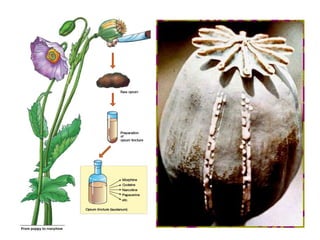
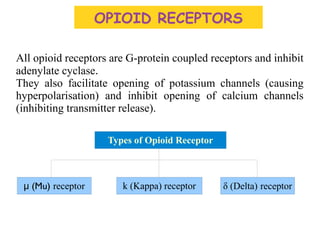
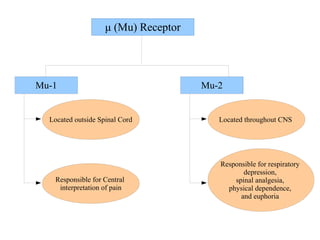
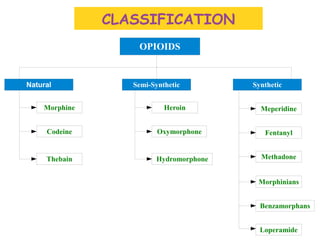
This document provides information about opioid analgesics including opium, opioids, opioid receptors, types of opioid receptors, opioid classification, and therapeutic uses of certain opioids like morphine and codeine. It discusses how opioids selectively relieve pain by acting in the central nervous system or peripheral pain mechanisms without significantly altering consciousness. It also summarizes the effects of morphine poisoning and its antidote.