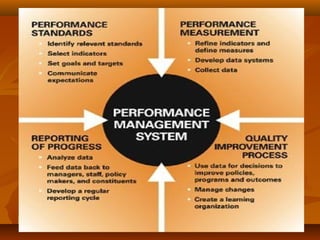
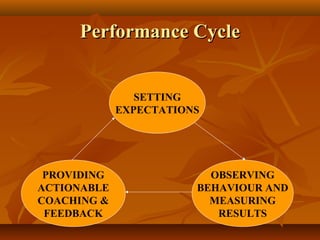
The document discusses performance management systems (PMS). It states that a PMS provides a structured approach to communicate business strategy, establish shared understandings of goals, facilitate self and peer management, measure and motivate performance. A PMS consists of setting employee expectations, maintaining dialogue to monitor performance, and conducting annual reviews. It is used to address underperformance, encourage development, and determine performance-based pay and promotions. Key aspects of an effective PMS include setting key result areas, providing feedback, and linking performance to rewards and career progression.