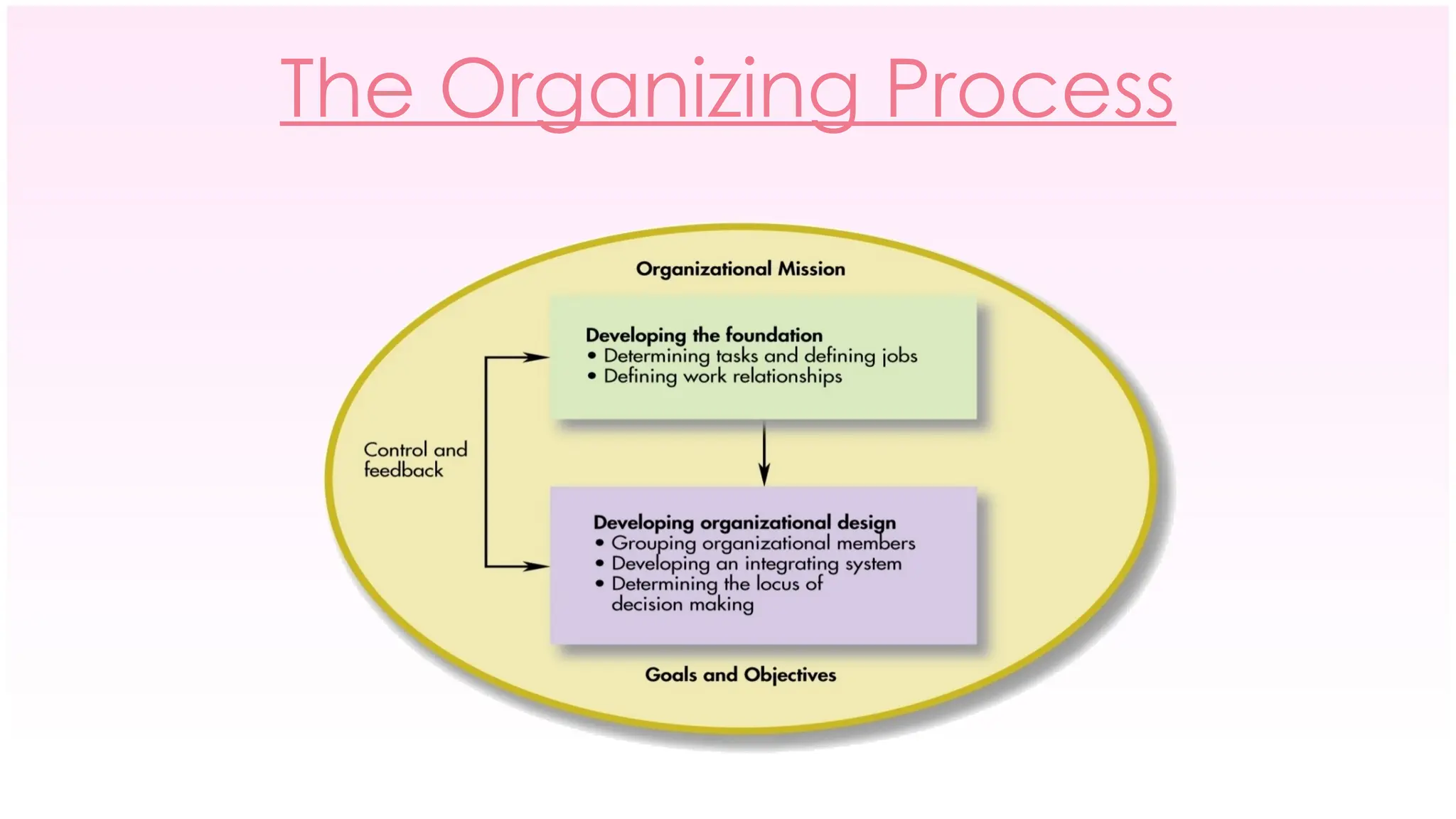
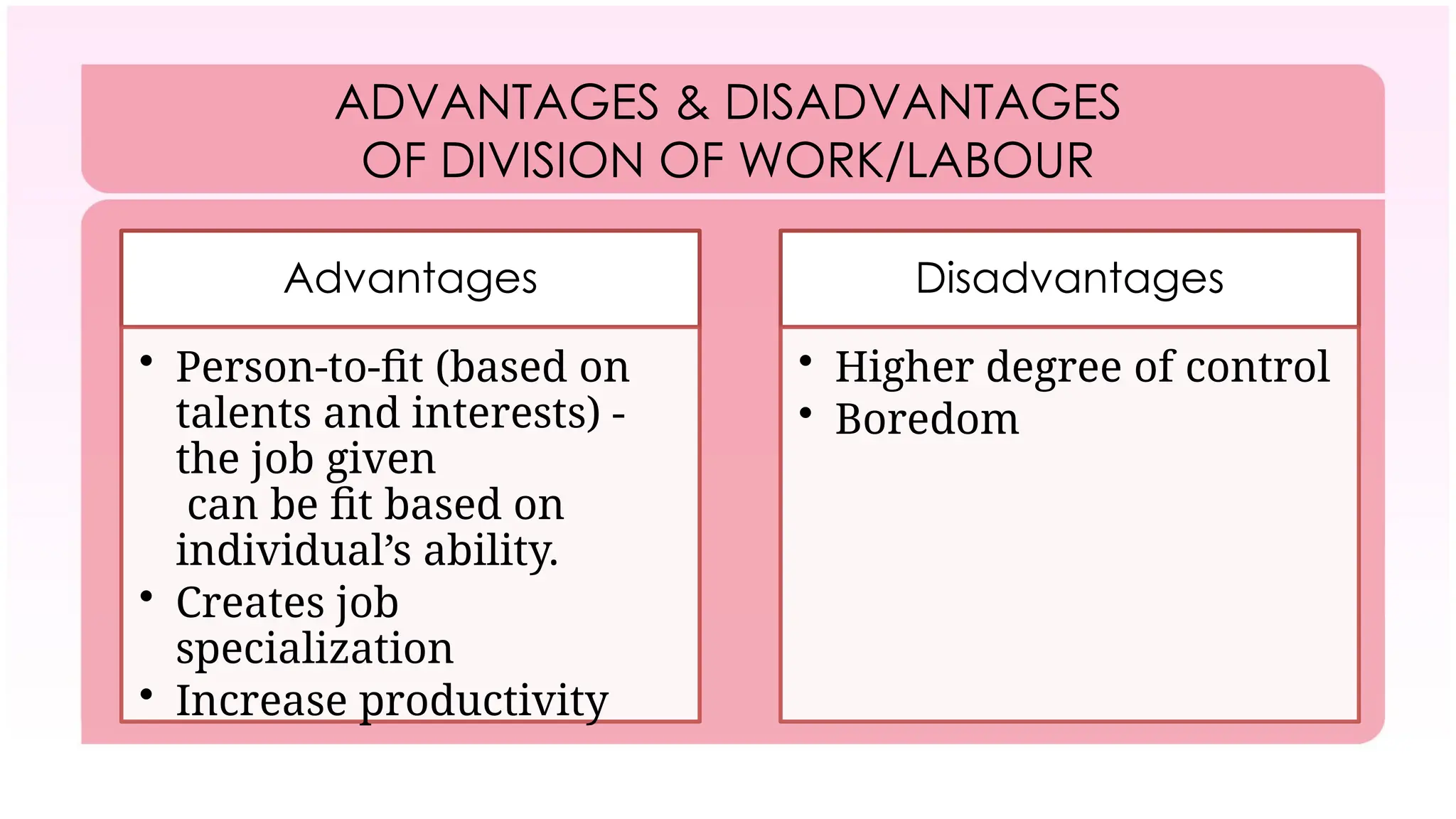
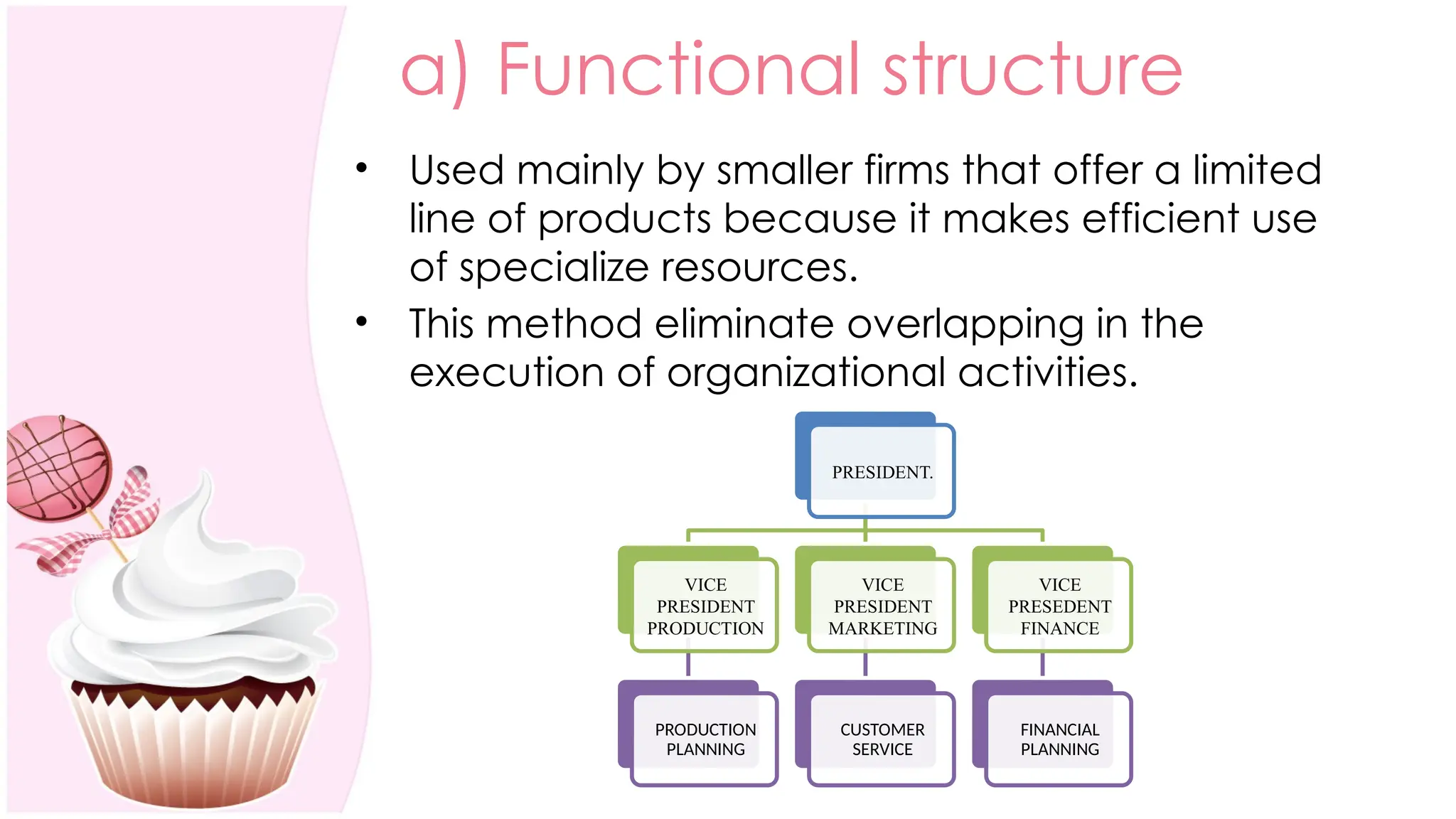
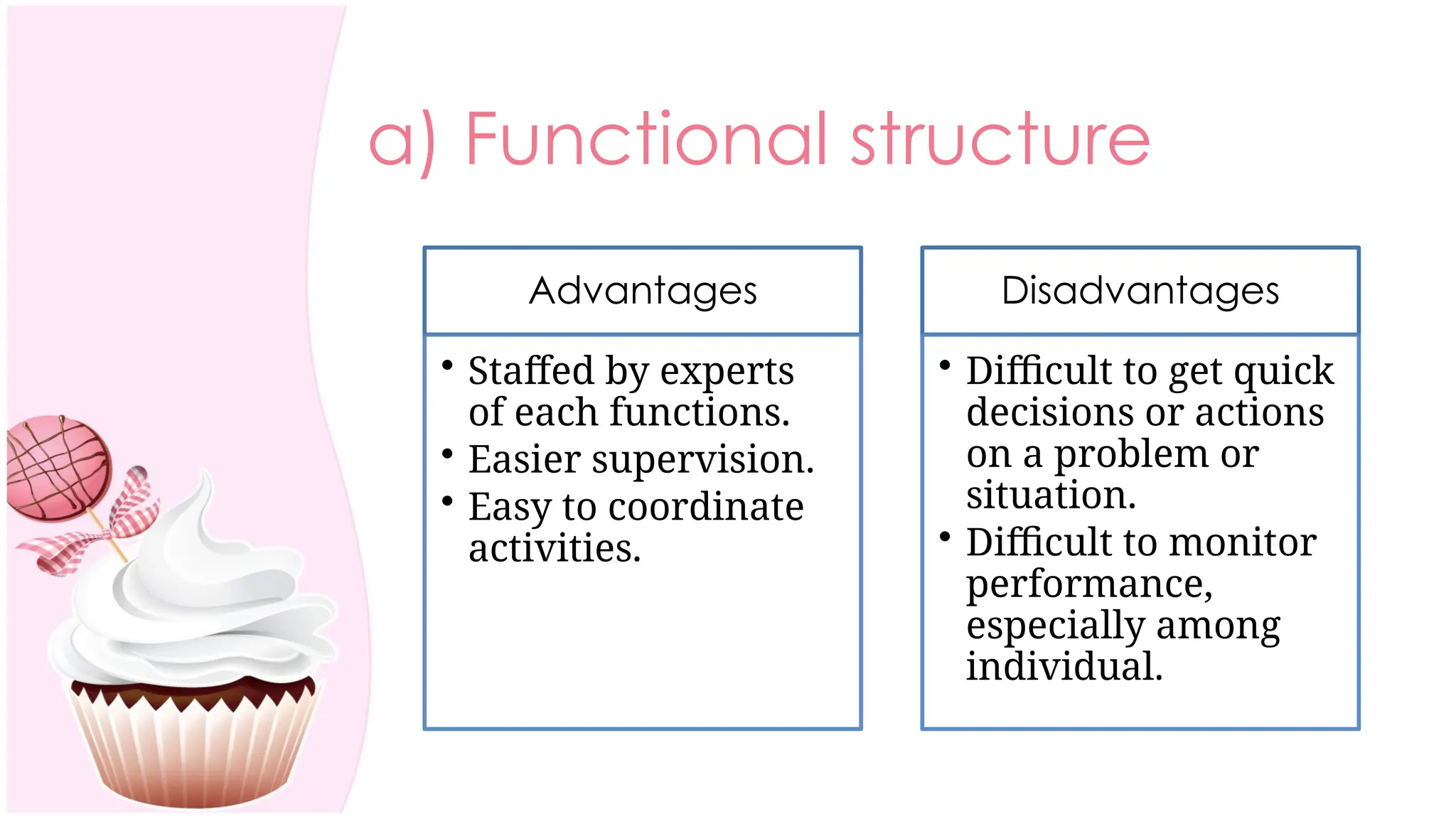
