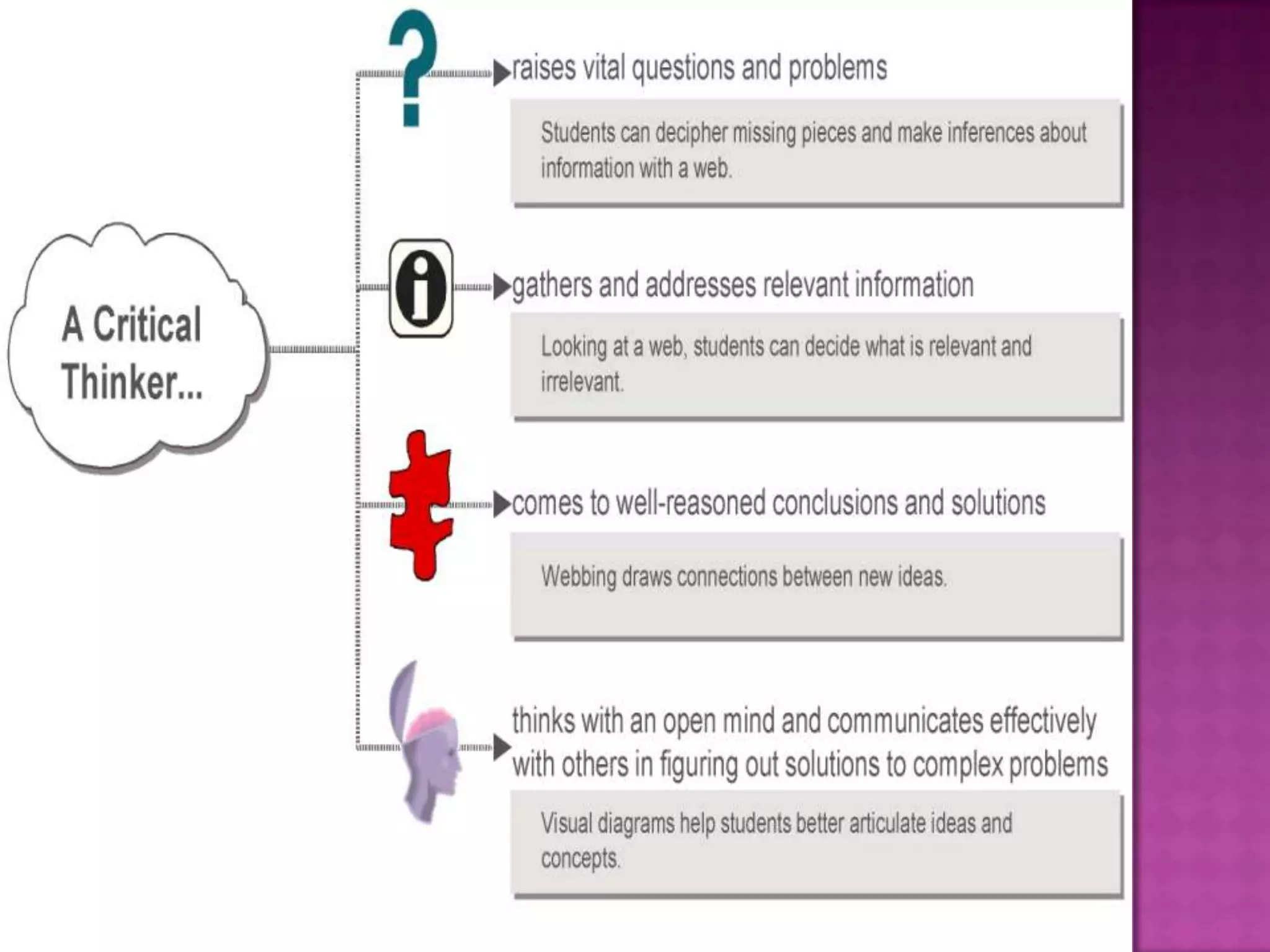
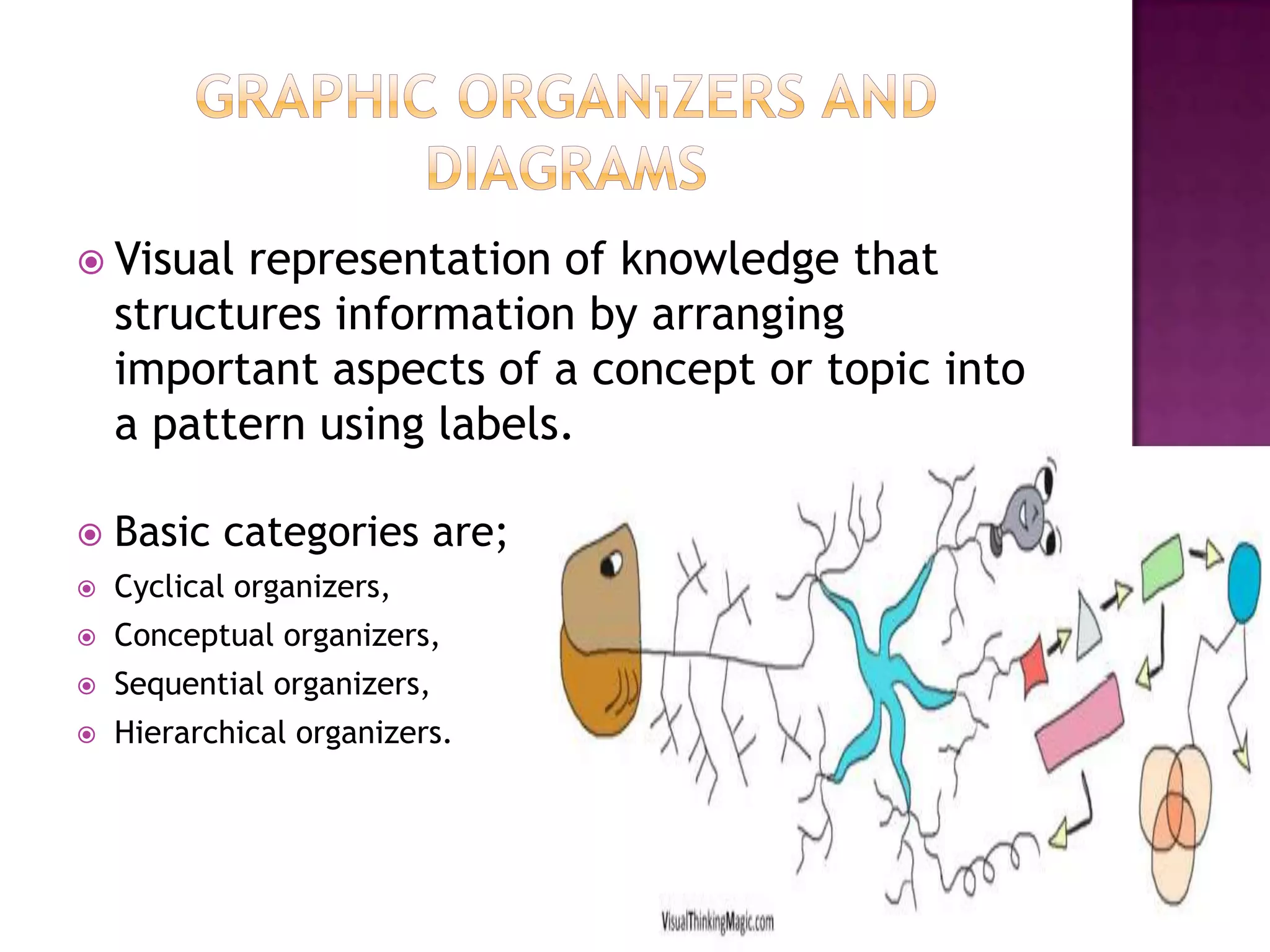
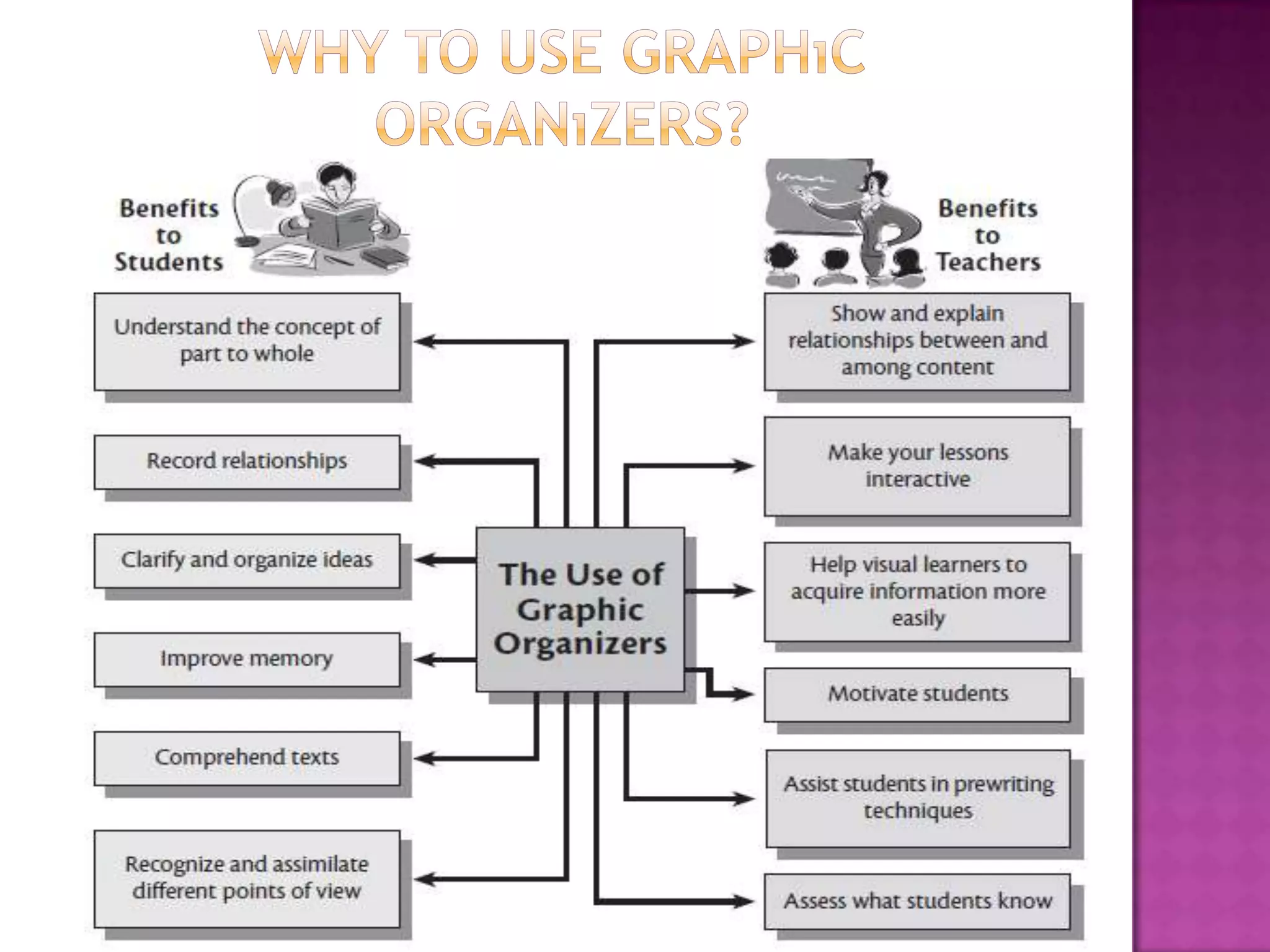
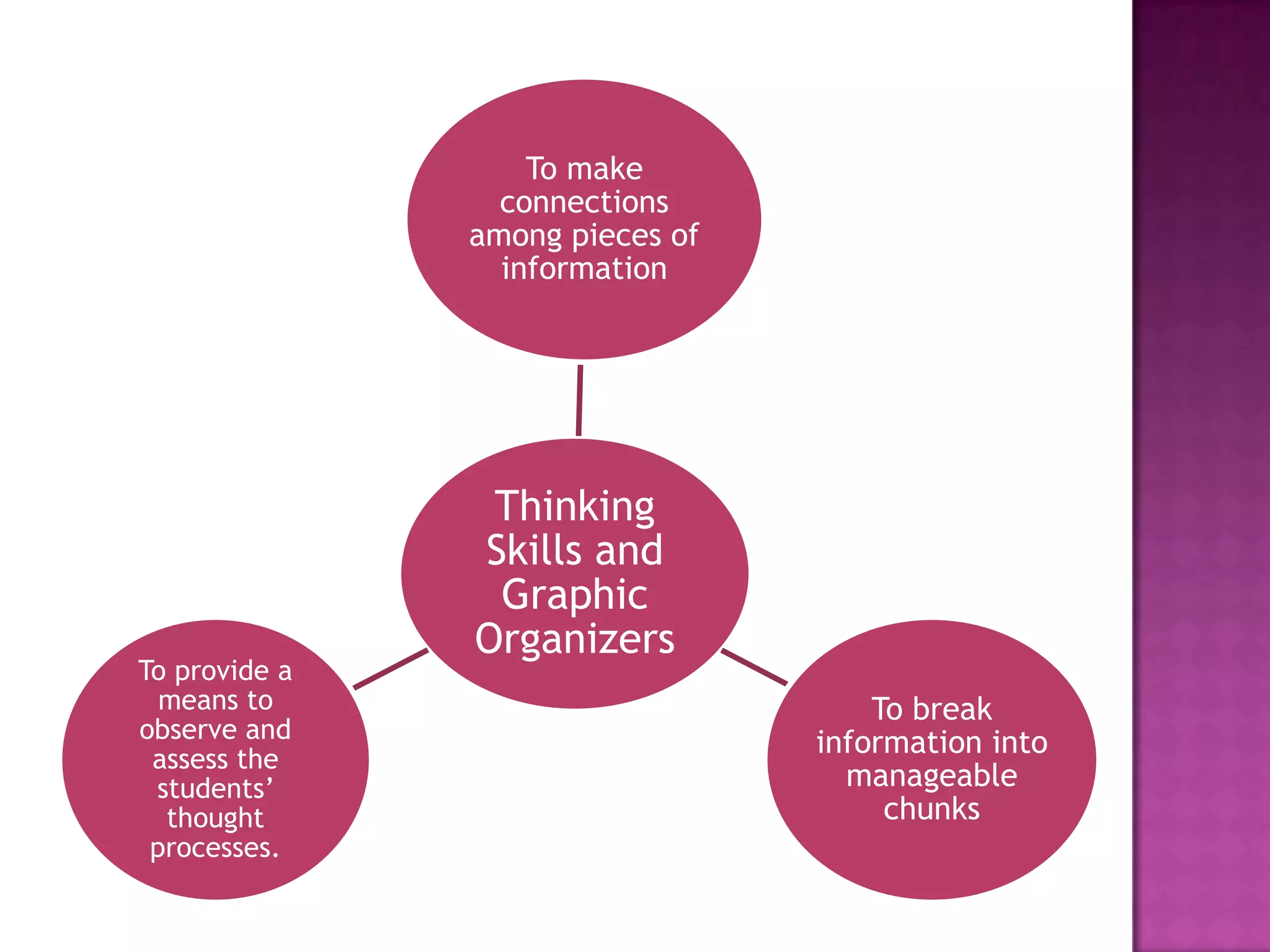
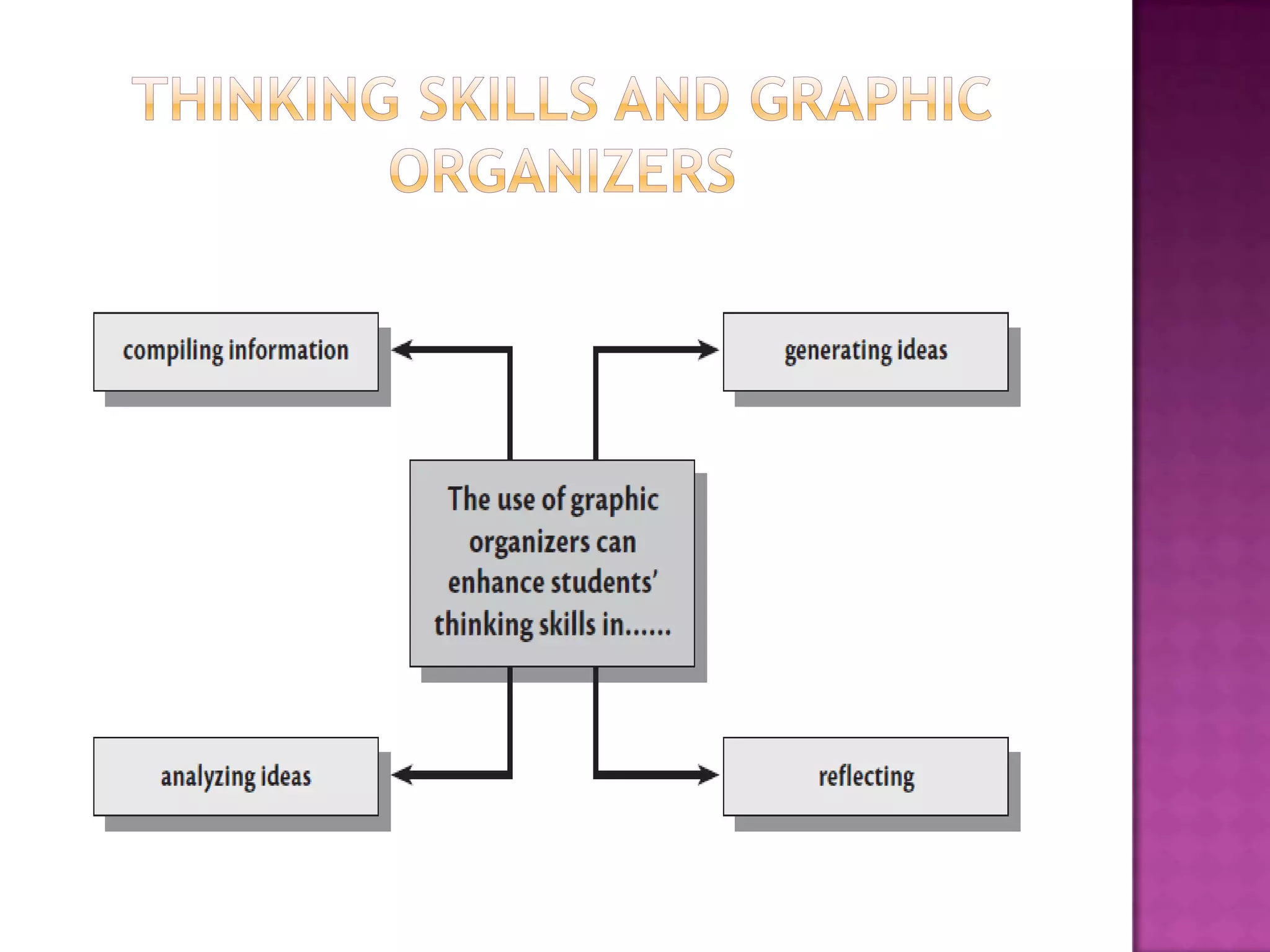
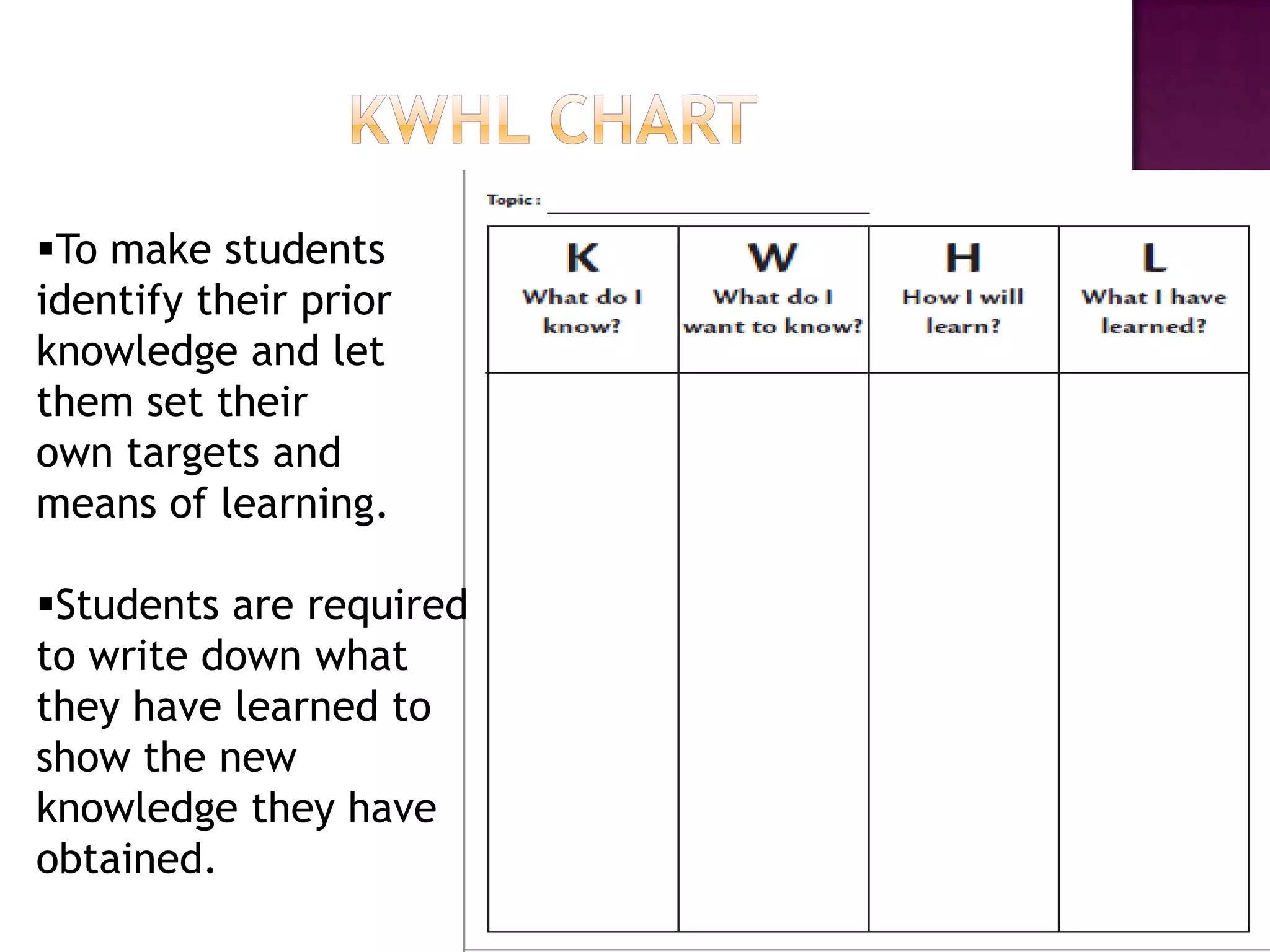
