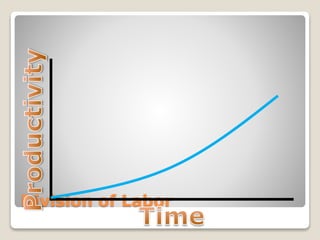
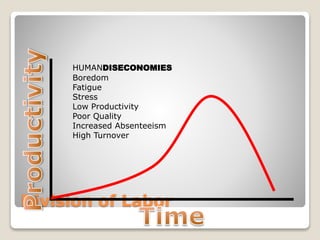
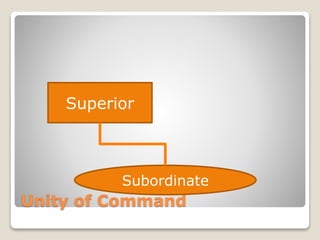
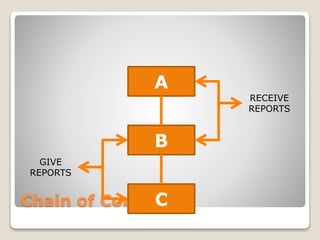
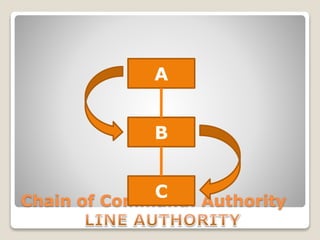
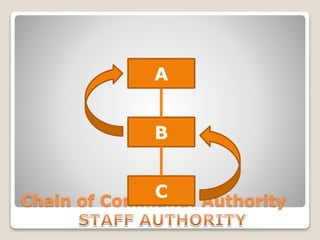
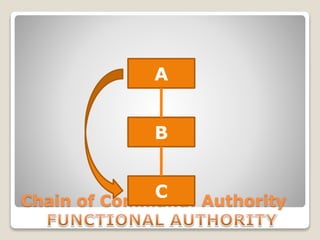
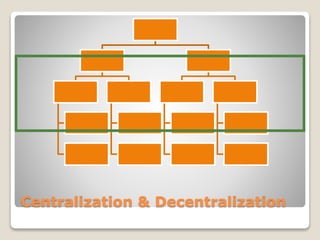
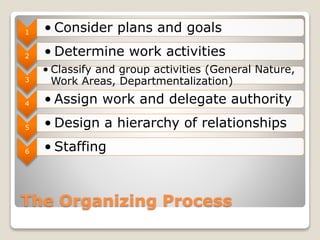
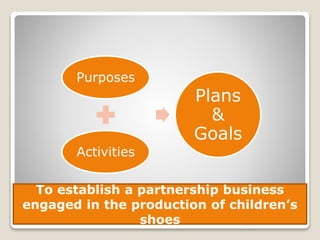
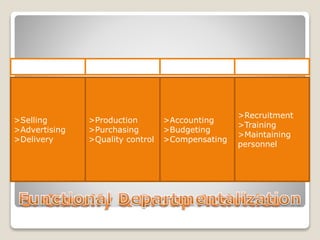
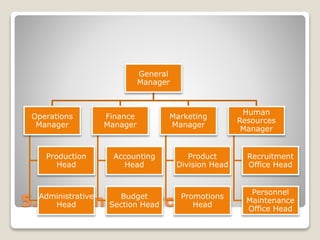
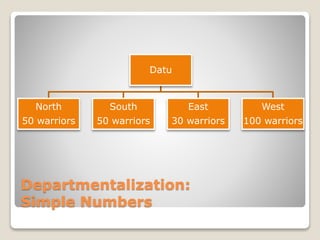
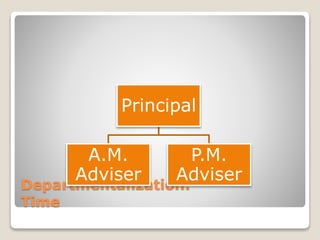
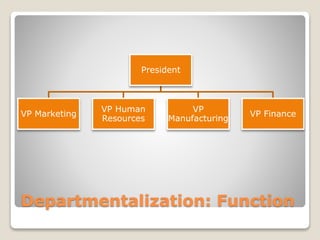
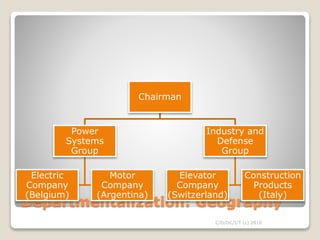
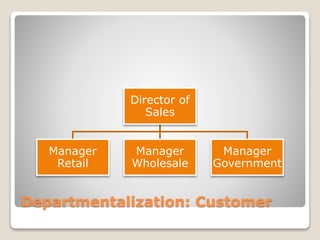
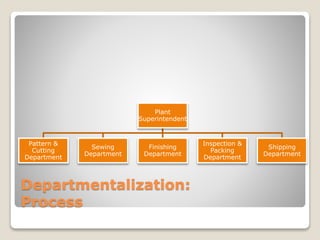
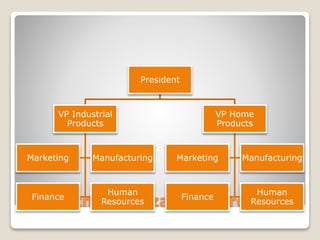
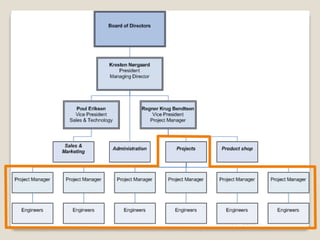
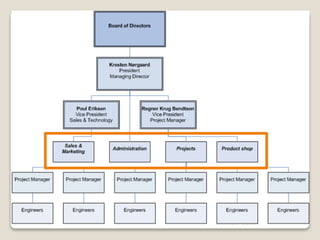
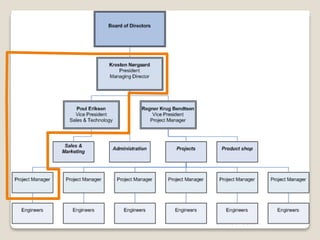
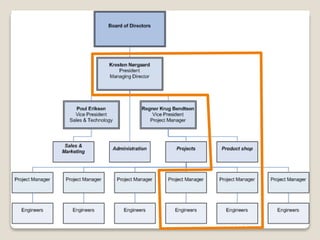
The document discusses various perspectives on organizing from authors like Barnard, Clayton State University, and Attner & Morgan. It also covers important aspects of organizing like the division of labor, departmentalization, centralization versus decentralization, and the difference between formal and informal organizational structures. Effective organizing involves classifying work activities, assigning roles and authority, establishing reporting relationships and departments, and staffing positions to achieve organizational goals.