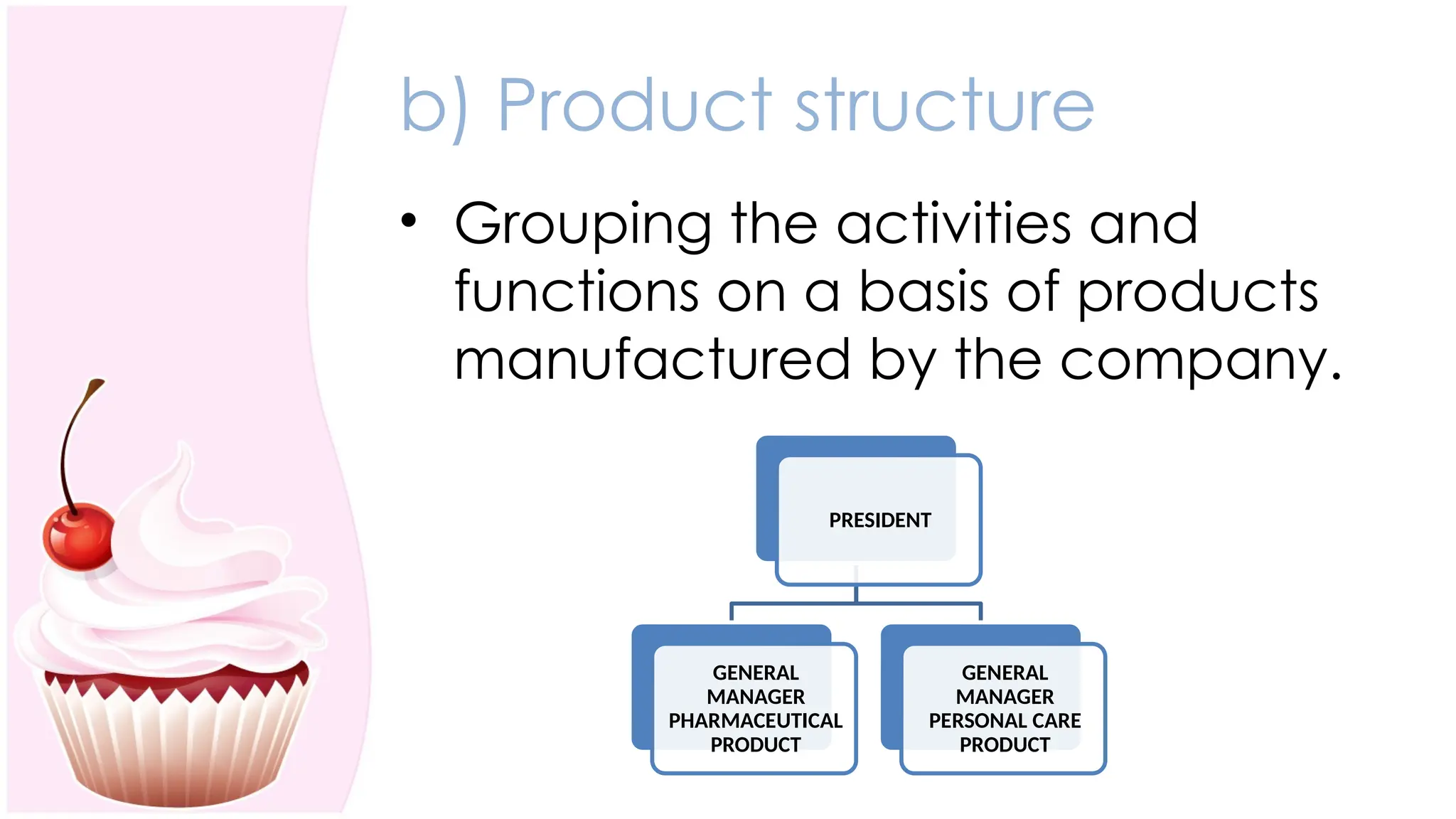
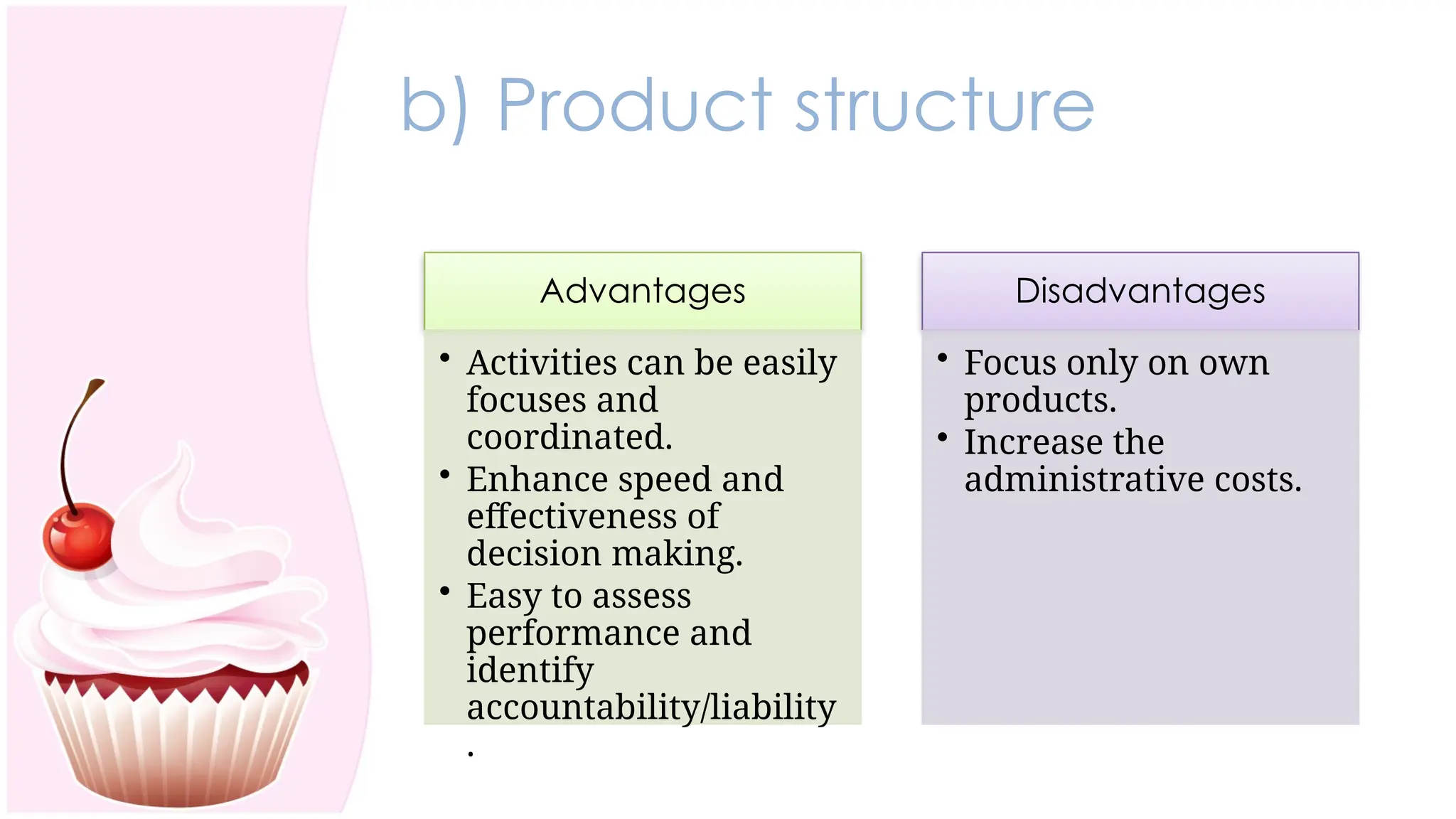
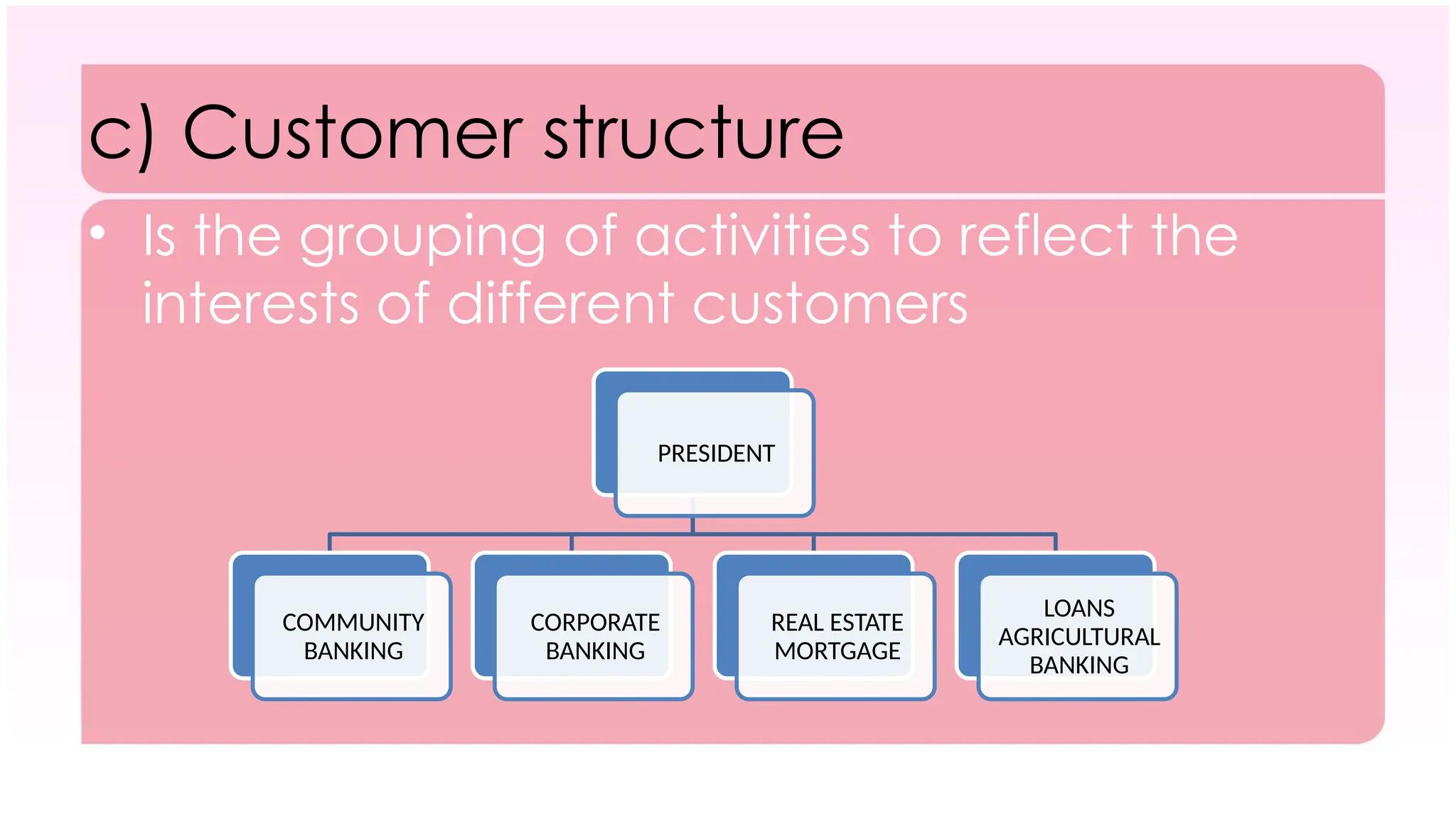
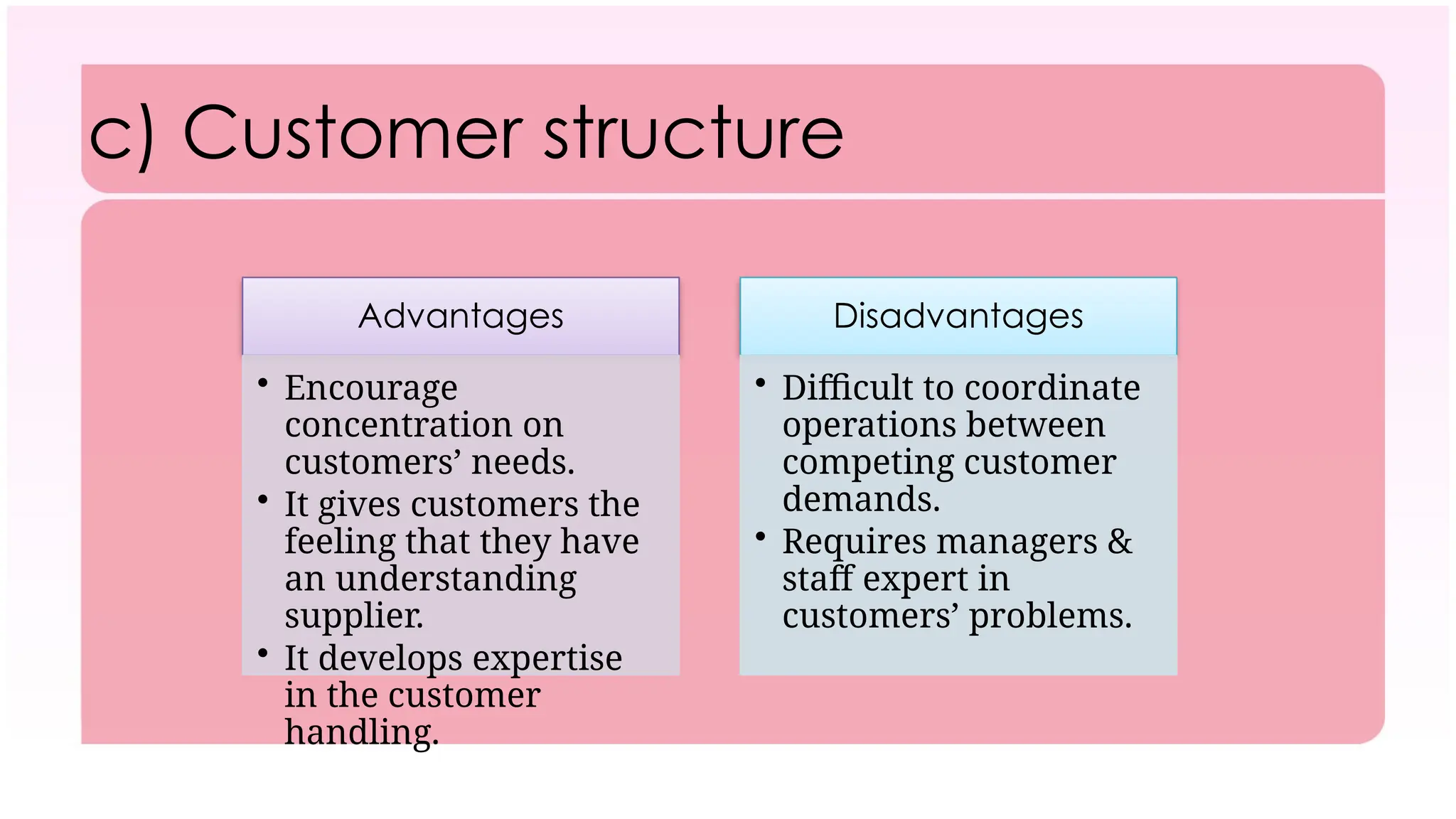