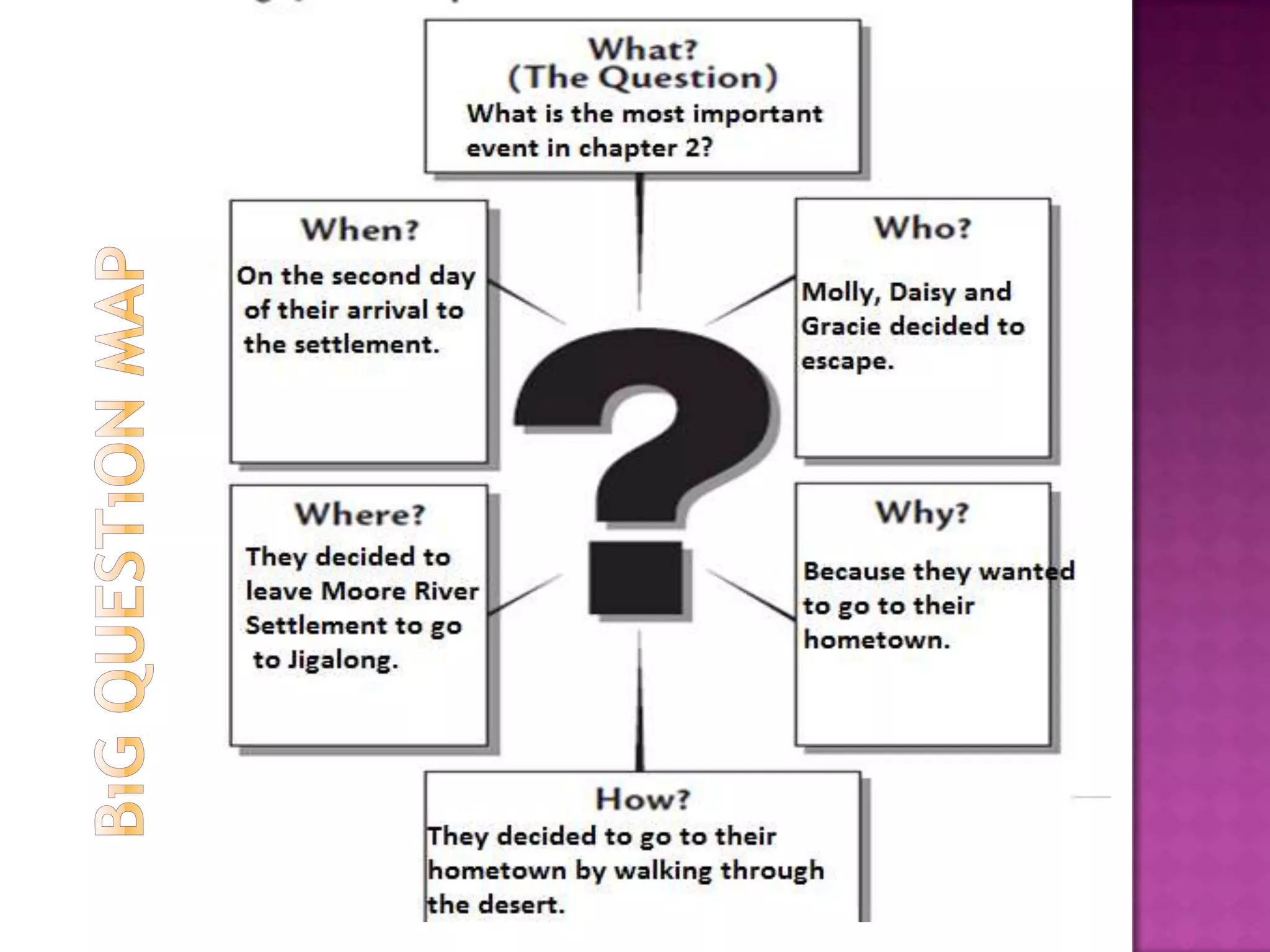
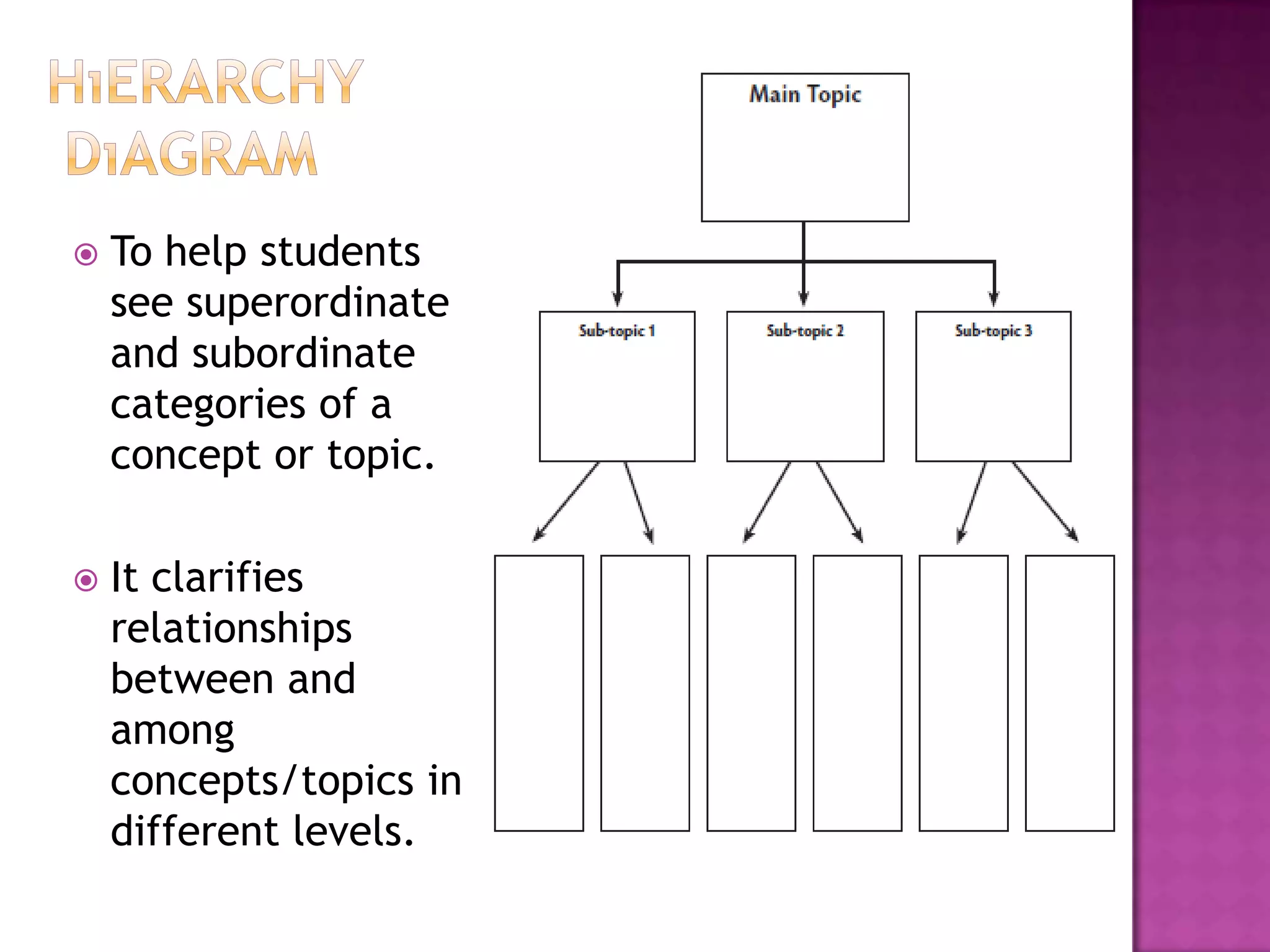
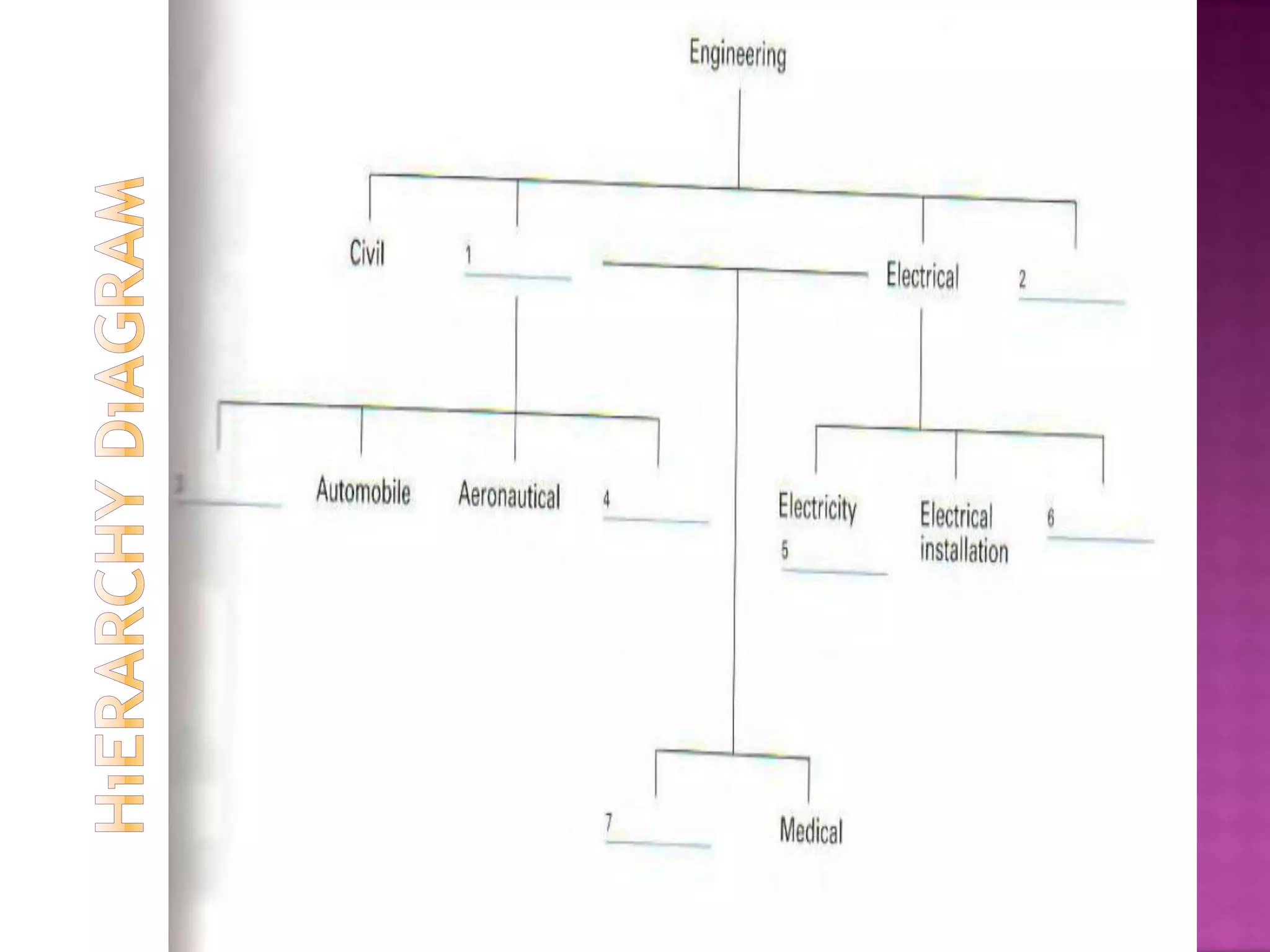
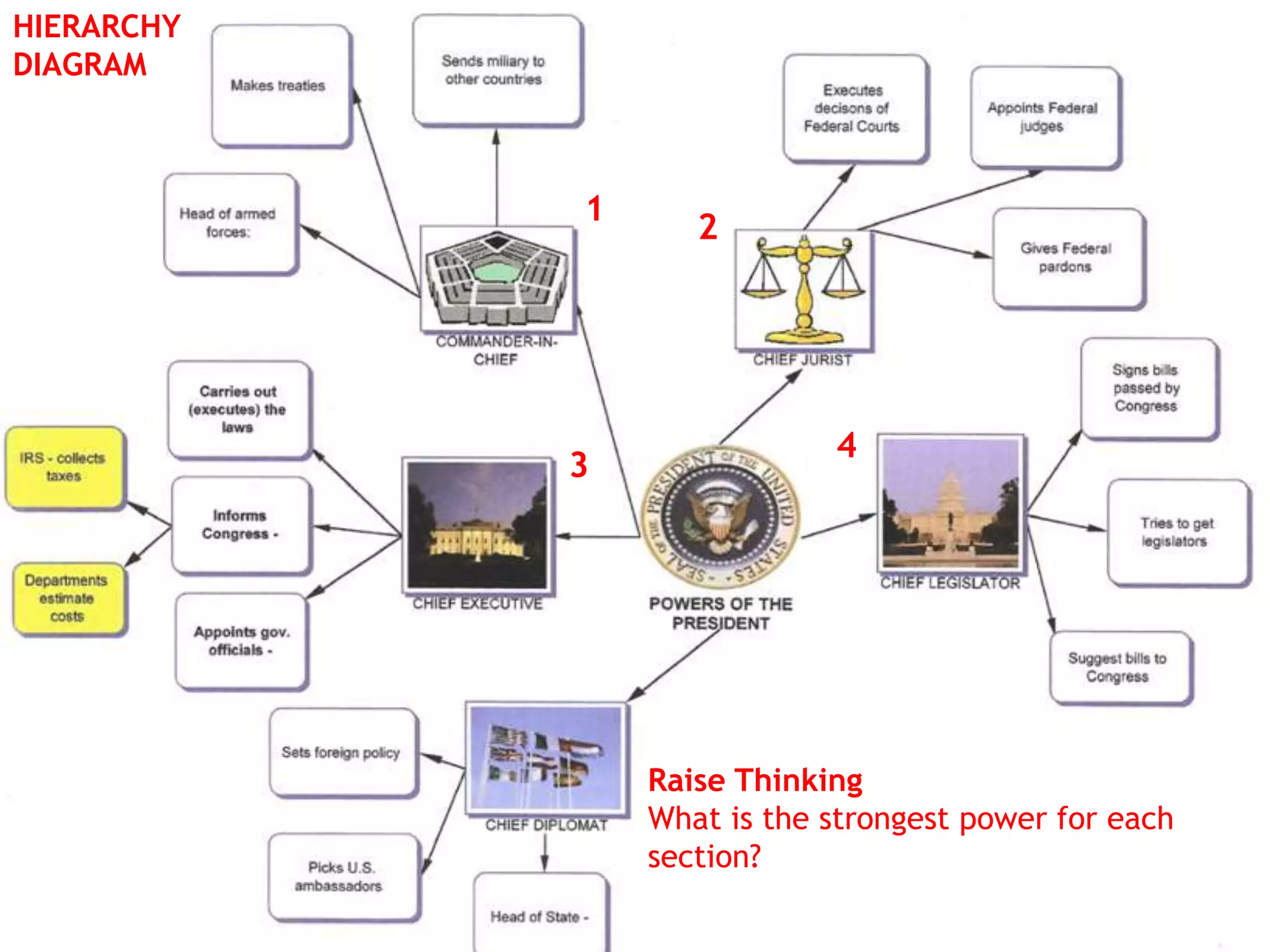
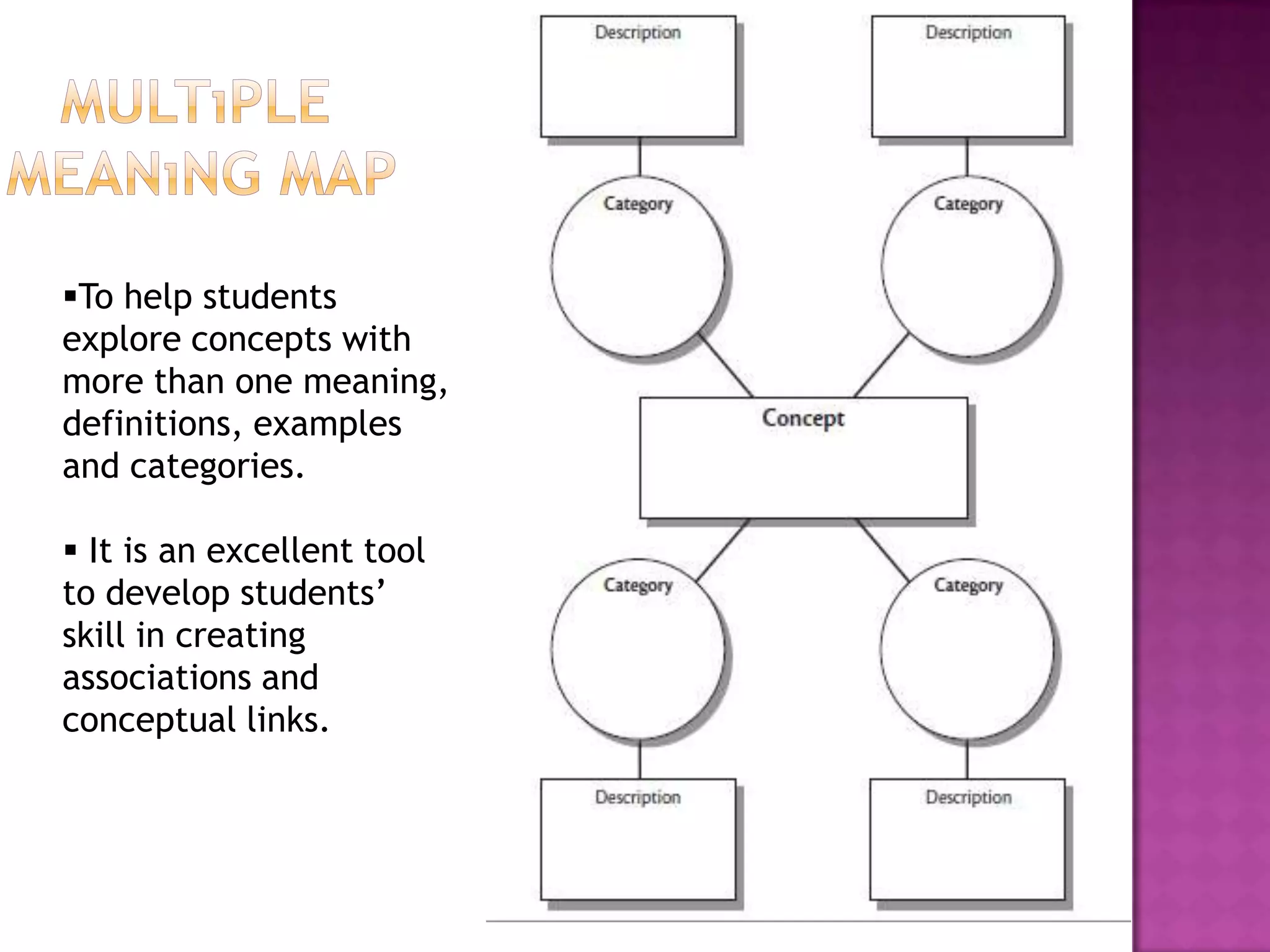
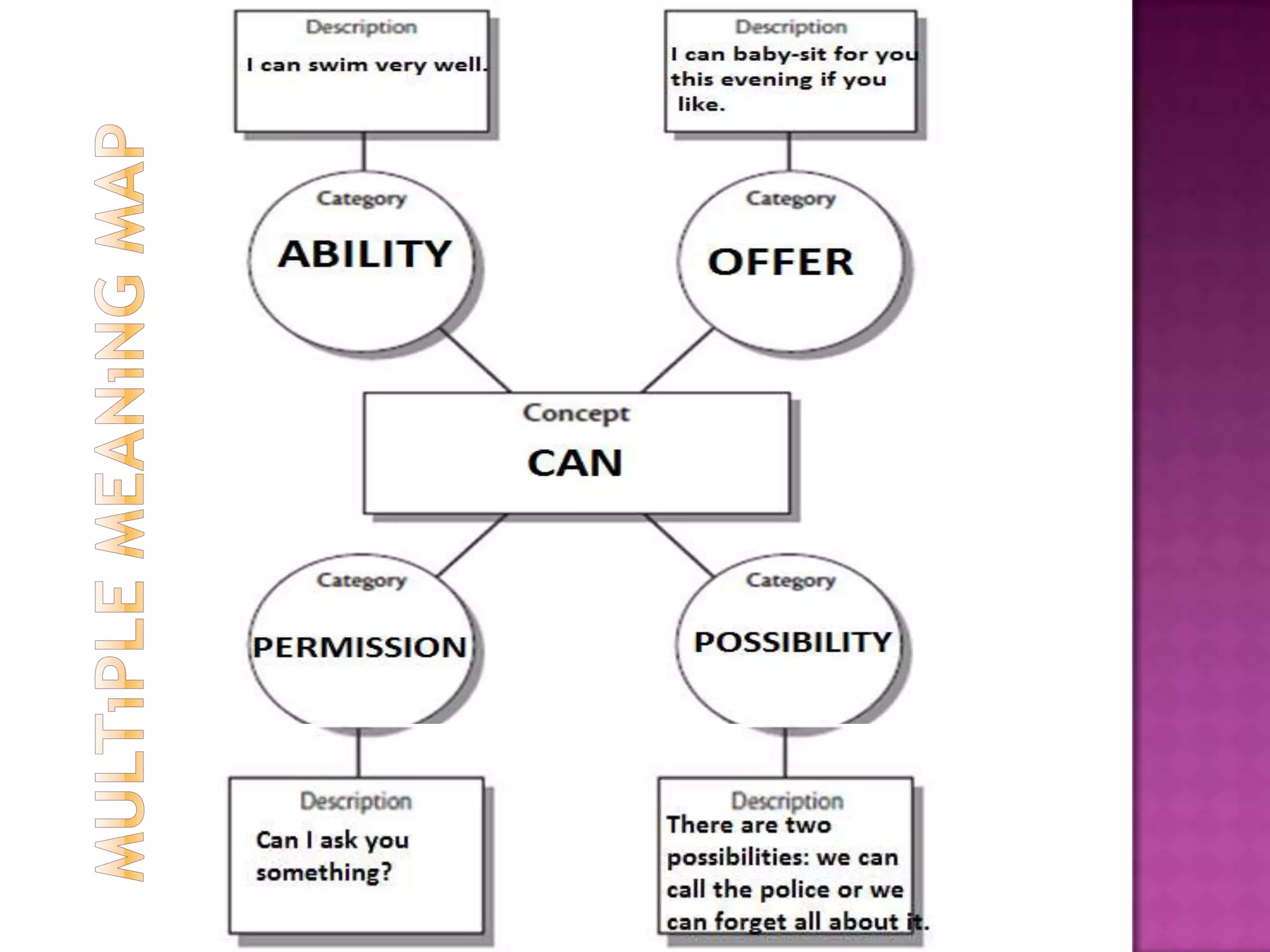
