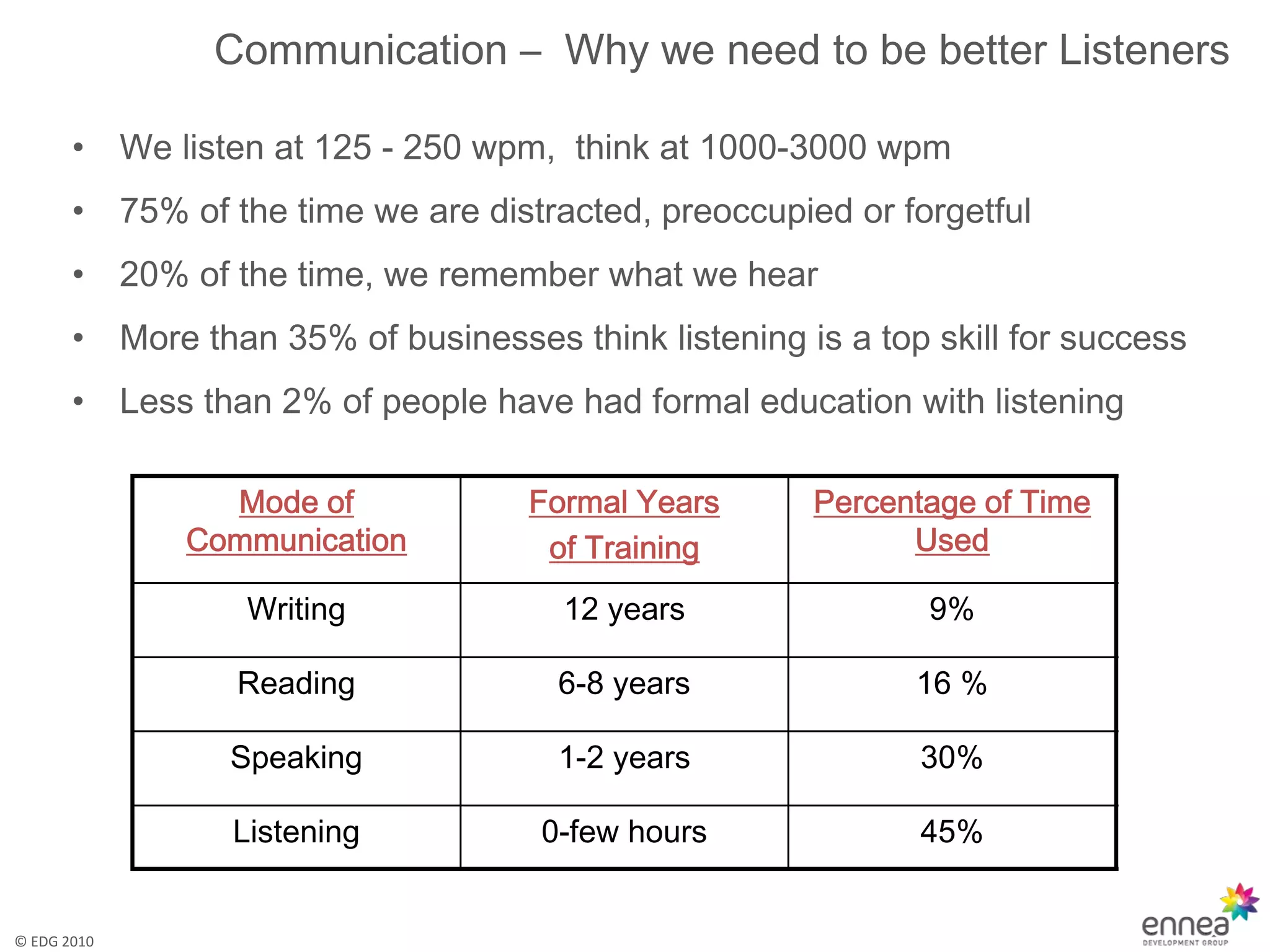
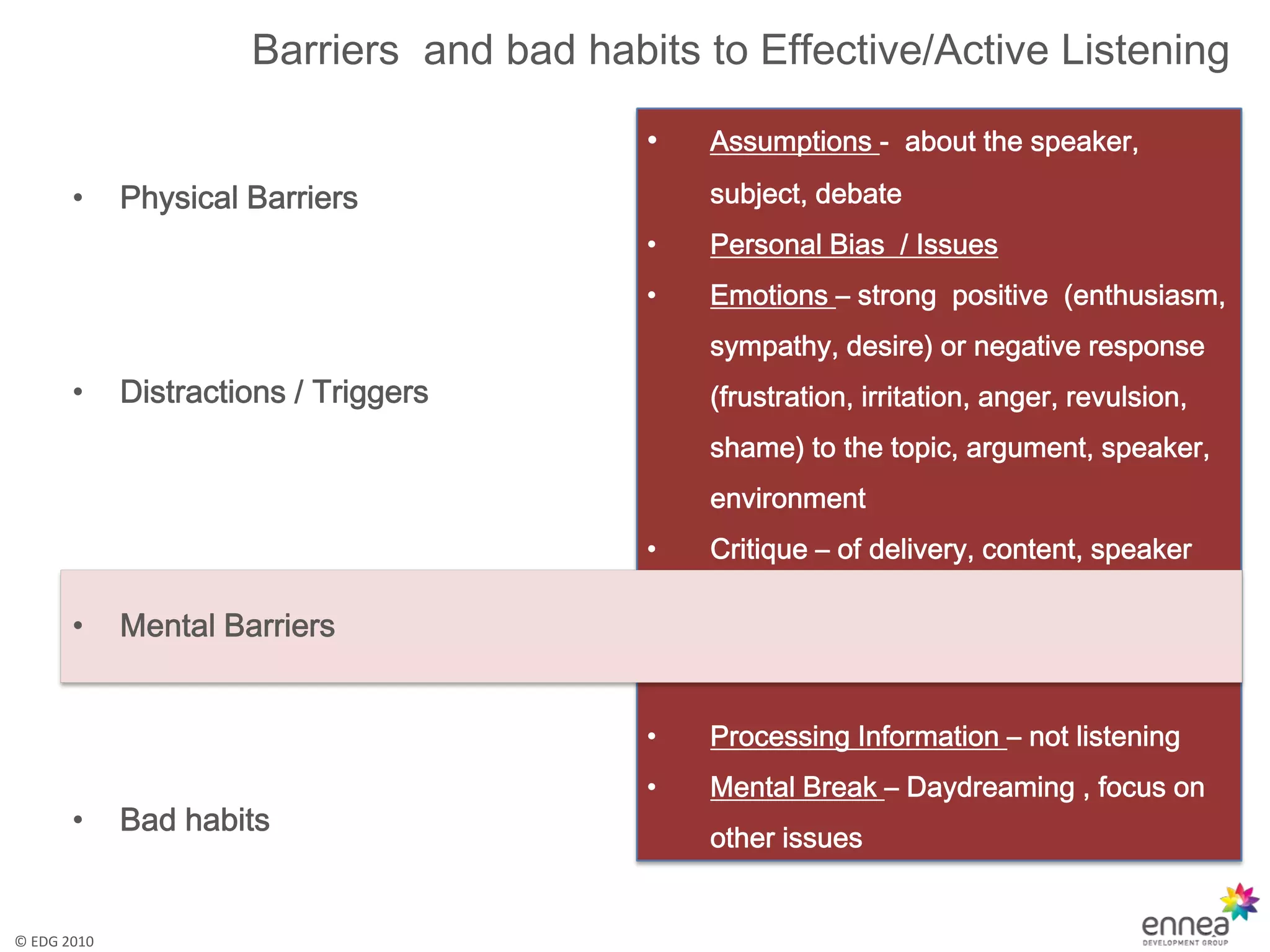
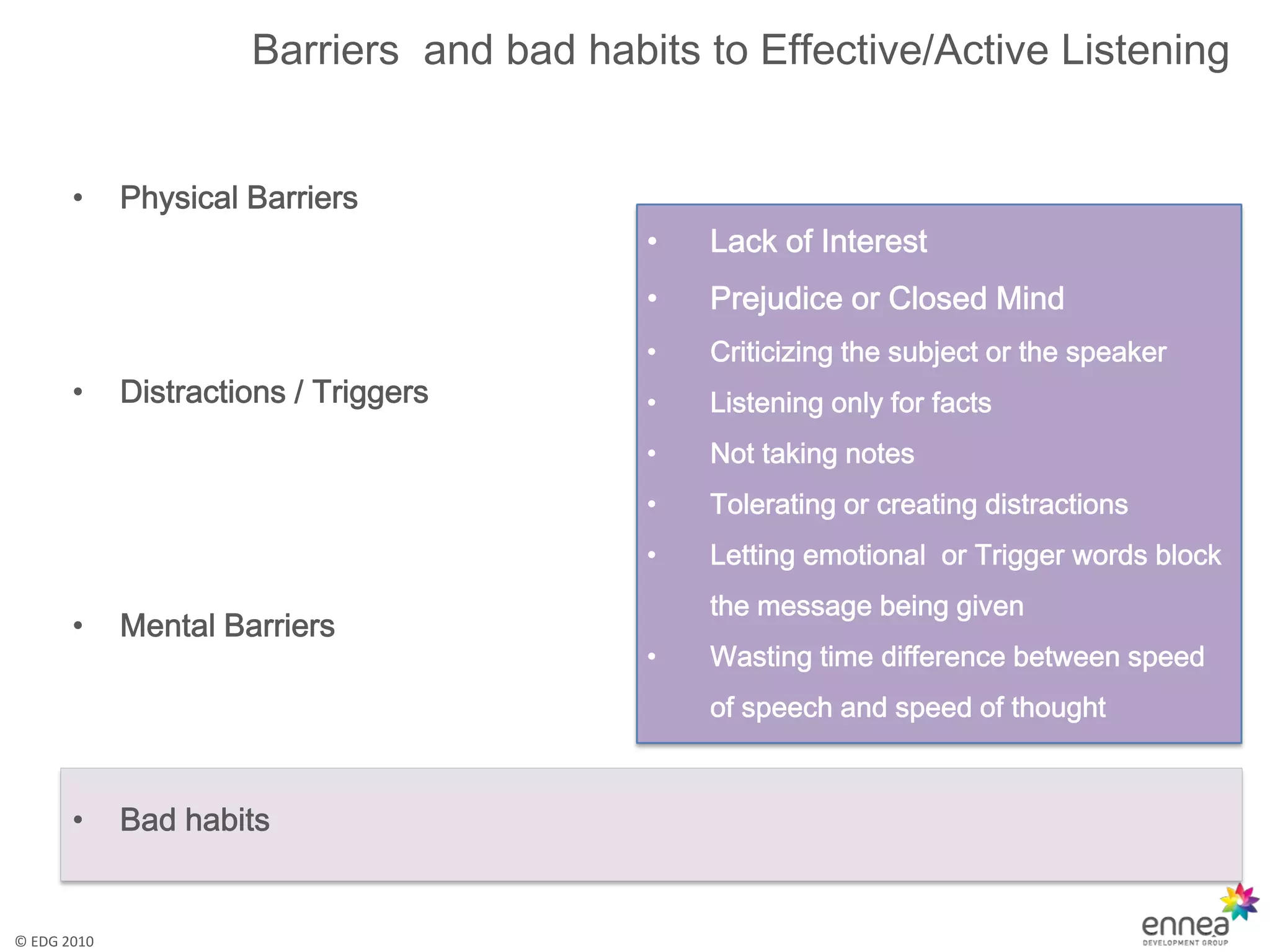
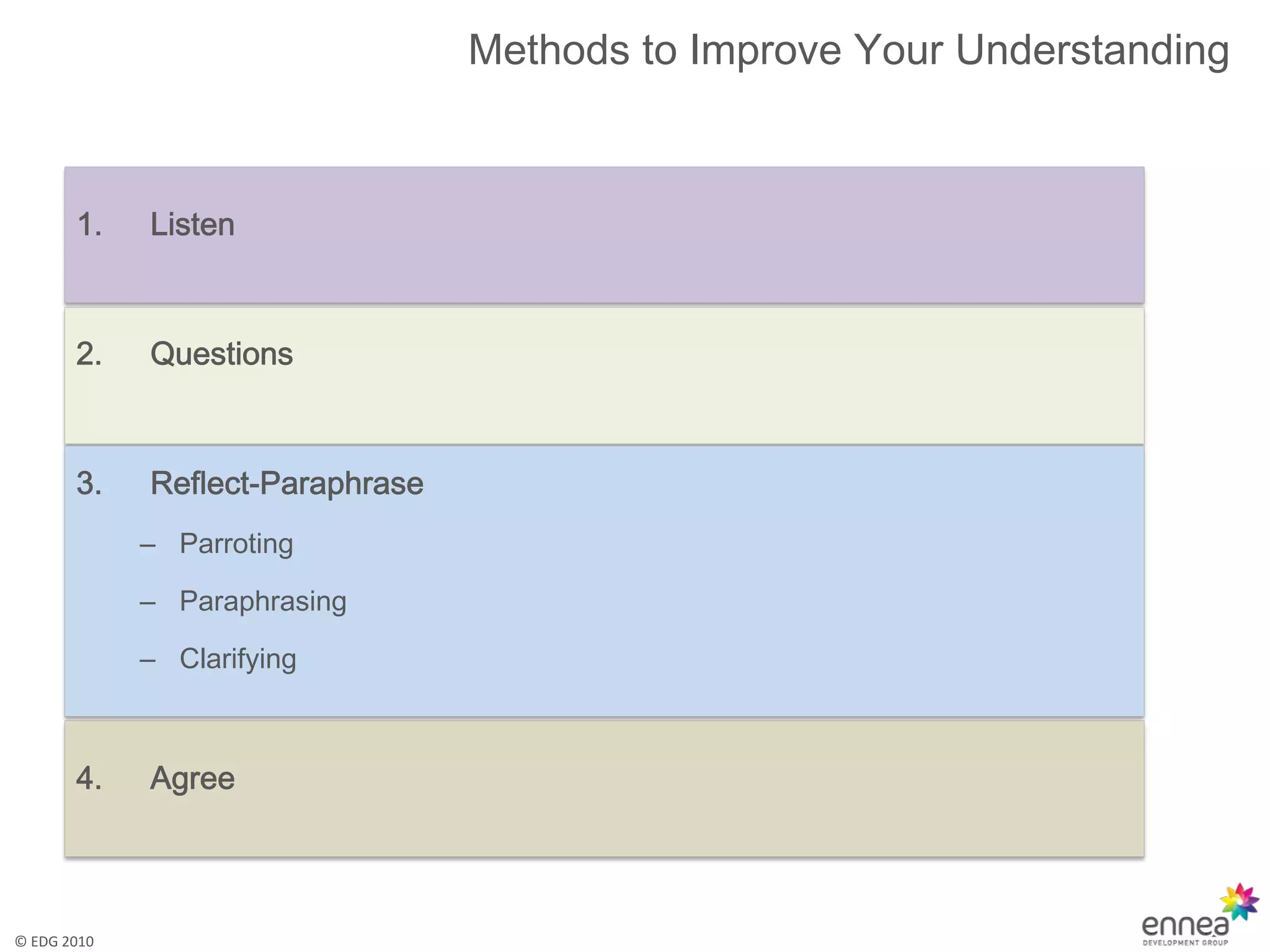
The document discusses effective and active listening. It defines listening as receiving, constructing meaning from, and responding to spoken and nonverbal messages. It then outlines barriers to listening like distractions, mental barriers, and bad habits. Finally, it provides tips for active listening including focusing on the speaker, using verbal and nonverbal cues, and offering feedback to ensure understanding.