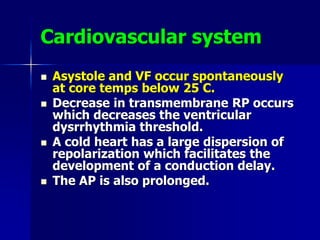
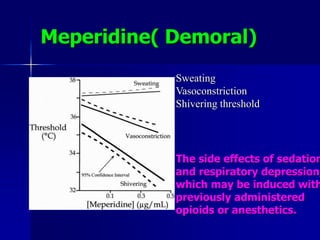
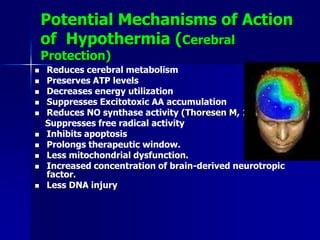
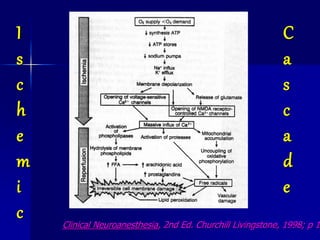
Hypothermia is defined as a core body temperature below 36°C and can be classified as mild (35-32°C), moderate (32-28°C), or severe (<28°C). It carries significant risks such as cardiovascular instability, coagulopathy, and impaired drug metabolism. Prevention techniques include warming intravenous fluids and the operating room. Treatment involves initially allowing passive rewarming, but active internal rewarming may be necessary for more severe hypothermia using methods like warmed intravenous or intraperitoneal fluids. Pharmacological agents that can treat shivering include meperidine, nalbuphine, tramadol, clonidine, and opioids like morphine.