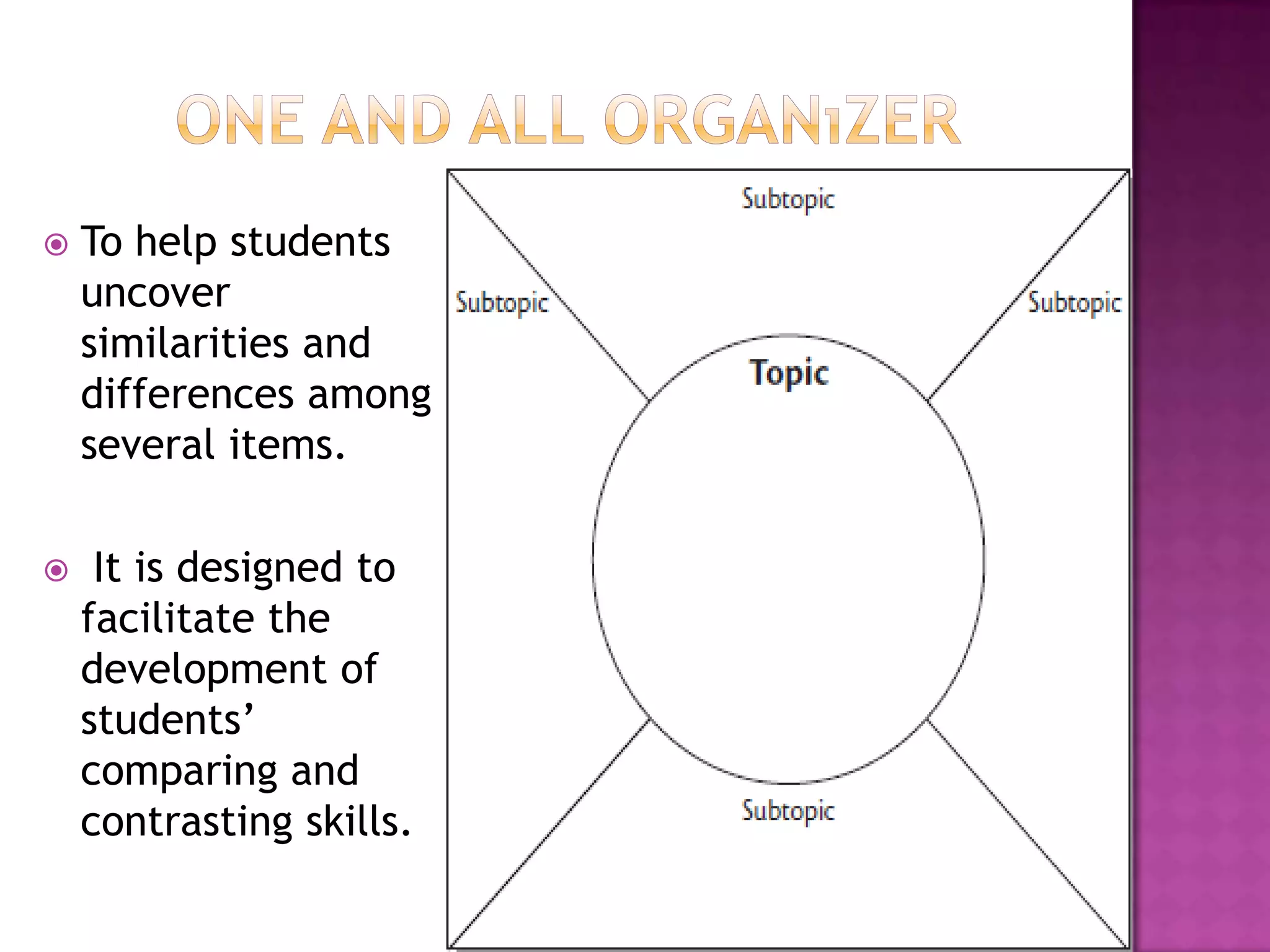
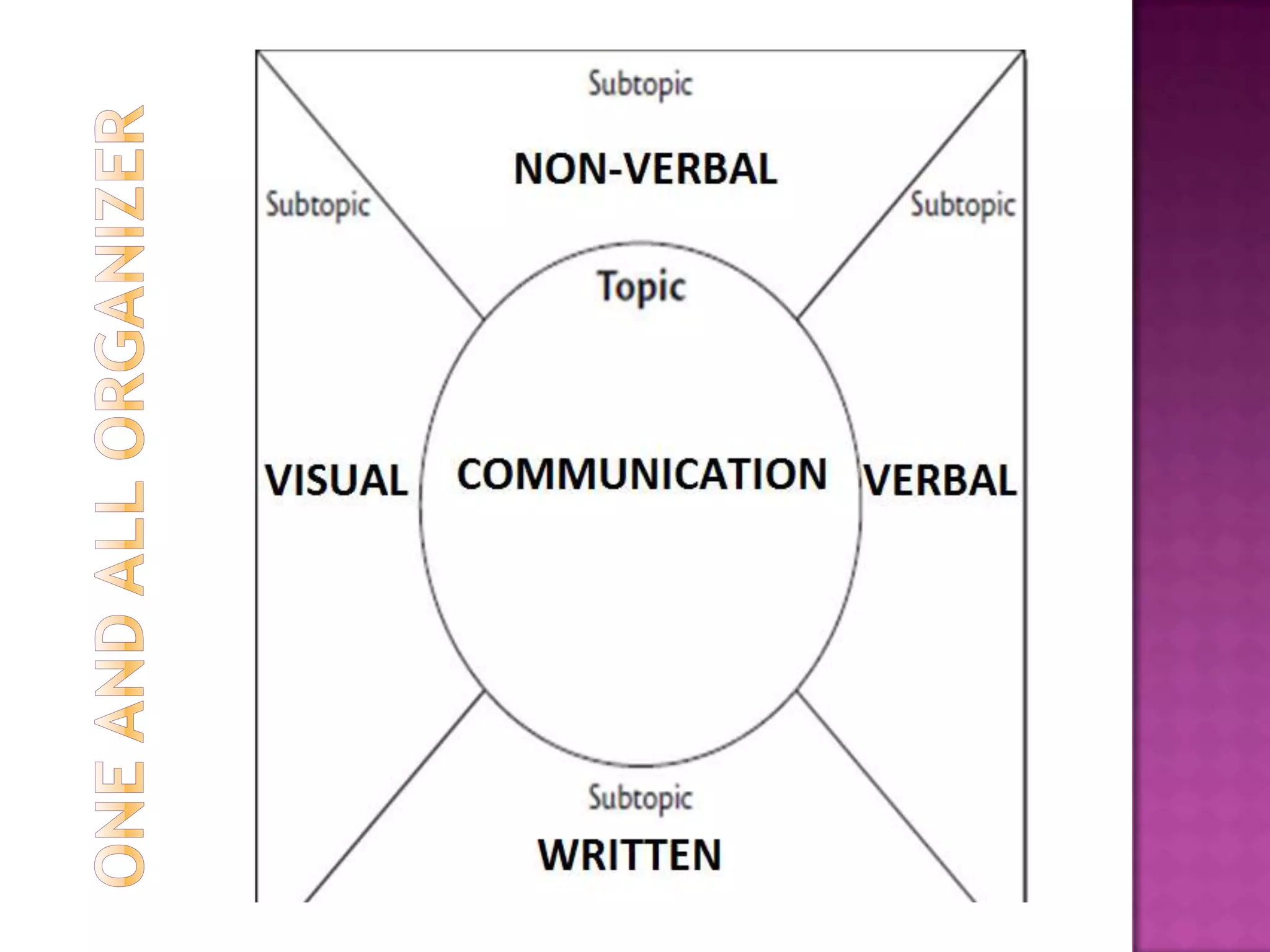
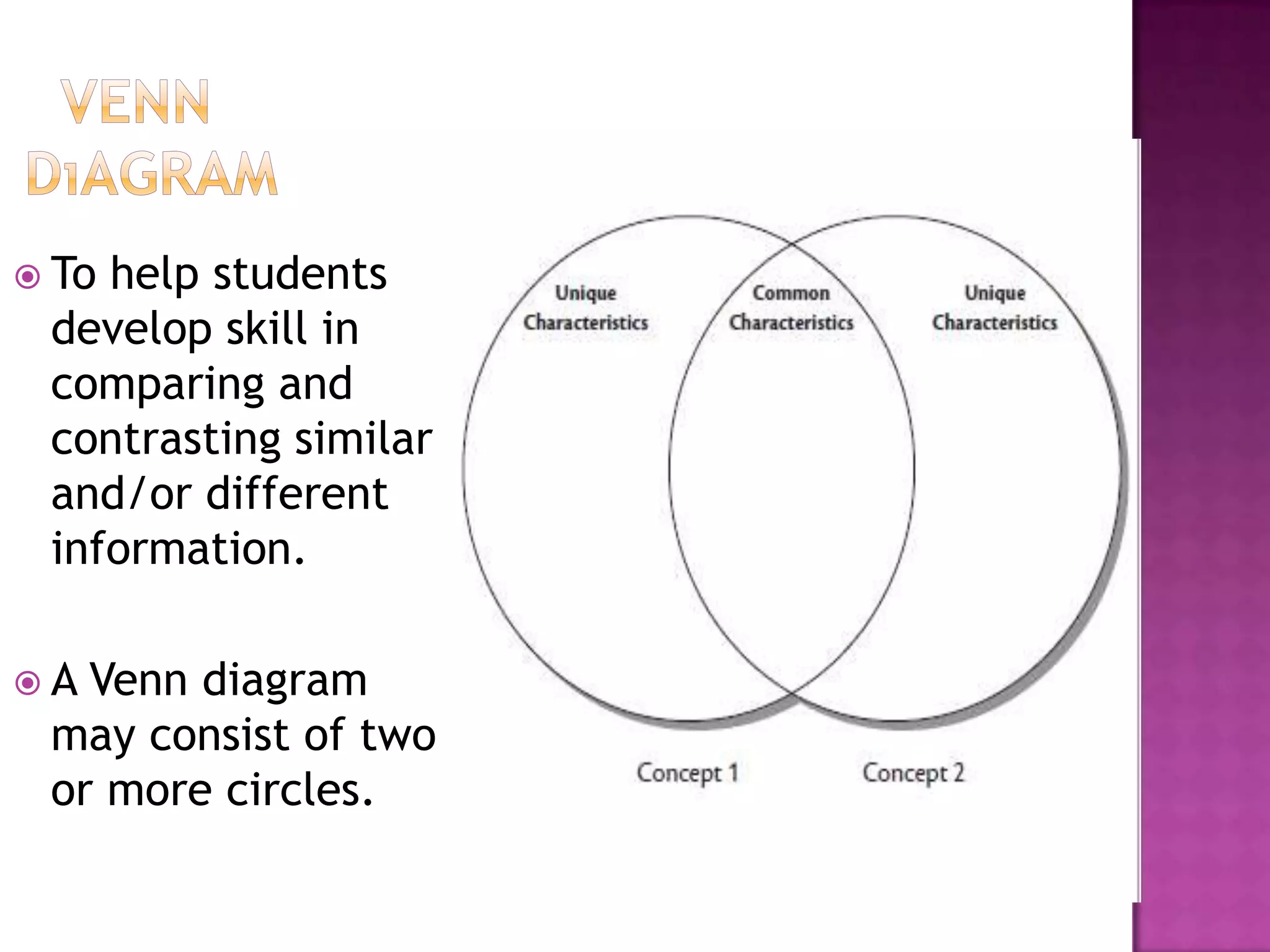
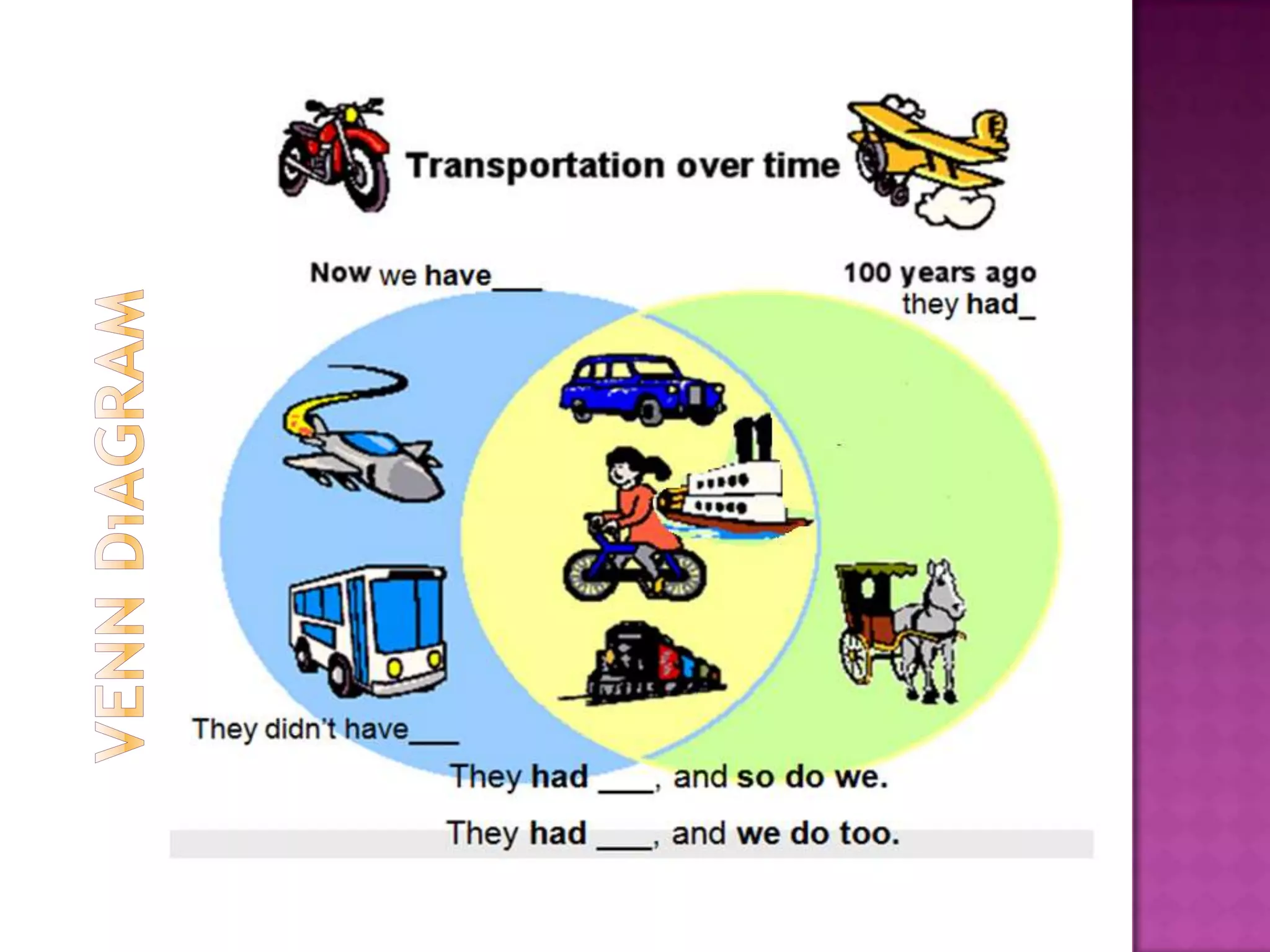
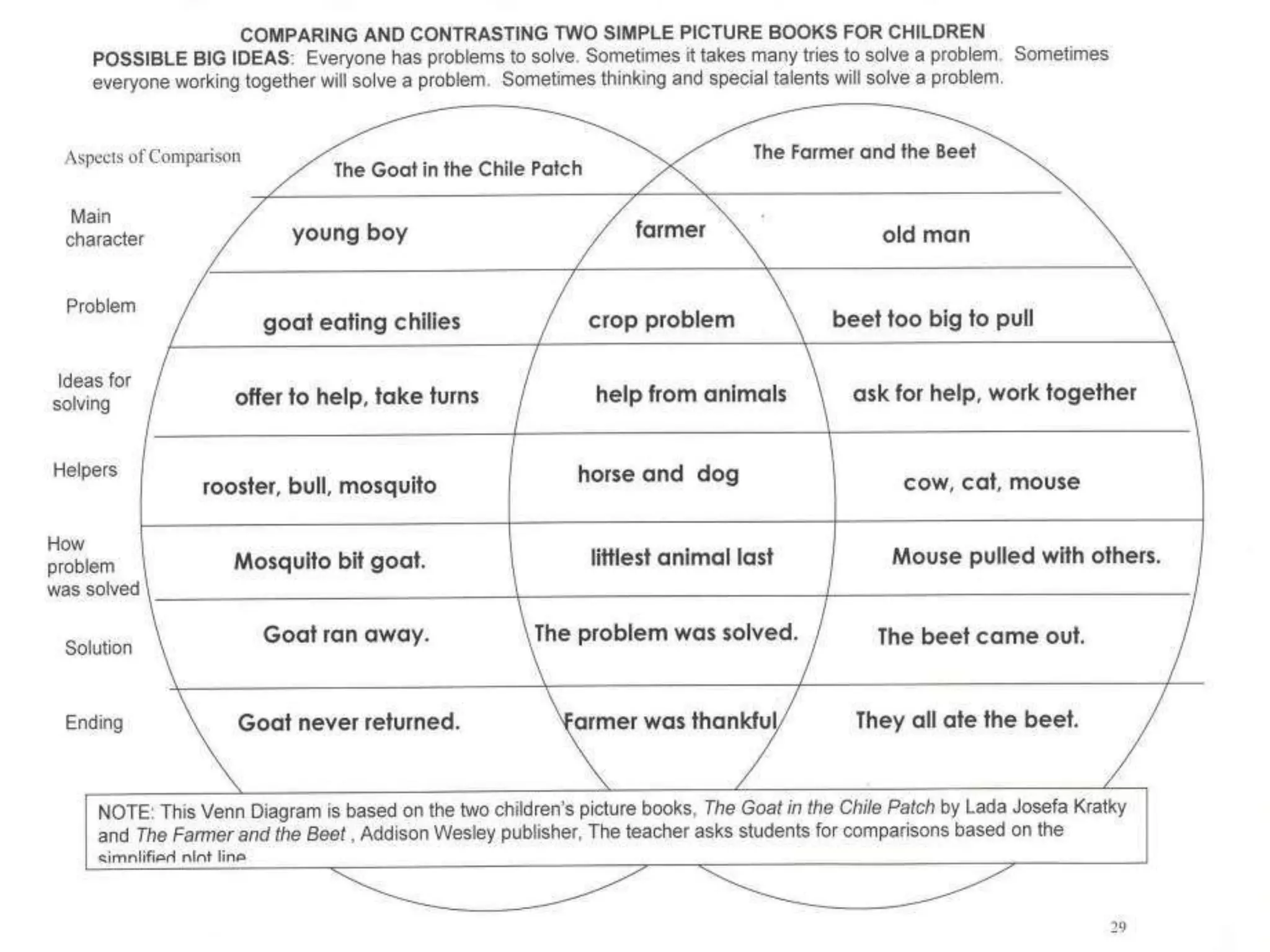
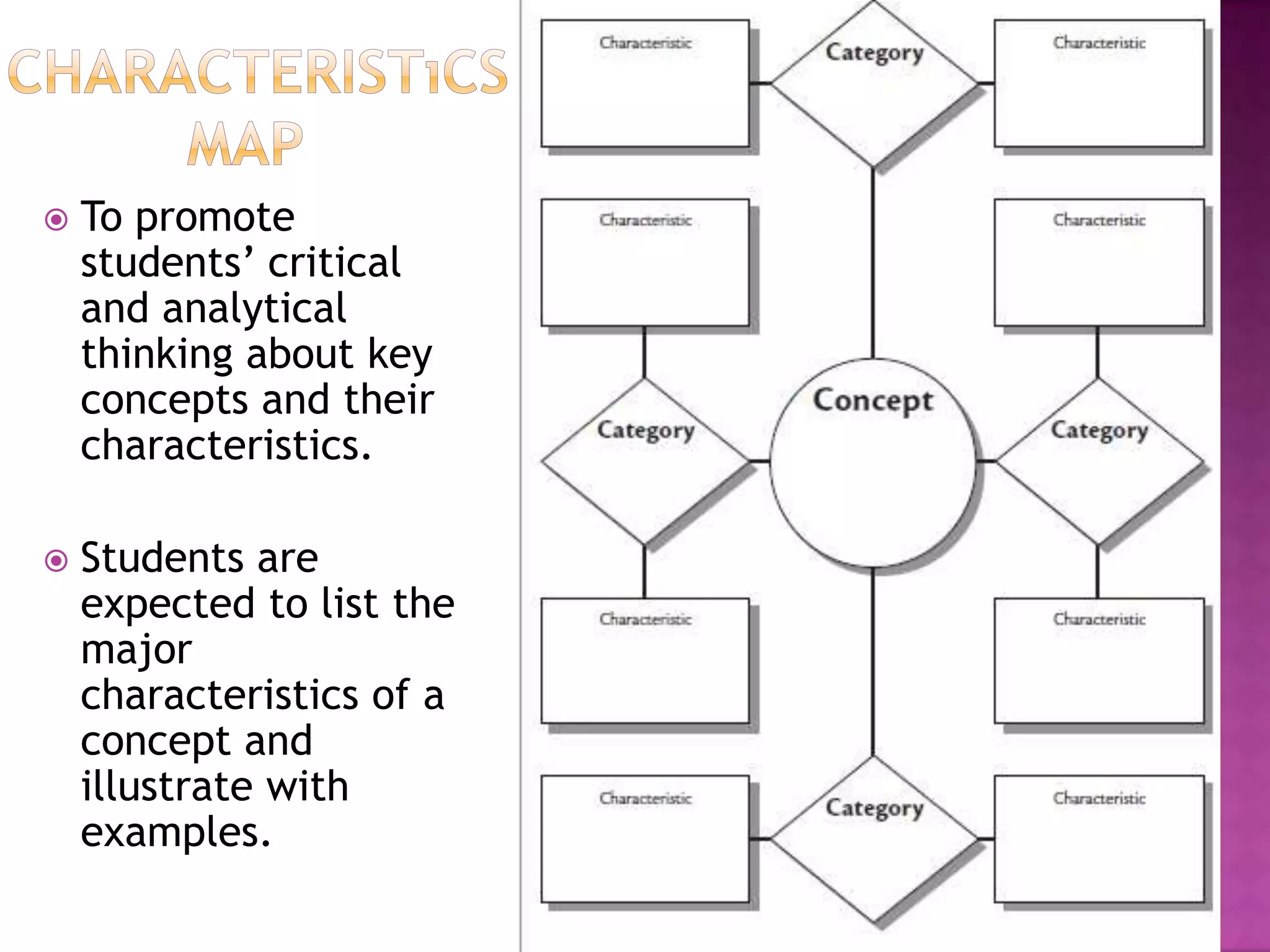
