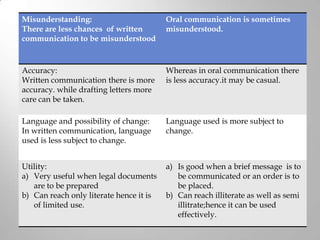
This document discusses various communication skills including oral communication, written communication, listening skills, questioning skills, feedback skills, presentation skills, and group discussion skills. It provides details on the differences between oral and written communication. It also outlines best practices for skills like telephone communication, public speaking, conducting presentations, active listening, asking effective questions, and giving constructive feedback. The overall document serves as a guide to developing strong interpersonal and professional communication abilities.