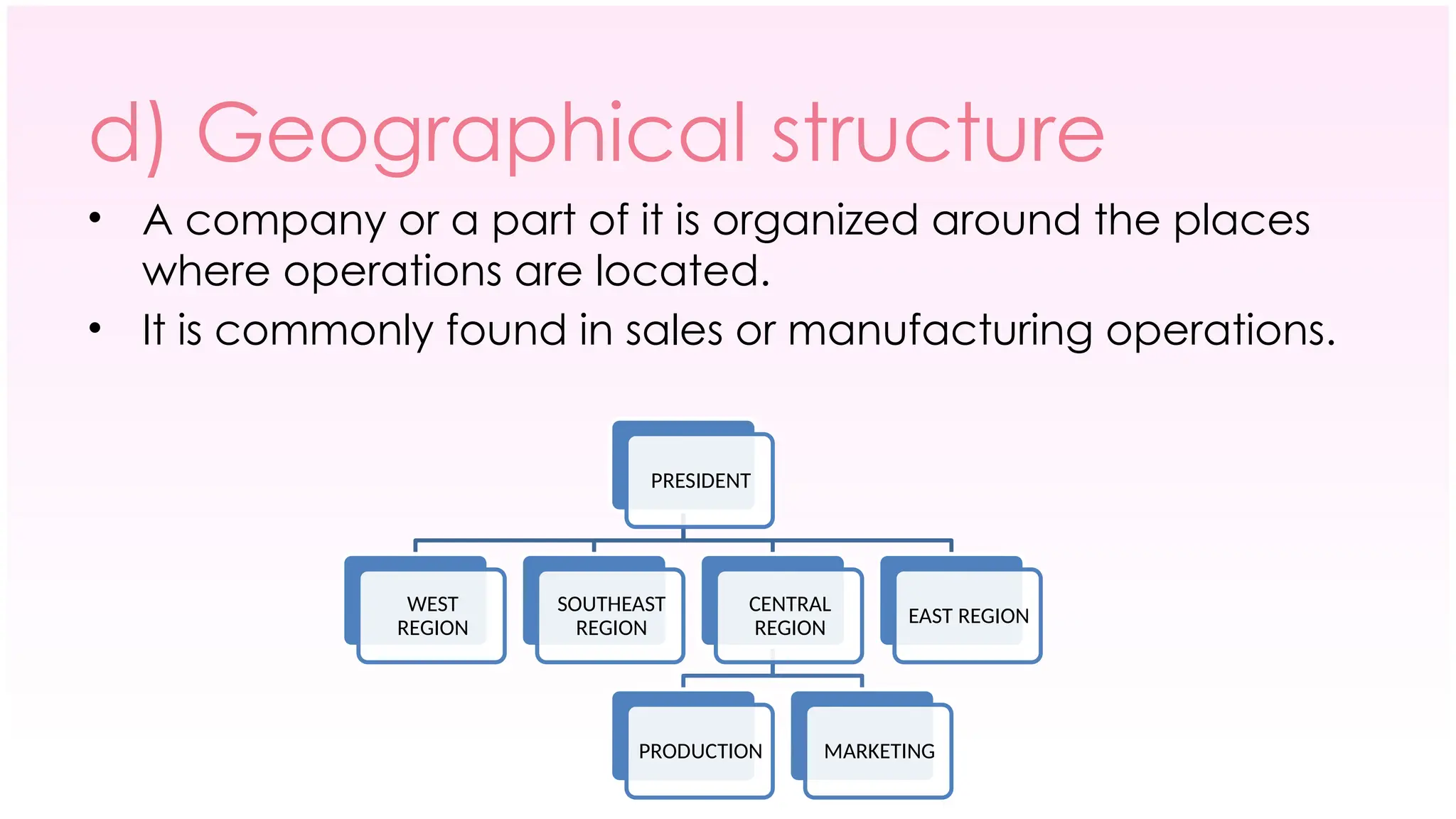
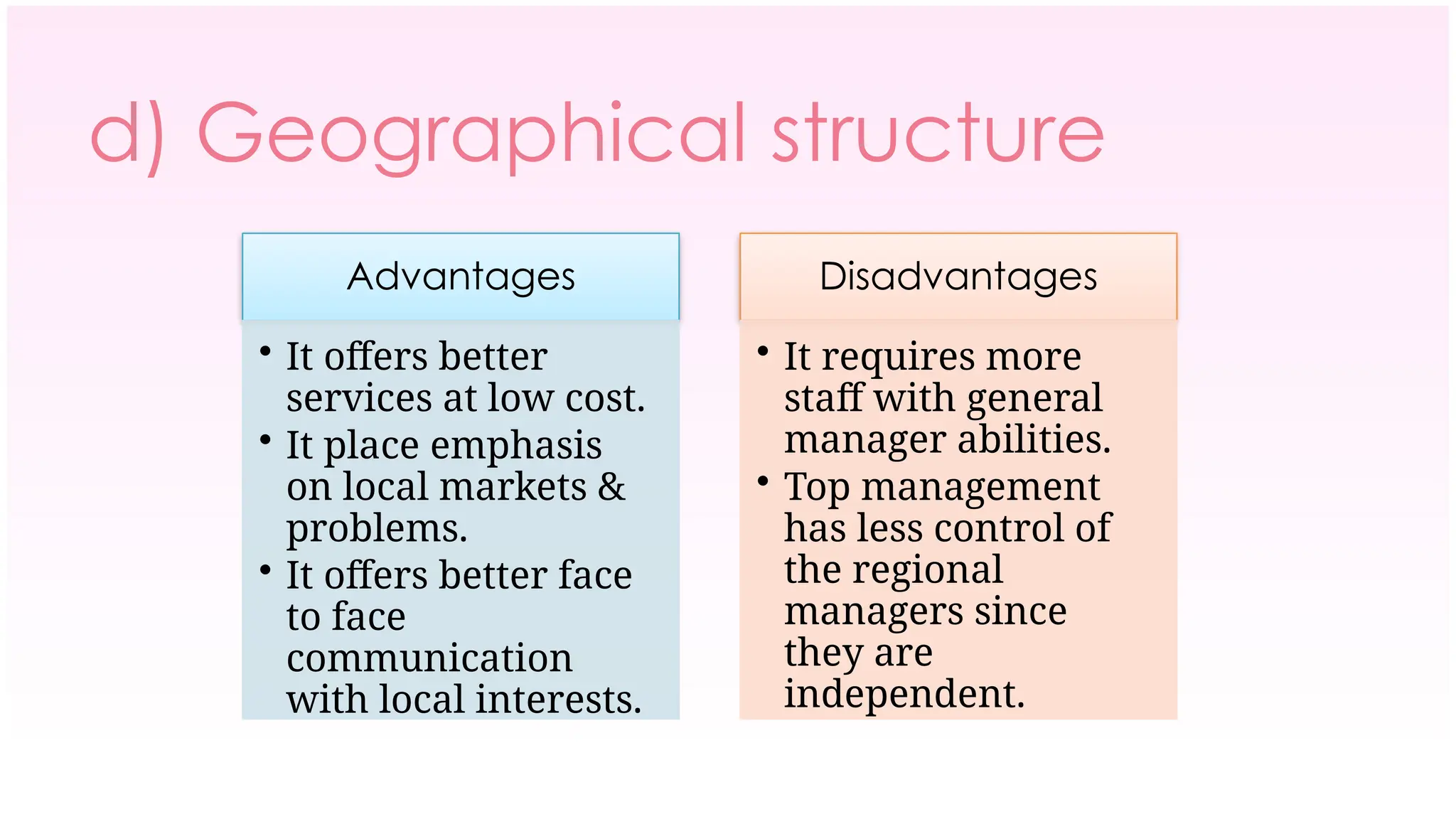
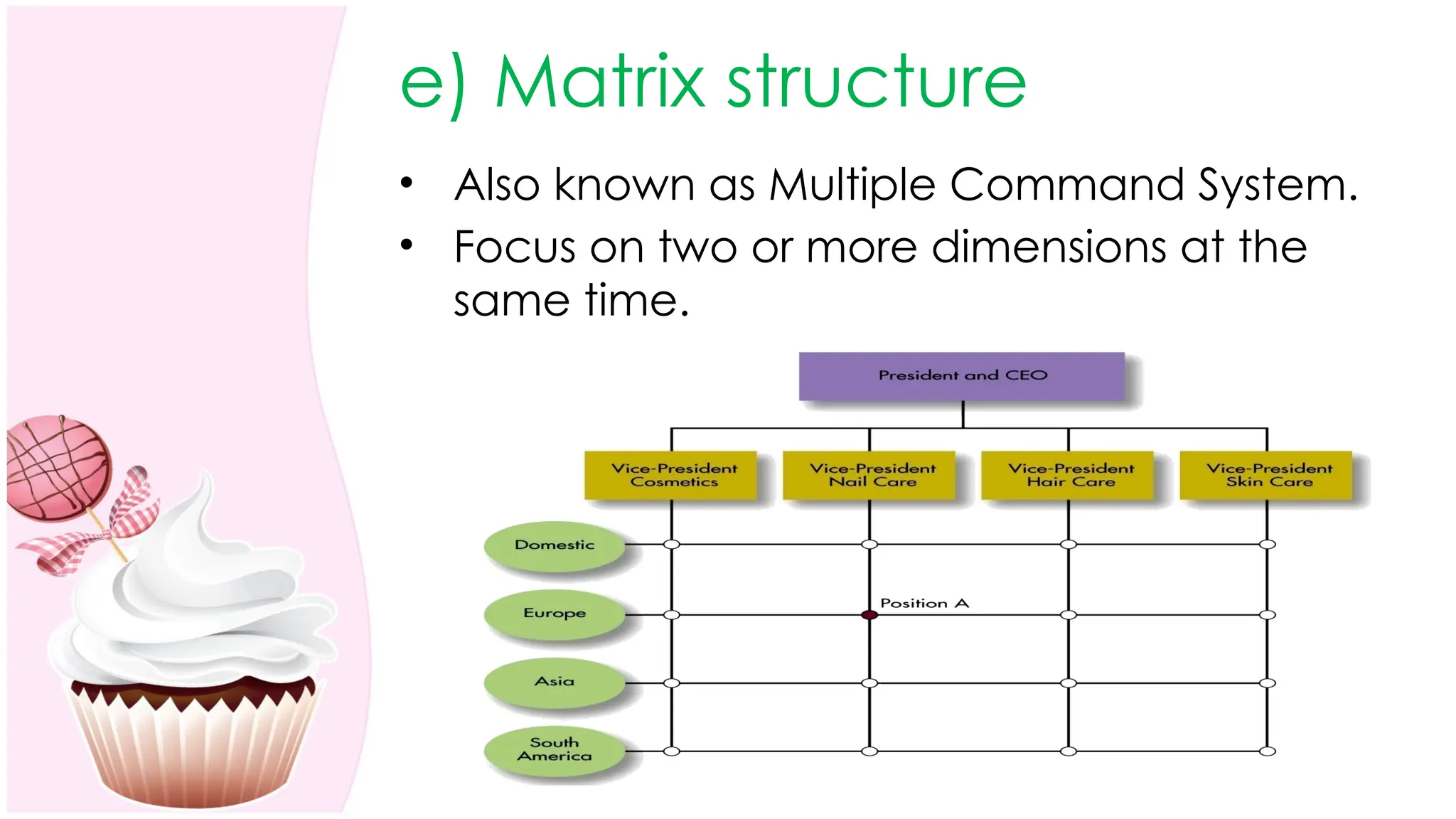
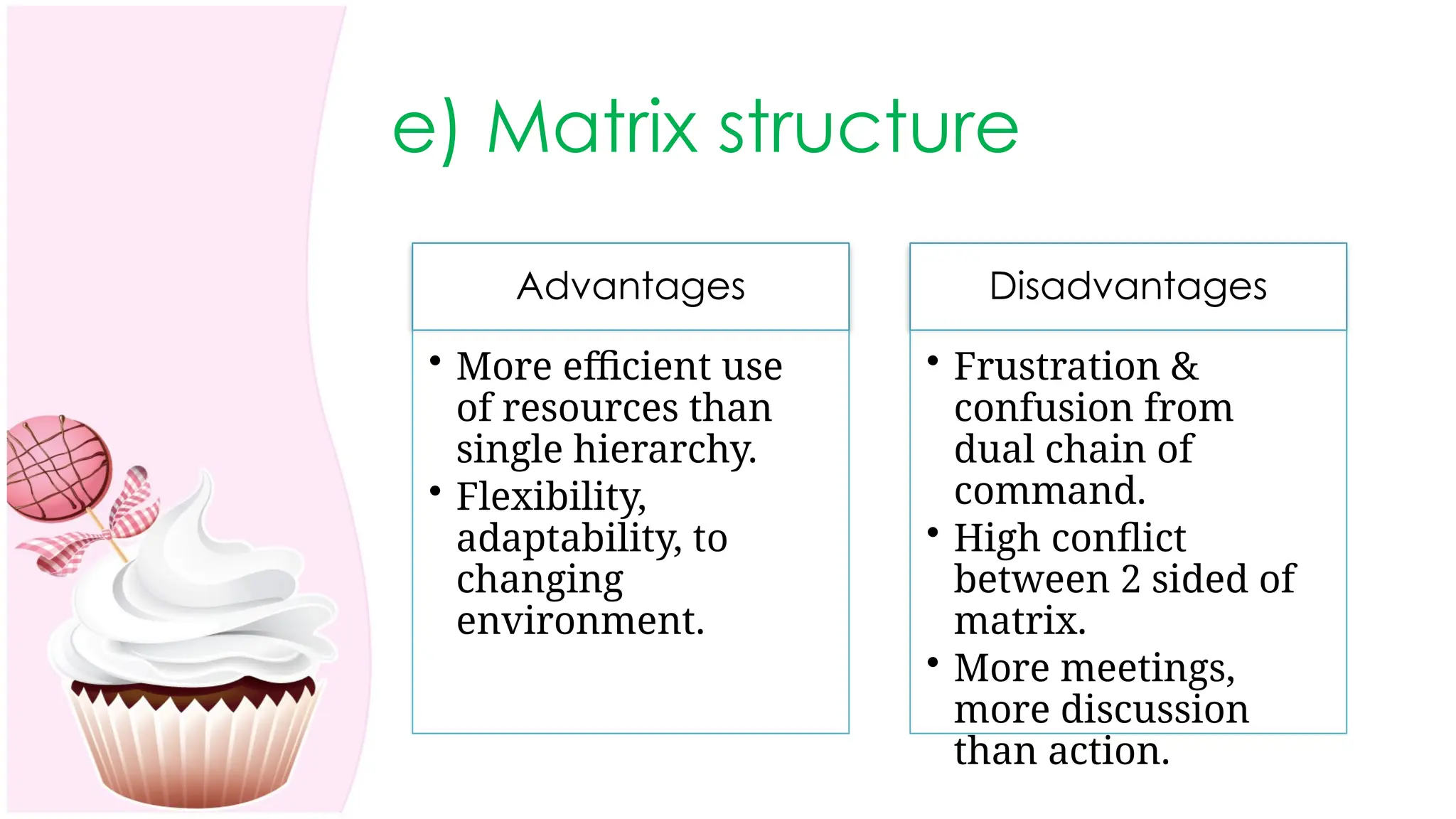