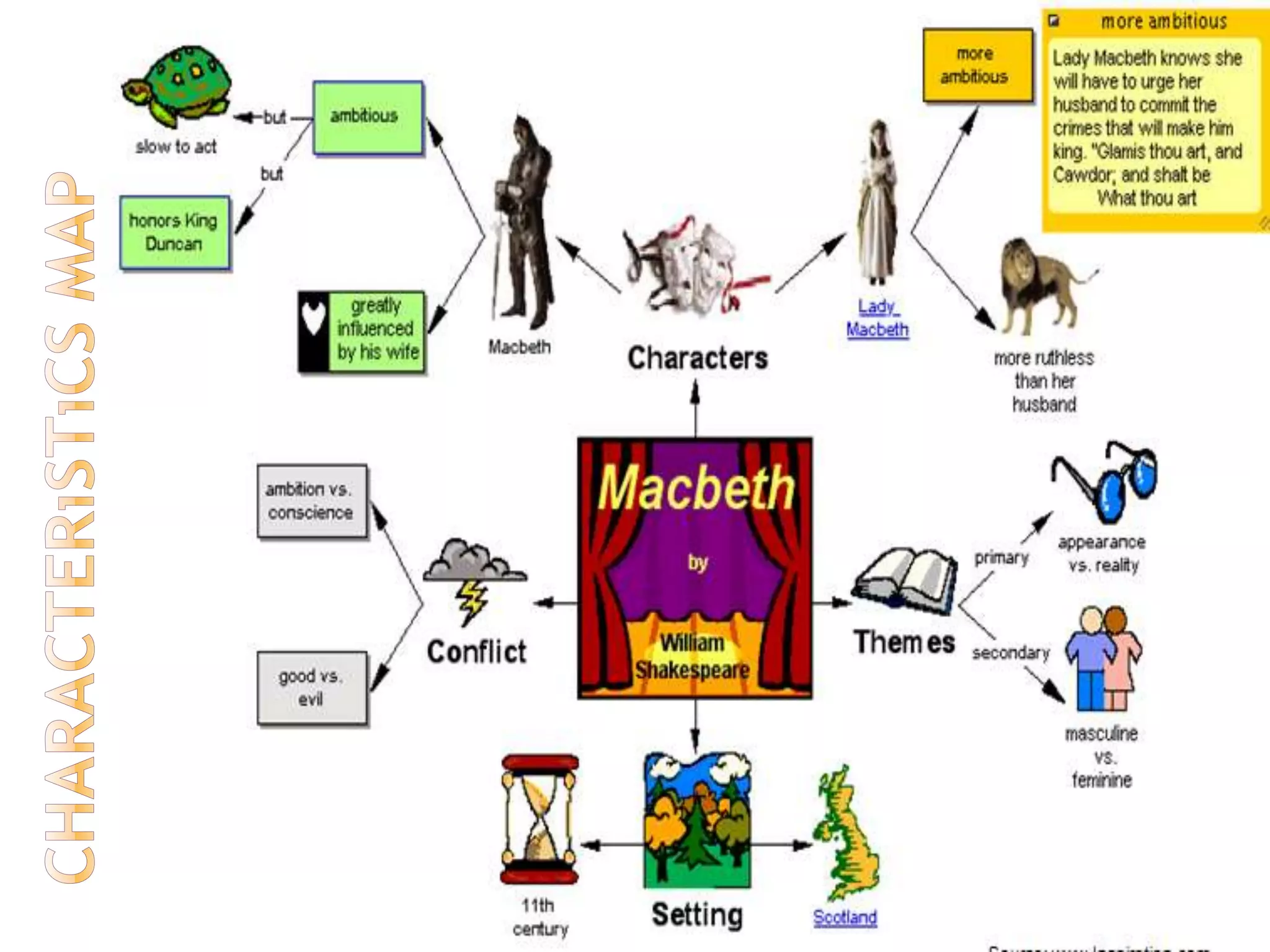
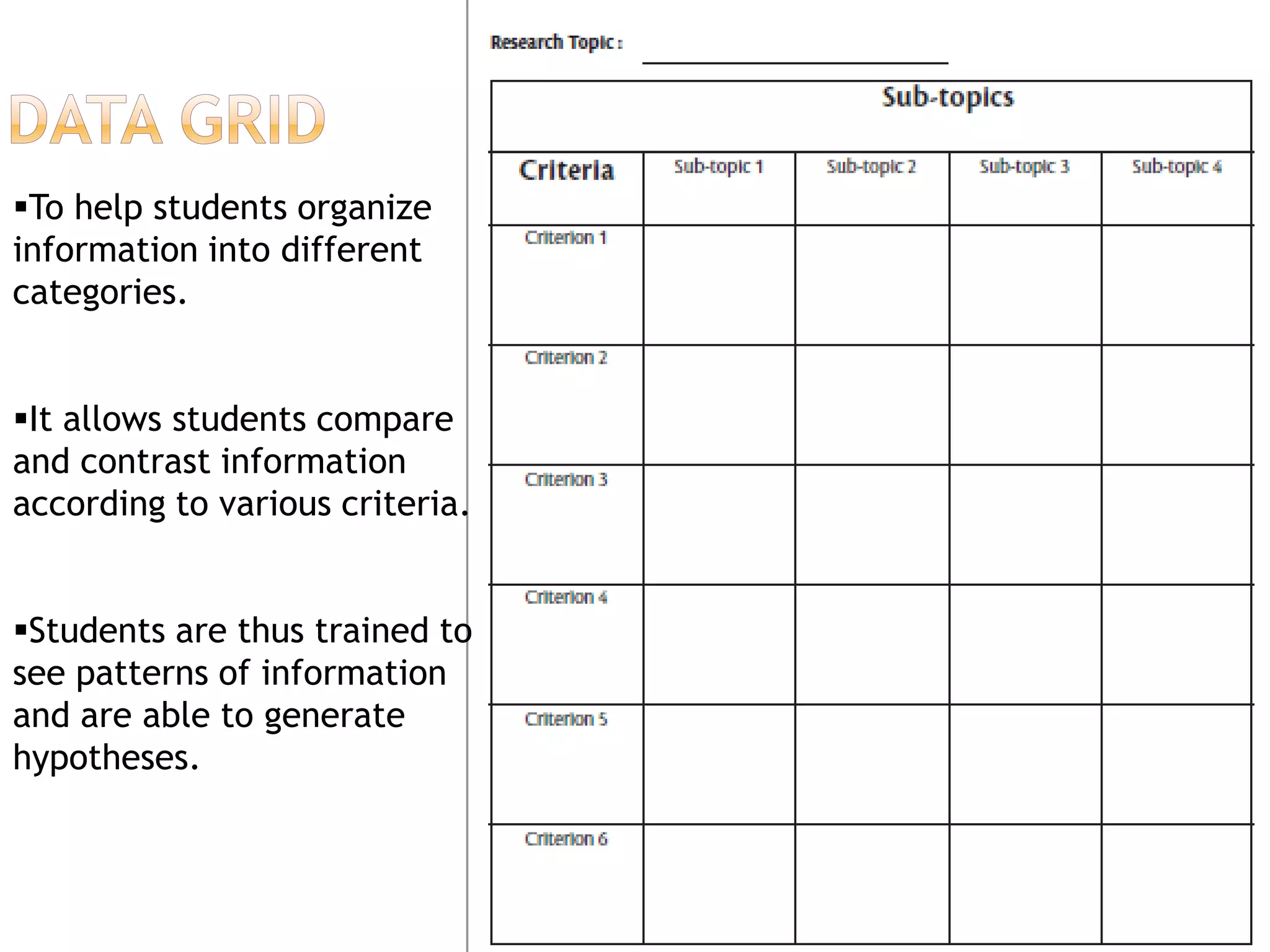
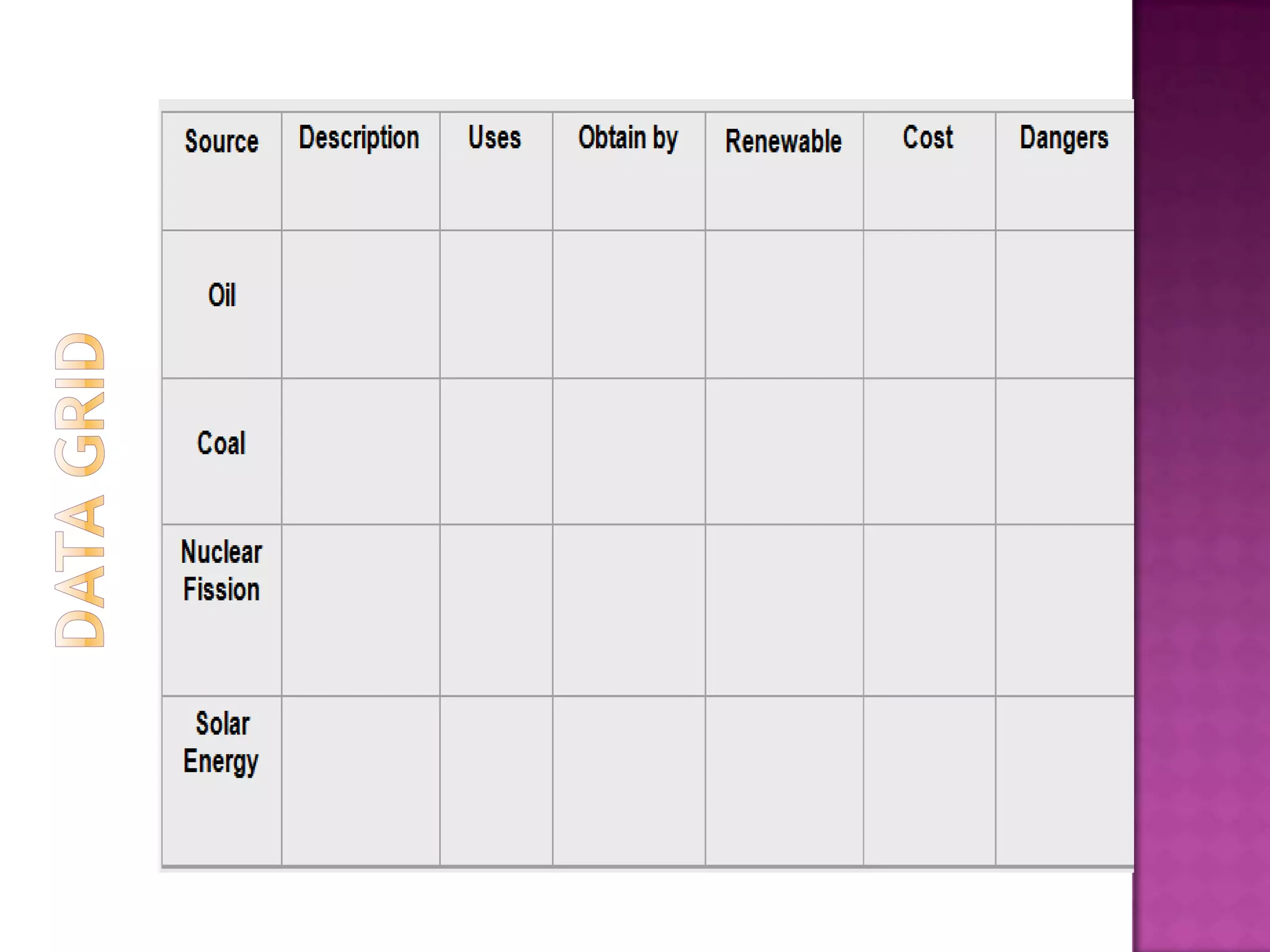
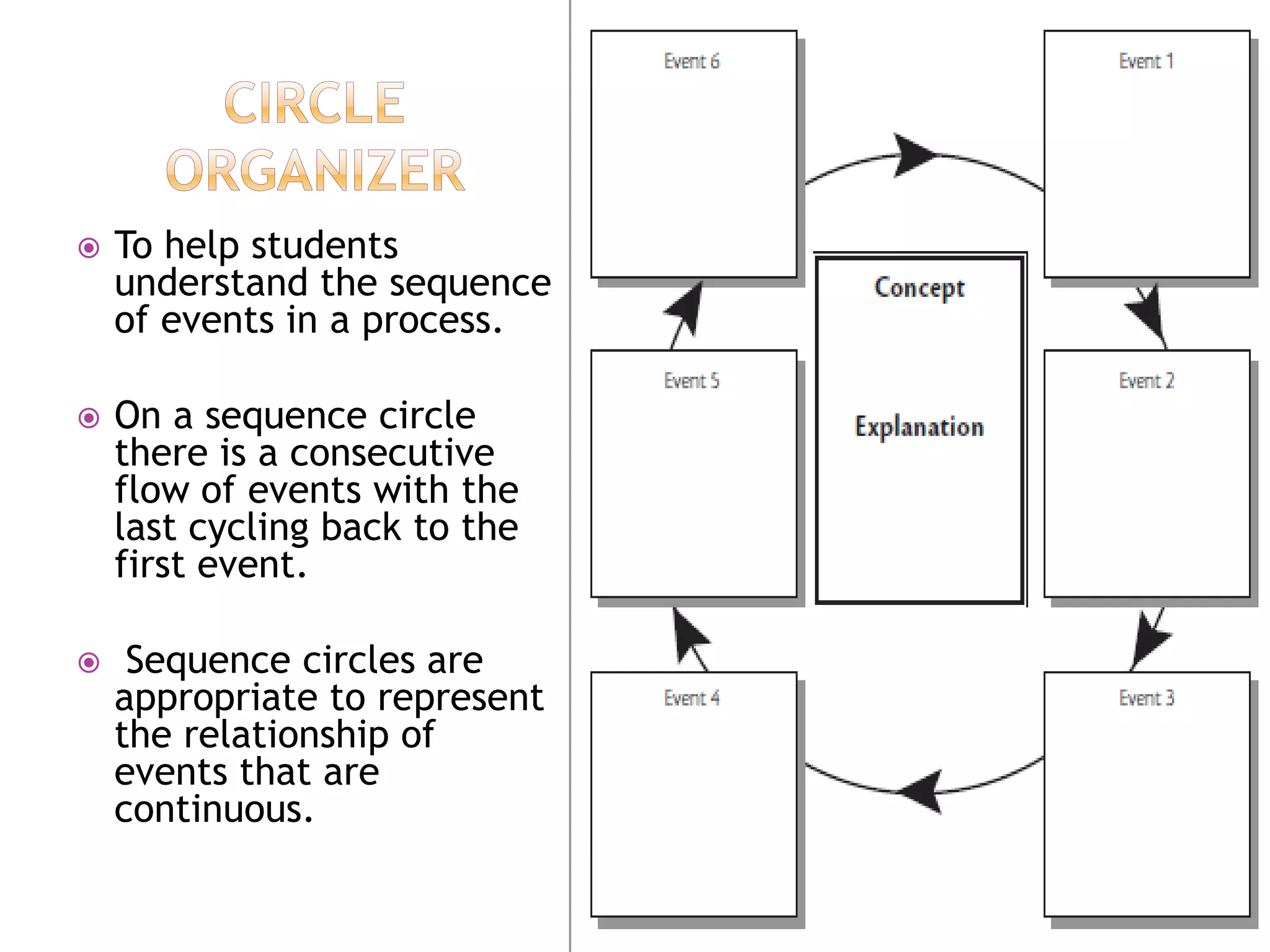
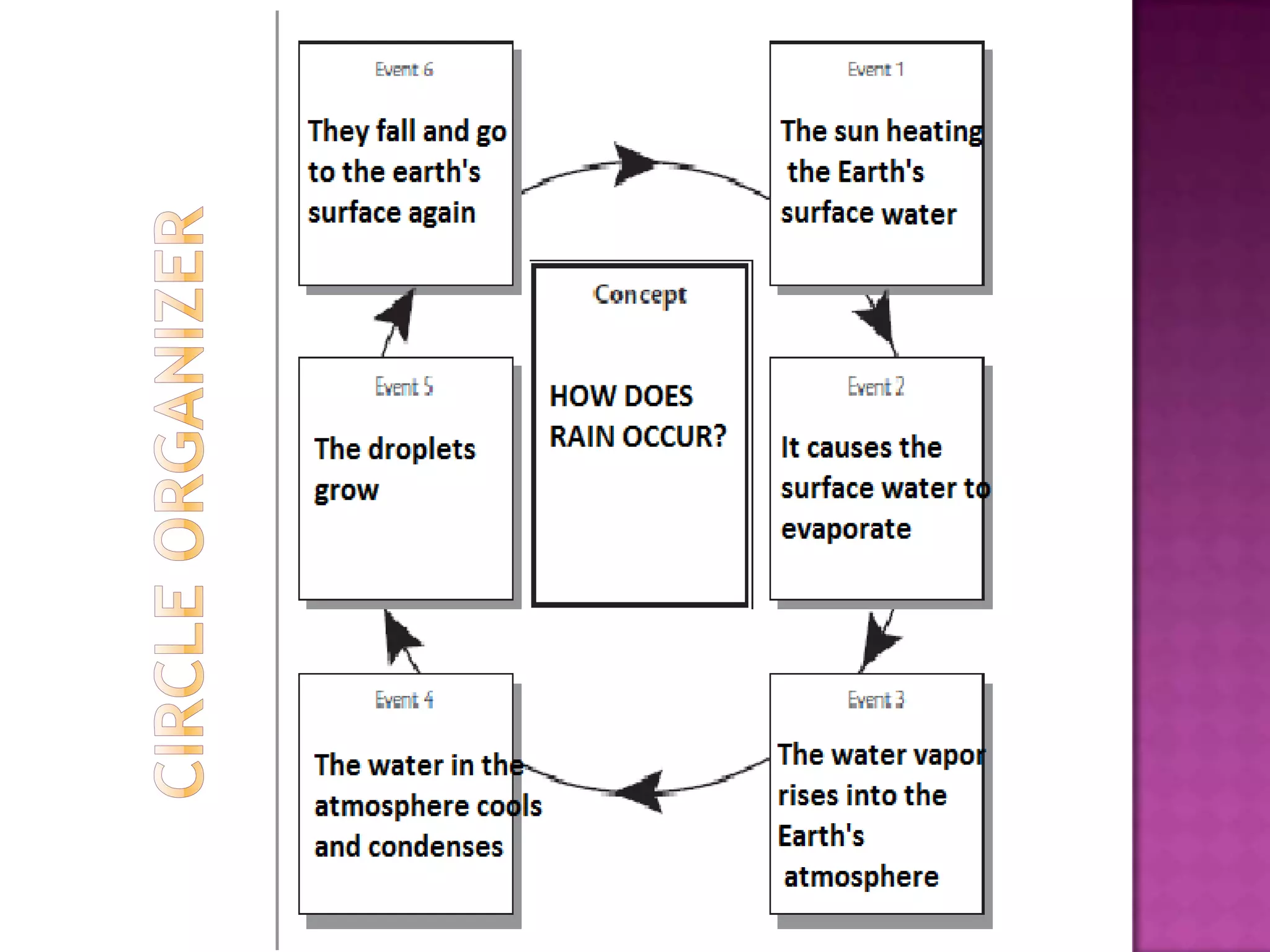
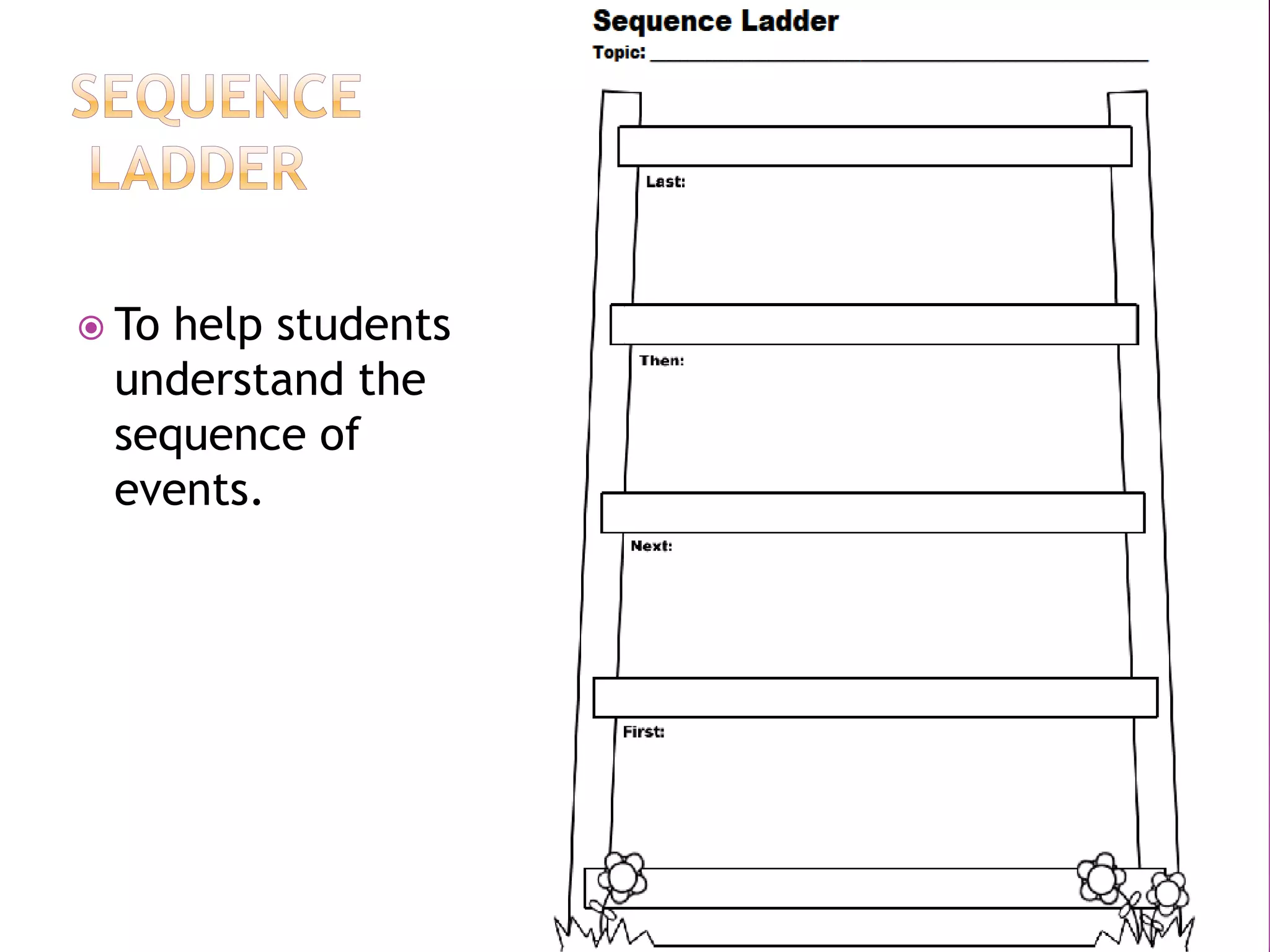
