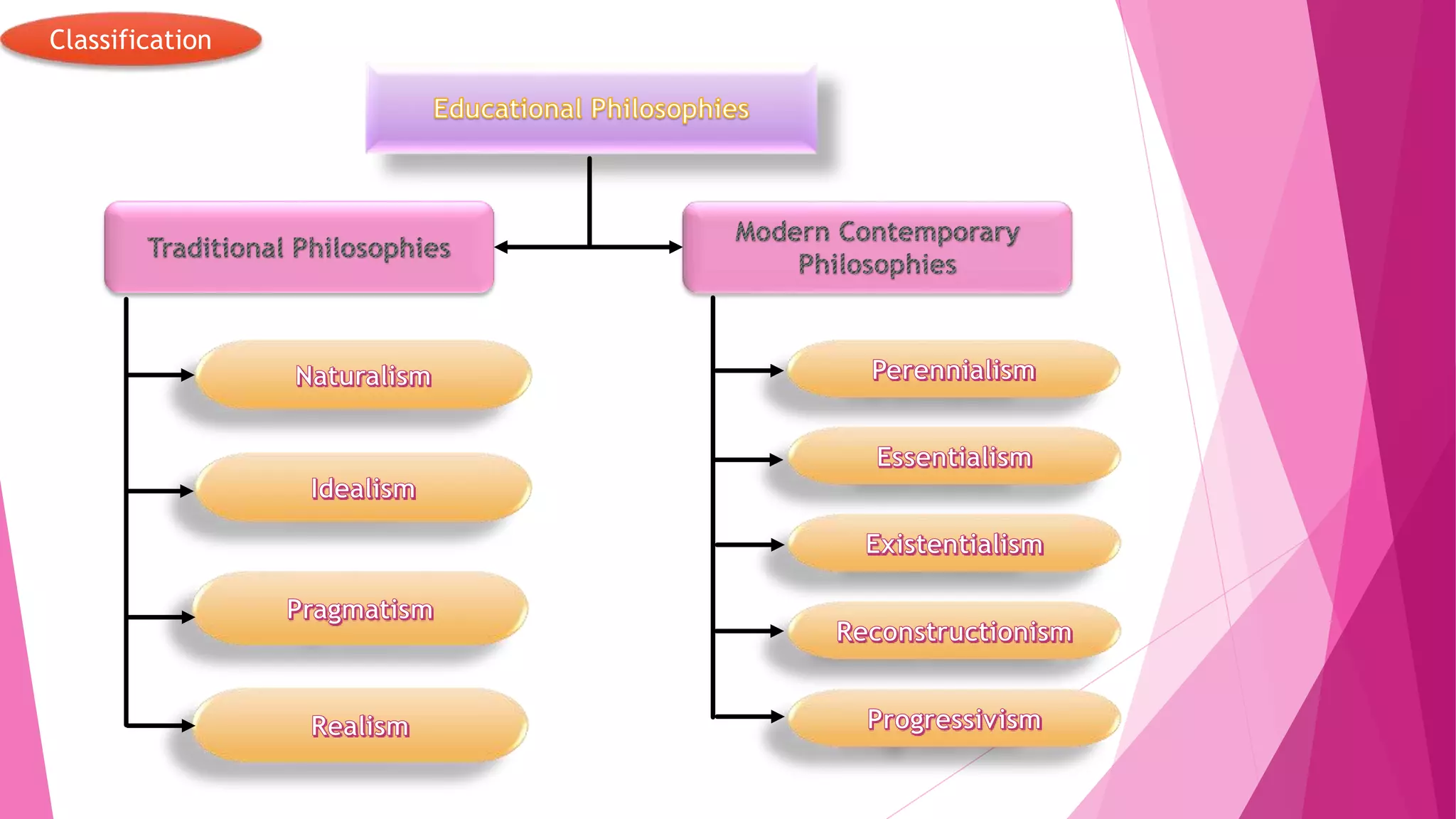
The document discusses several educational philosophies, both traditional and modern. Traditional philosophies include naturalism, idealism, pragmatism, and realism. Naturalism focuses on educating through direct experiences with nature. Idealism emphasizes developing intellectual, aesthetic, and moral values through formal classroom teaching. Pragmatism views education as a social process and favors activity-based learning. Realism aims to equip students with vocational skills. Modern philosophies include perennialism, which teaches timeless ideas and values liberalism, tolerance, and discretion through teacher-guided discussion and reading great books.