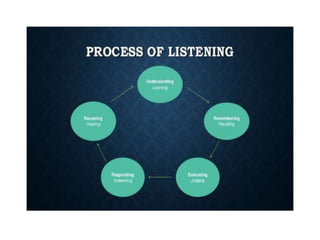
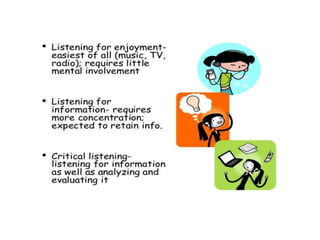
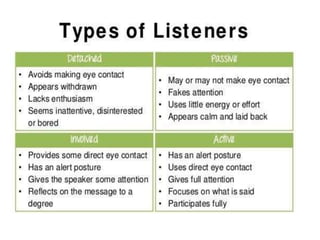
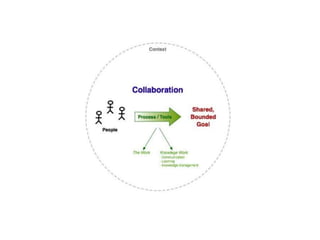
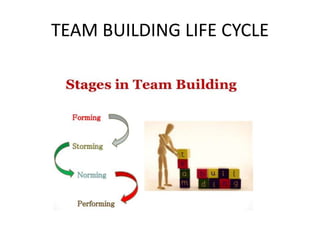
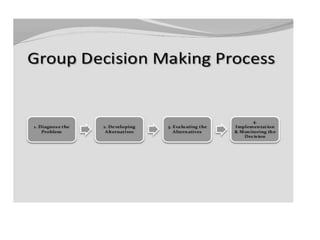
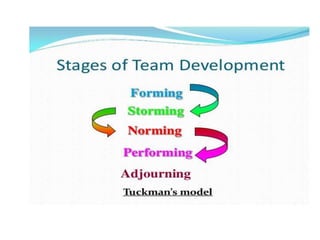
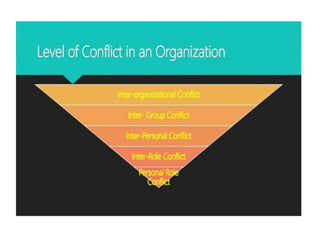
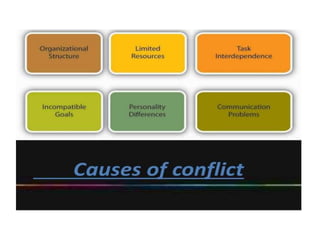
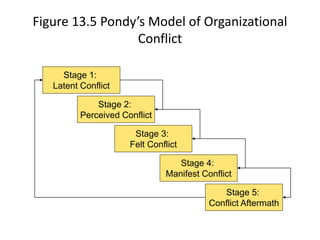
This document discusses various types of interpersonal communication including verbal, written, nonverbal, and intercultural communication. It also discusses listening as an active process of receiving, interpreting, and reacting to messages from the communication sender. Several barriers to effective listening are outlined such as inadequate background information, selective perception, and distractions. Collaboration in the workplace is defined as groups working together through idea sharing to accomplish common goals. Effective decision making techniques for teams include brainstorming, the nominal group technique, and the Delphi technique. Models of organizational conflict include Pondy's five stage model of latent, perceived, felt, manifest, and aftermath conflicts.