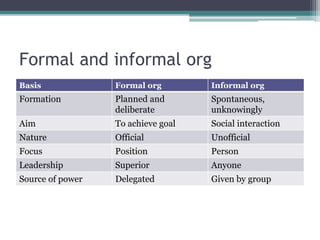
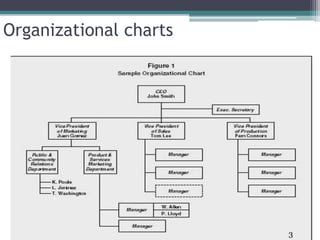
This document discusses the process of organizing as a management function. It defines organizing as dividing work activities into departments and groups, assigning duties, and establishing authority and responsibility. The key steps in organizing are determining objectives, listing activities, grouping activities, determining positions, delegating duties, and establishing relationships between positions. Organizing establishes the formal organizational structure through departments, charts, and allocation of authority. Informal organization also occurs naturally through social groups.