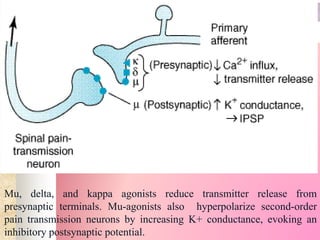
Opioid analgesics work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord to reduce pain. There are several types of opioid receptors that endogenous opioid peptides and exogenous opioids can bind to, including mu, delta, and kappa receptors. Opioids are well absorbed orally or parenterally and distributed widely throughout the body. They are metabolized in the liver mainly by conjugation with glucuronic acid and excreted in urine. Opioids produce analgesia, sedation, respiratory depression, nausea, vomiting, and constipation by acting on central and peripheral opioid receptors. Tolerance and physical dependence may develop with repeated use.