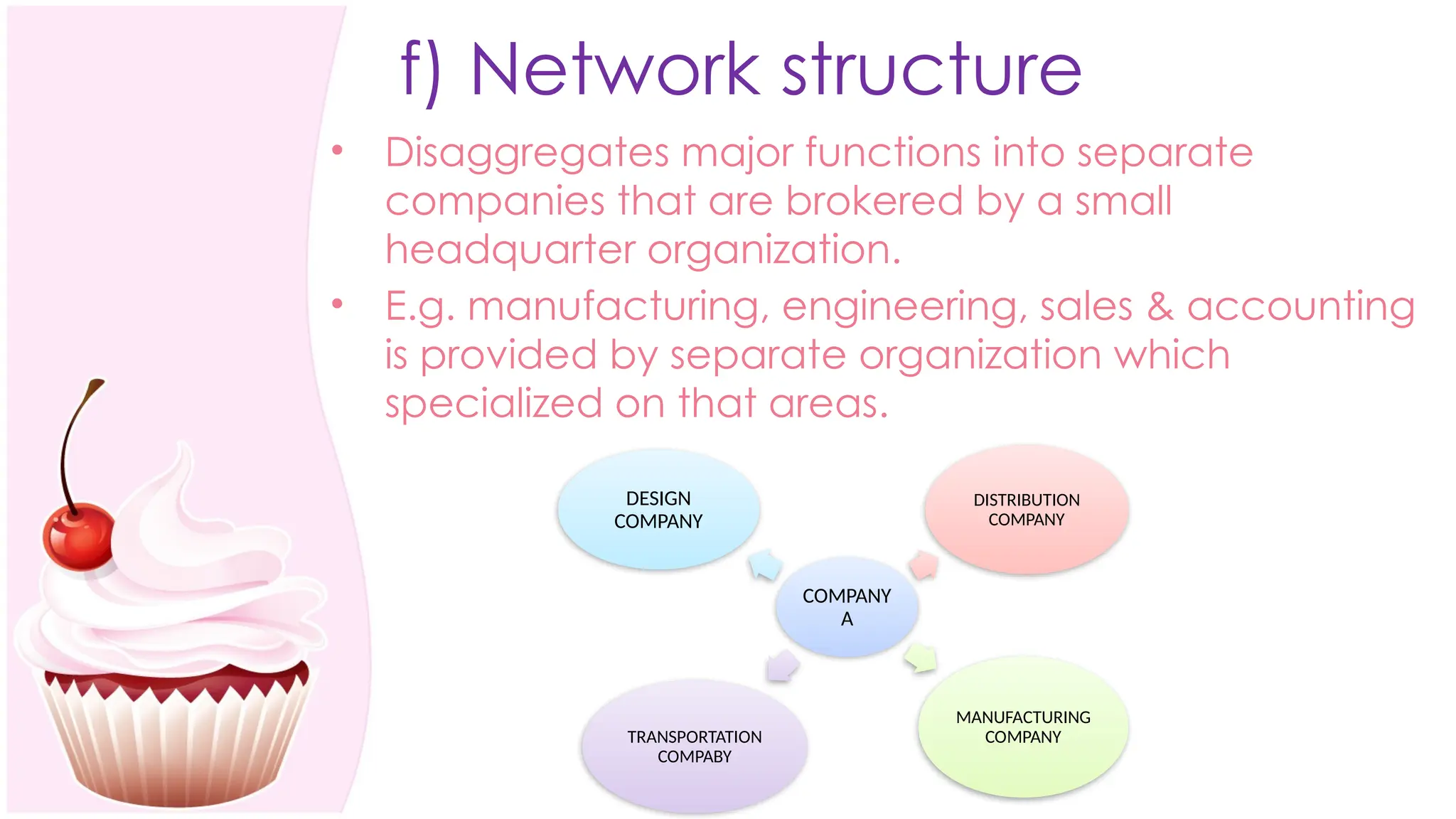
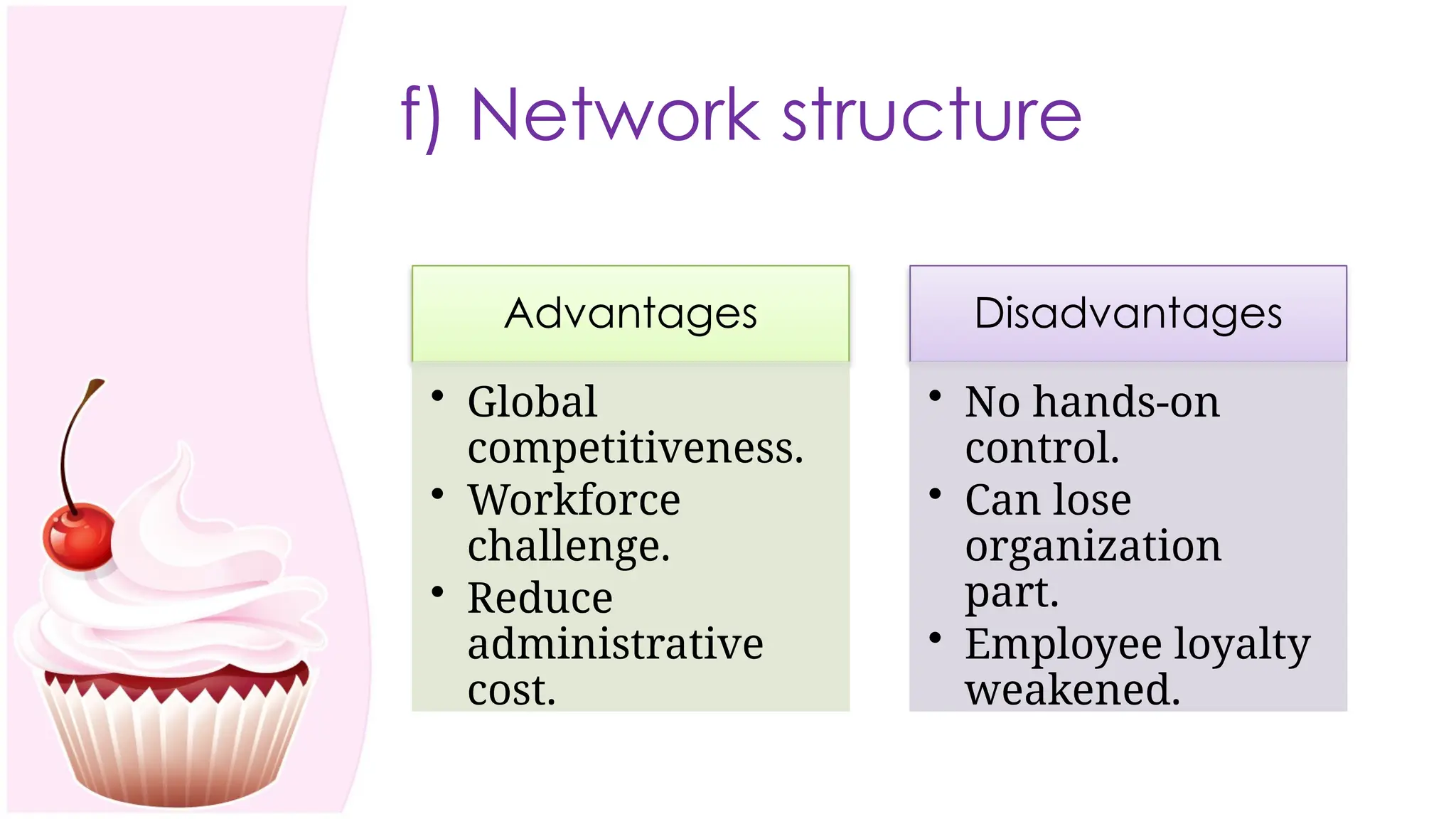
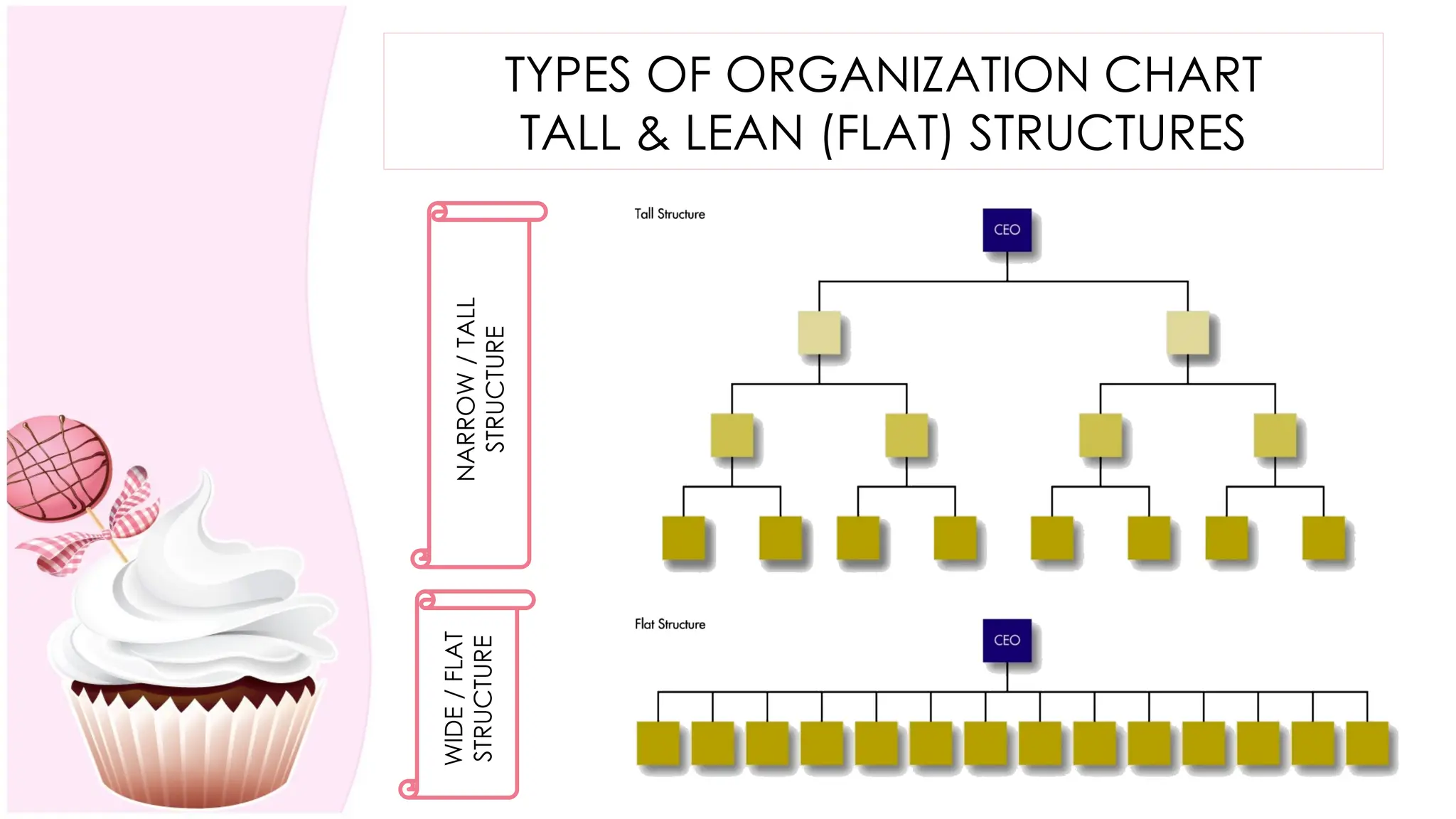
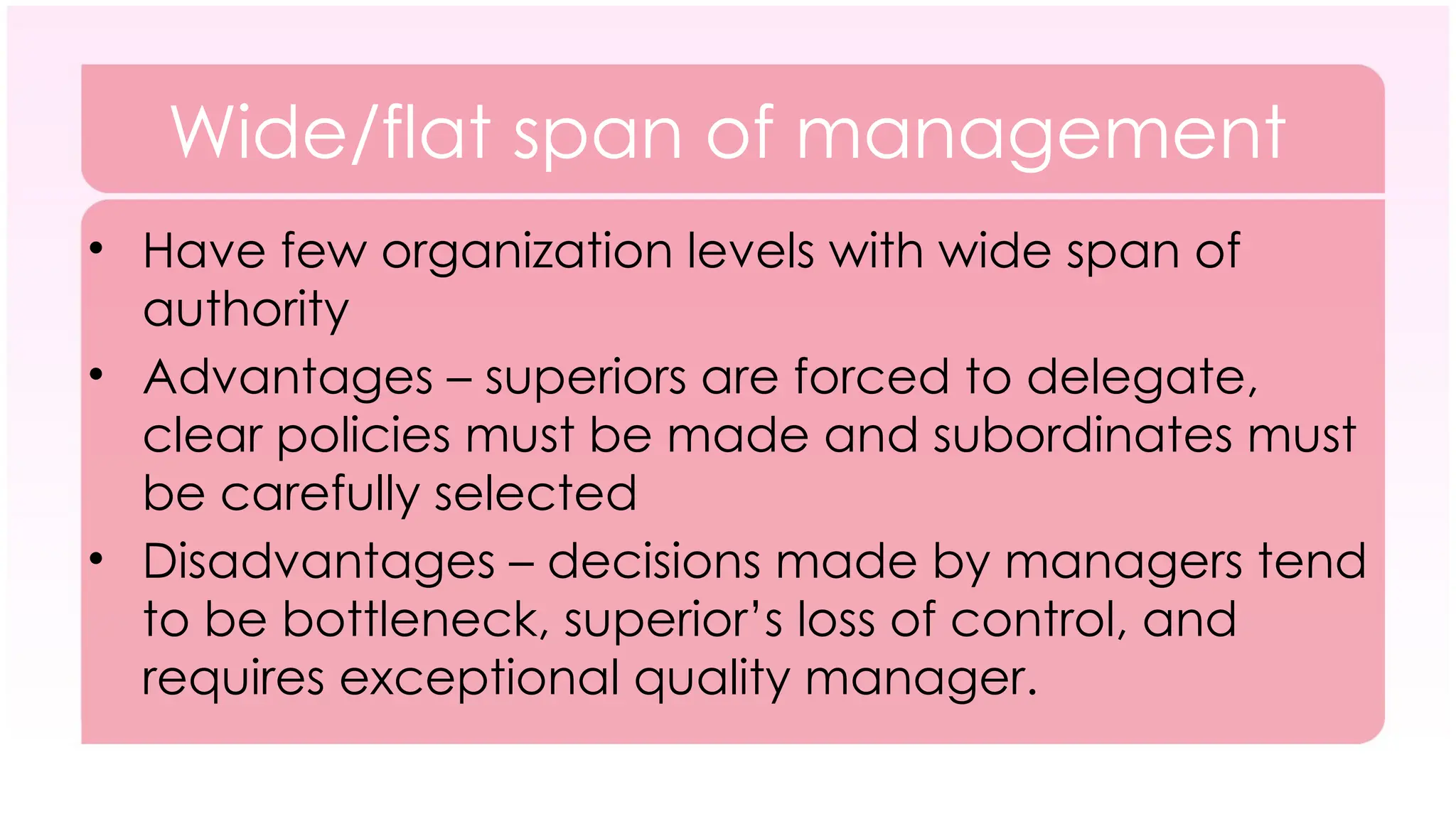
The document outlines the concept of organizing within management, defining it as the process of determining tasks, delegating responsibilities, and coordinating efforts to achieve organizational goals. It discusses the importance of organizational structure, the process of developing an organizational design, and various types of departmentalization, including functional, product, customer, geographical, matrix, and network structures, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Key aspects such as span of management, authority, delegation, centralization, and decentralization are also covered, emphasizing their roles in effective management.