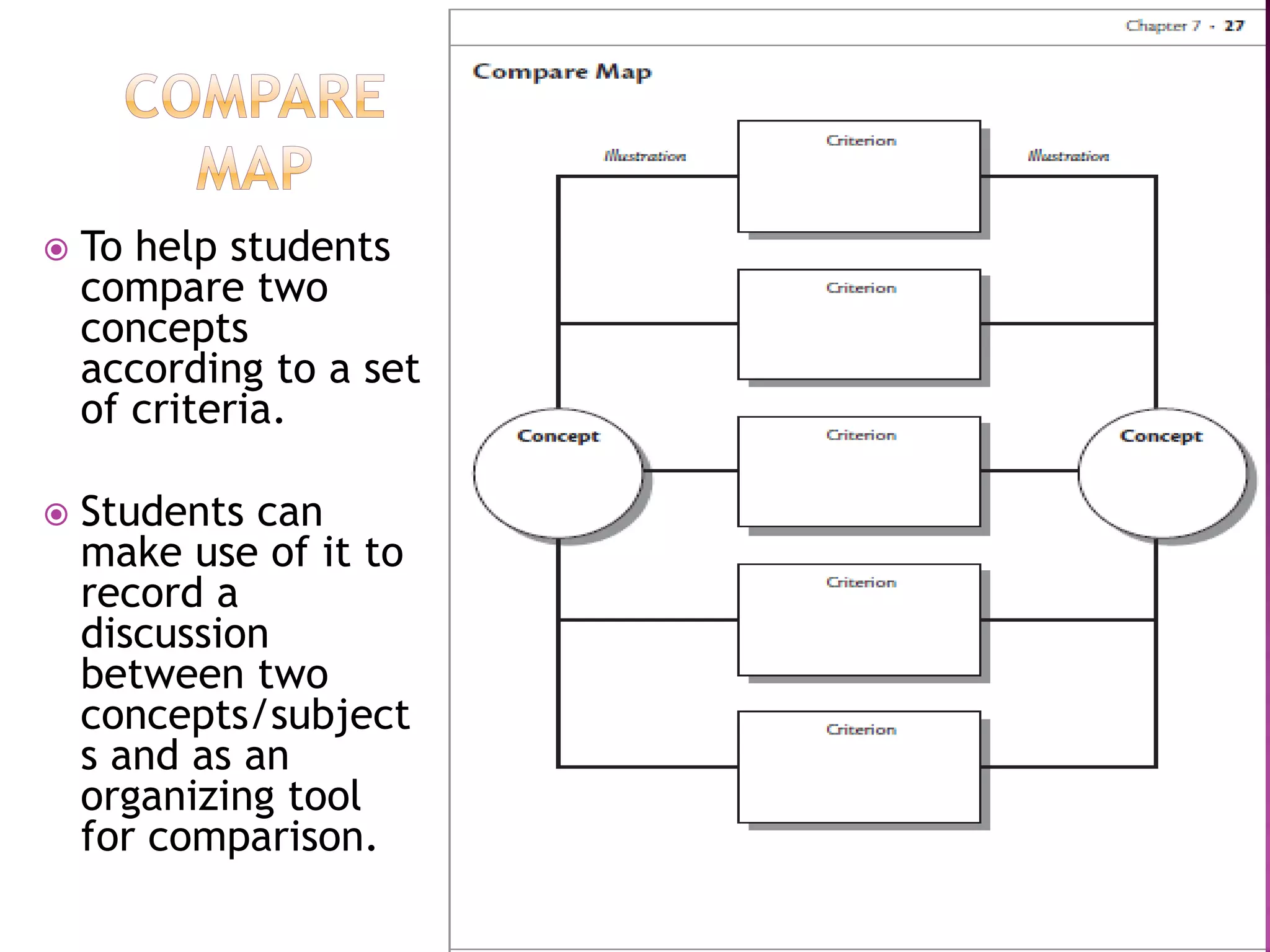
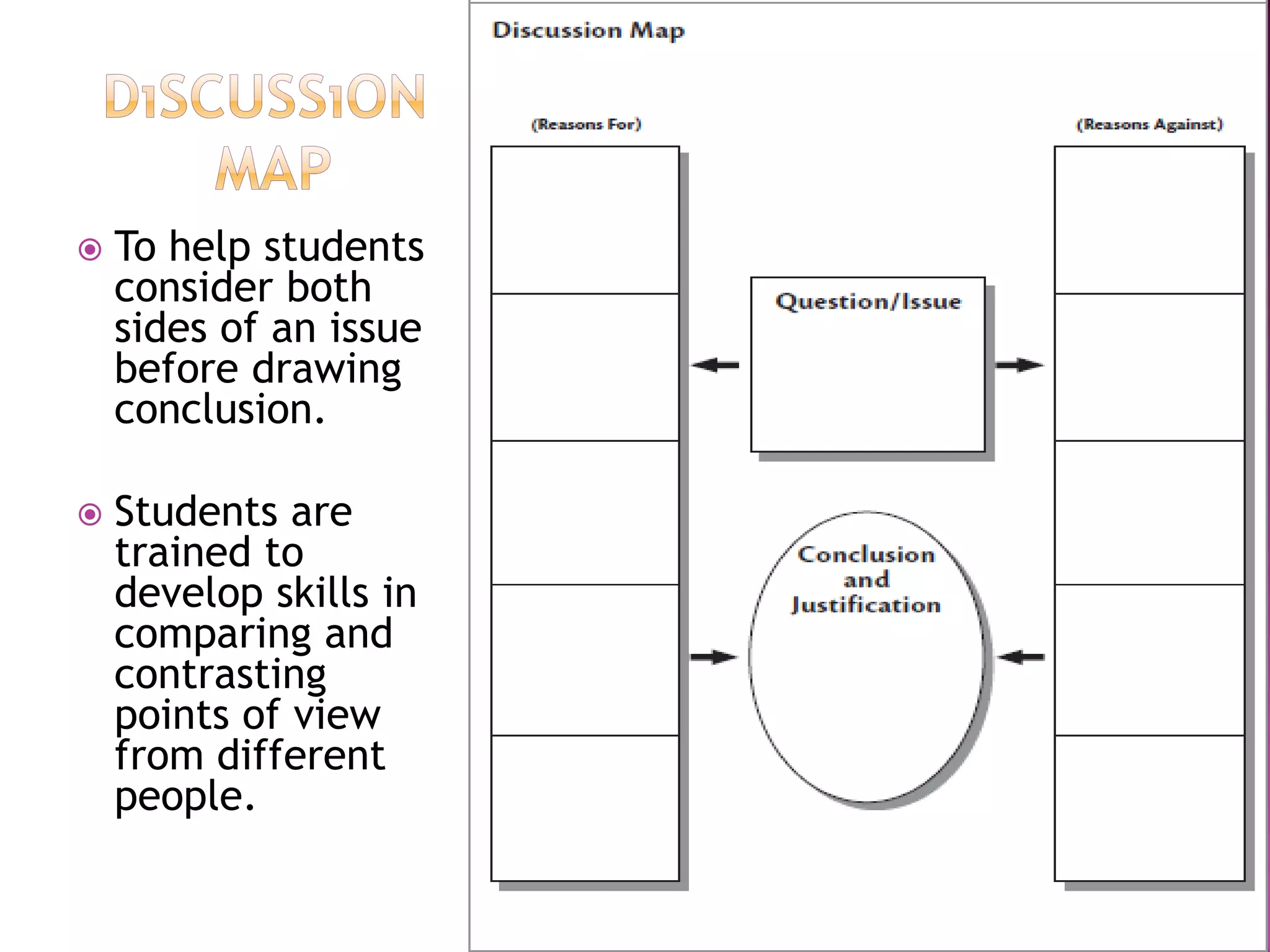
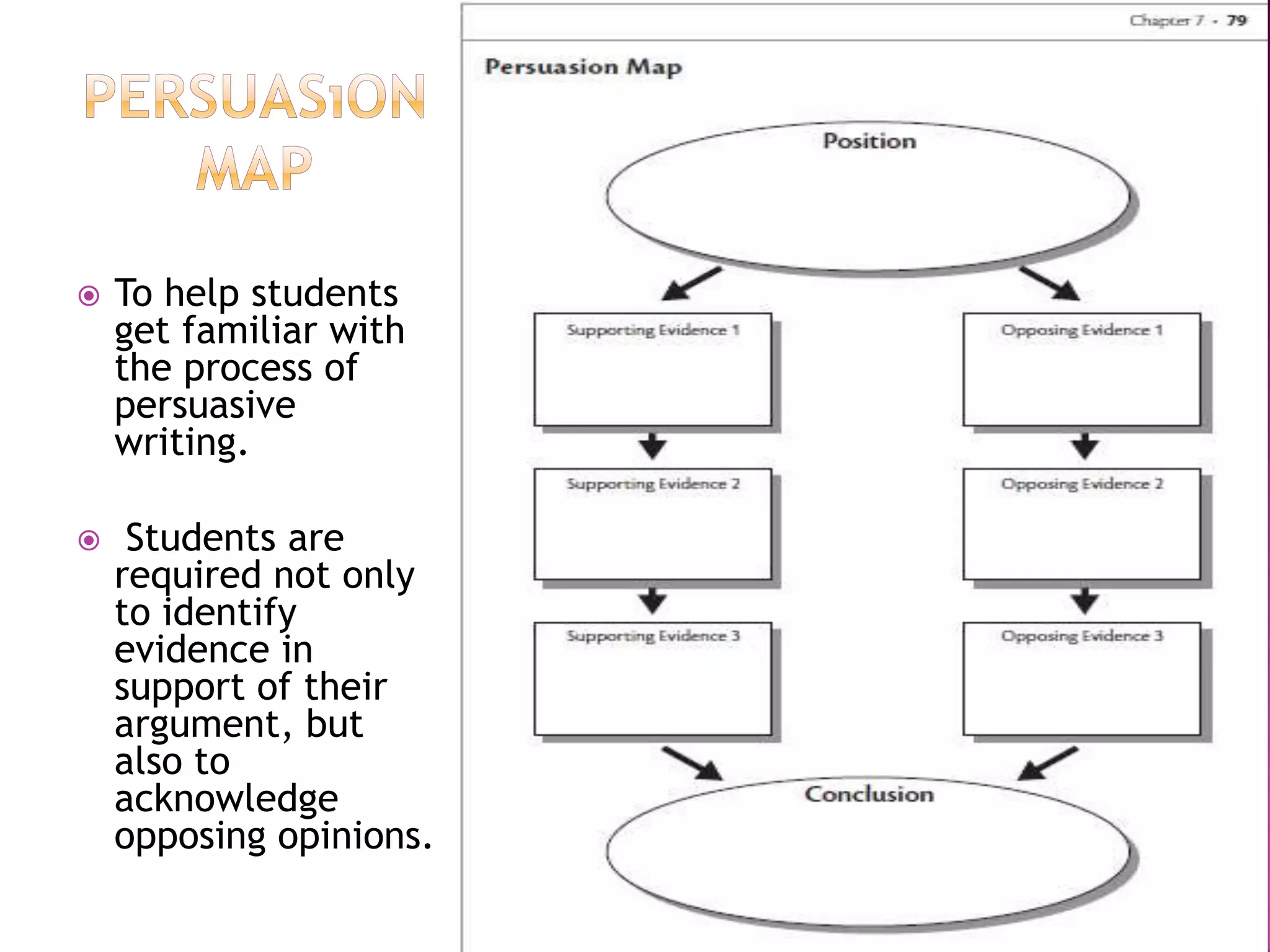
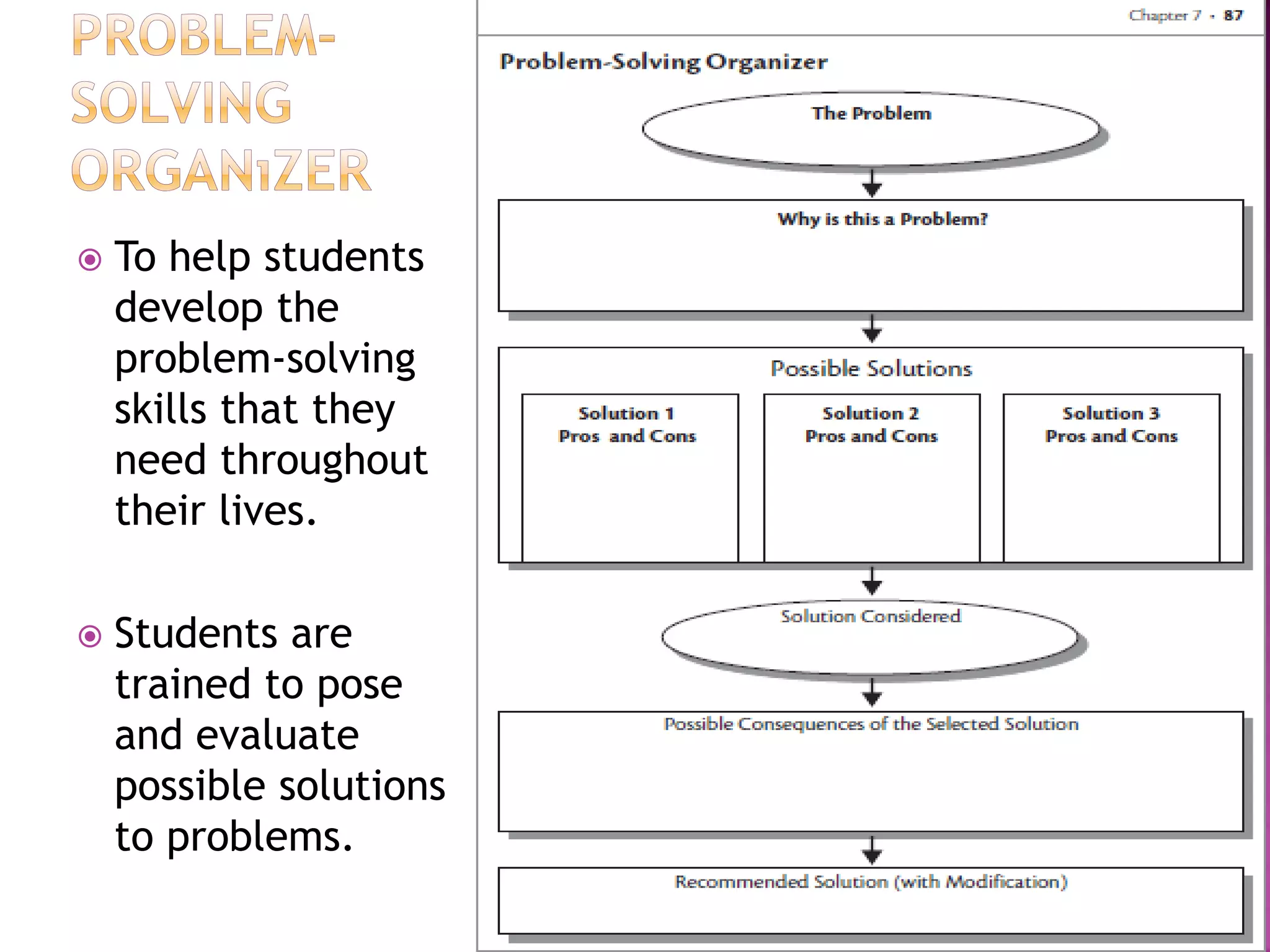
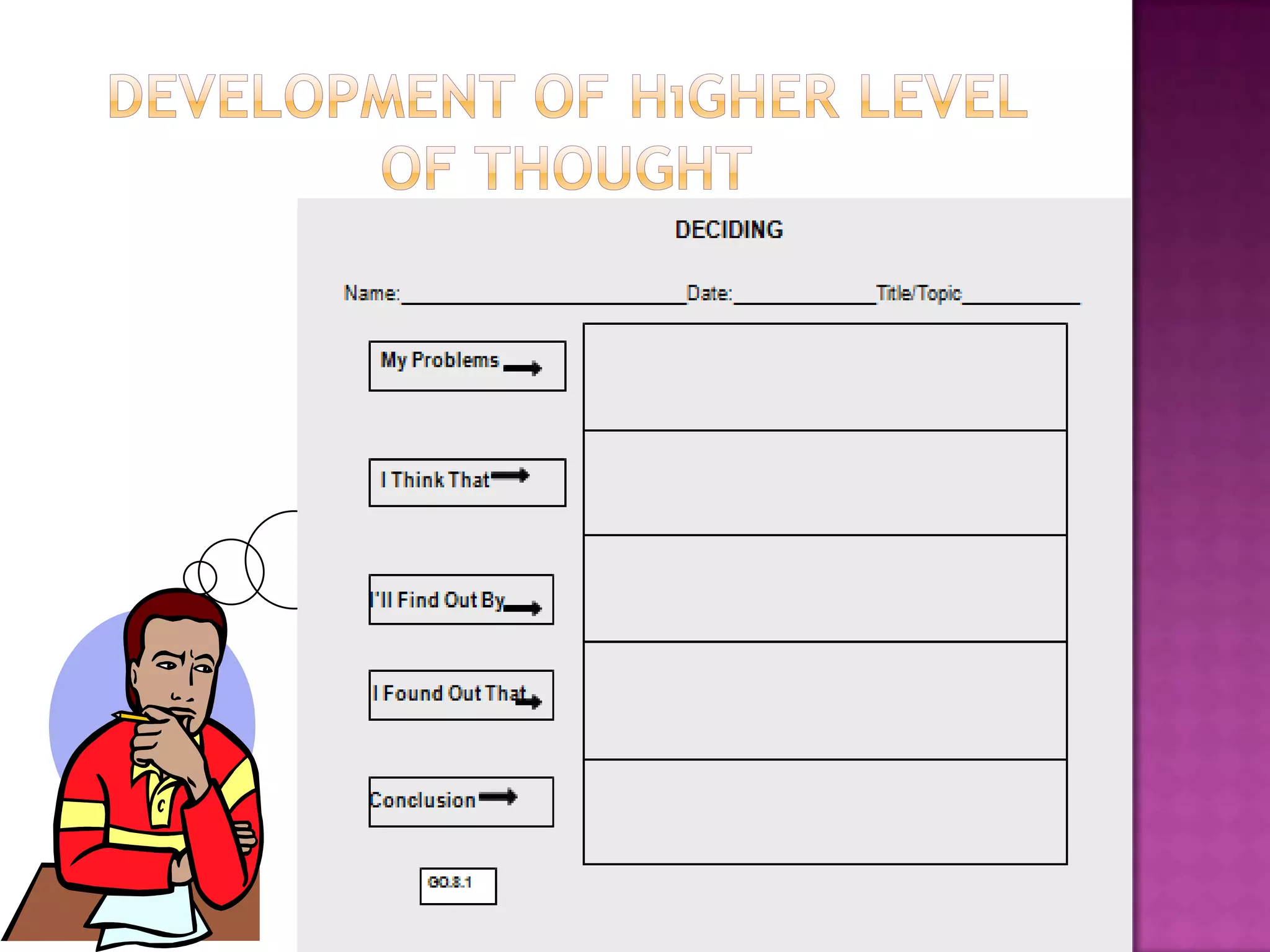
The document discusses how graphic organizers can be used to improve critical thinking skills. It provides examples of different types of graphic organizers like cyclical organizers, conceptual organizers, and sequential organizers. Graphic organizers help students make connections between information, break information into manageable chunks, identify prior knowledge, and improve research and problem-solving abilities. Specific organizers like Venn diagrams, concept maps, and cause-and-effect diagrams are explained as tools to help students compare/contrast, organize categories, and understand processes and relationships between concepts. The document emphasizes how graphic organizers promote higher-level thinking and language development when students summarize and discuss information.