Thiopentone (also known as thiopental sodium) is a short-acting barbiturate used for inducing anesthesia. It works by enhancing the effects of the neurotransmitter GABA at GABAA receptors in the brain, which increases chloride conductance and inhibits neuronal activity. Thiopentone is administered intravenously as a 2.5% solution for induction of anesthesia in adults and children. Common side effects include respiratory depression, hypotension, and pain or tissue damage if accidentally injected into an artery. Proper dosage depends on factors like age, weight, and medical history. Thiopentone is metabolized in the liver and redistributes rapidly from the brain after administration, which allows for quick awakening.

























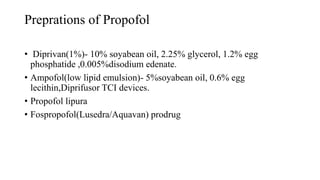





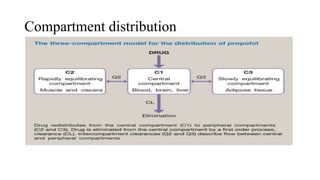



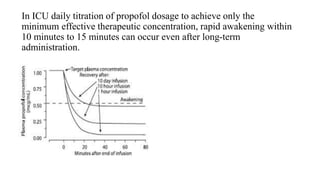
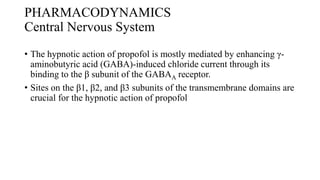

![• The onset of hypnosis after a dose of 2.5 mg/kg is rapid (one arm–
brain circulation), with a peak effect seen at 90 to 100 seconds.
• ED50 of propofol for loss of consciousness is 1 to 1.5 mg/kg after a
bolus.
• The duration of hypnosis 5 to 10 minutes after 2 to 2.5 mg/kg.
• Effect of age induction dose, which is highest at younger than 2 years
(95% effective dose [ED95], 2.88 mg/kg)
• Decreases with increasing age.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thiopentoneandpropofol-190120125918/85/Thiopentone-and-propofol-39-320.jpg)

























