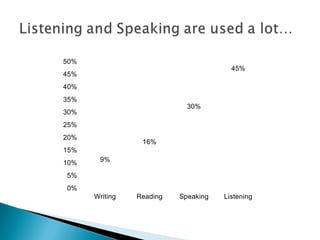
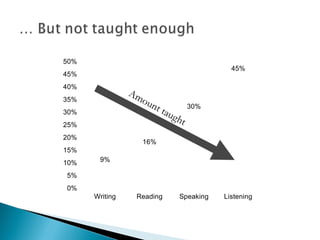
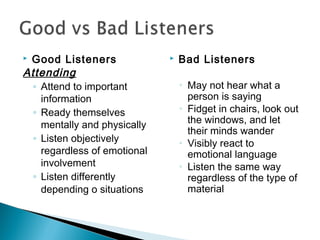
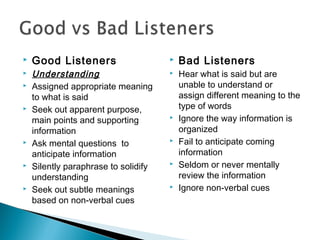
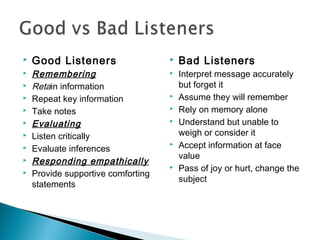
The document discusses listening skills and effective listening. It provides data showing Wasim Hasan's highest skill is listening at 45% and lowest is writing at 16%. The document also outlines the differences between listening and hearing, factors that influence listening ability, and steps to become an effective listener.