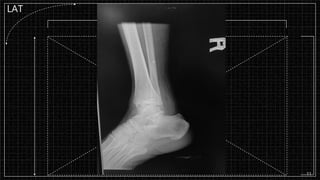
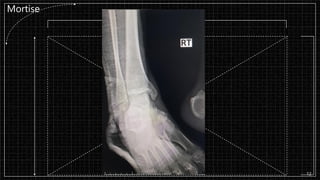
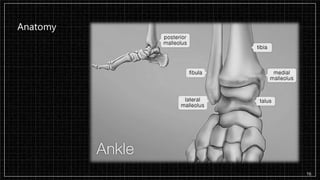
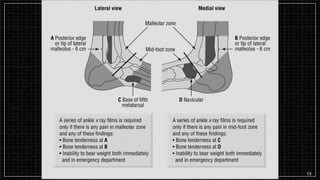
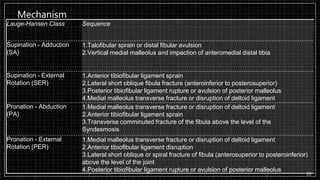
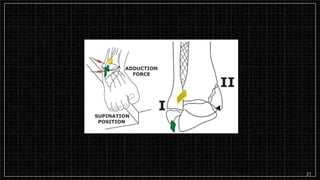
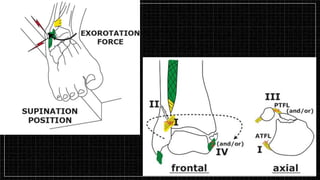
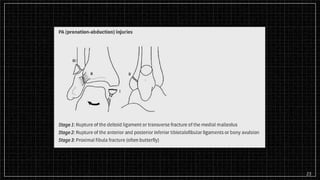
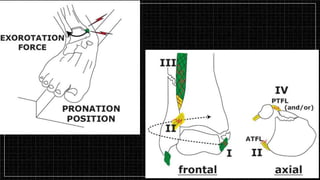
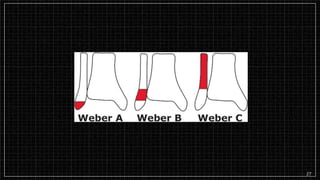
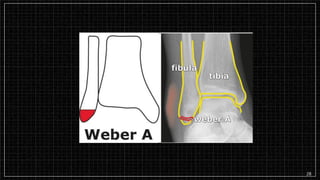
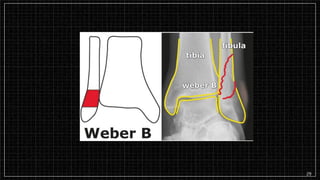
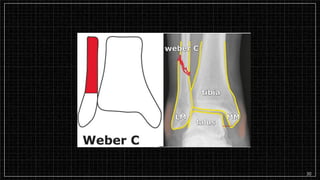
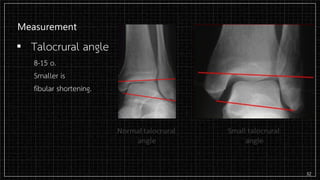
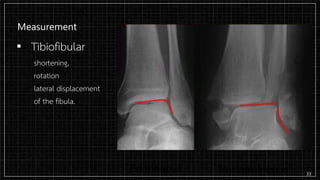
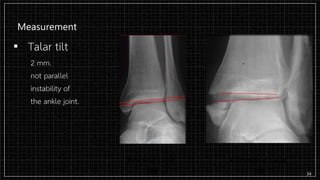
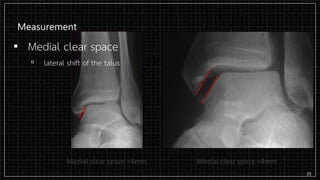
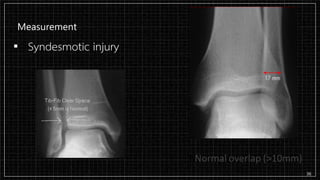
3. X-rays showed a closed bimalleolar fracture of the right ankle. He was admitted for pain control, immobilization, and pre-operative management.