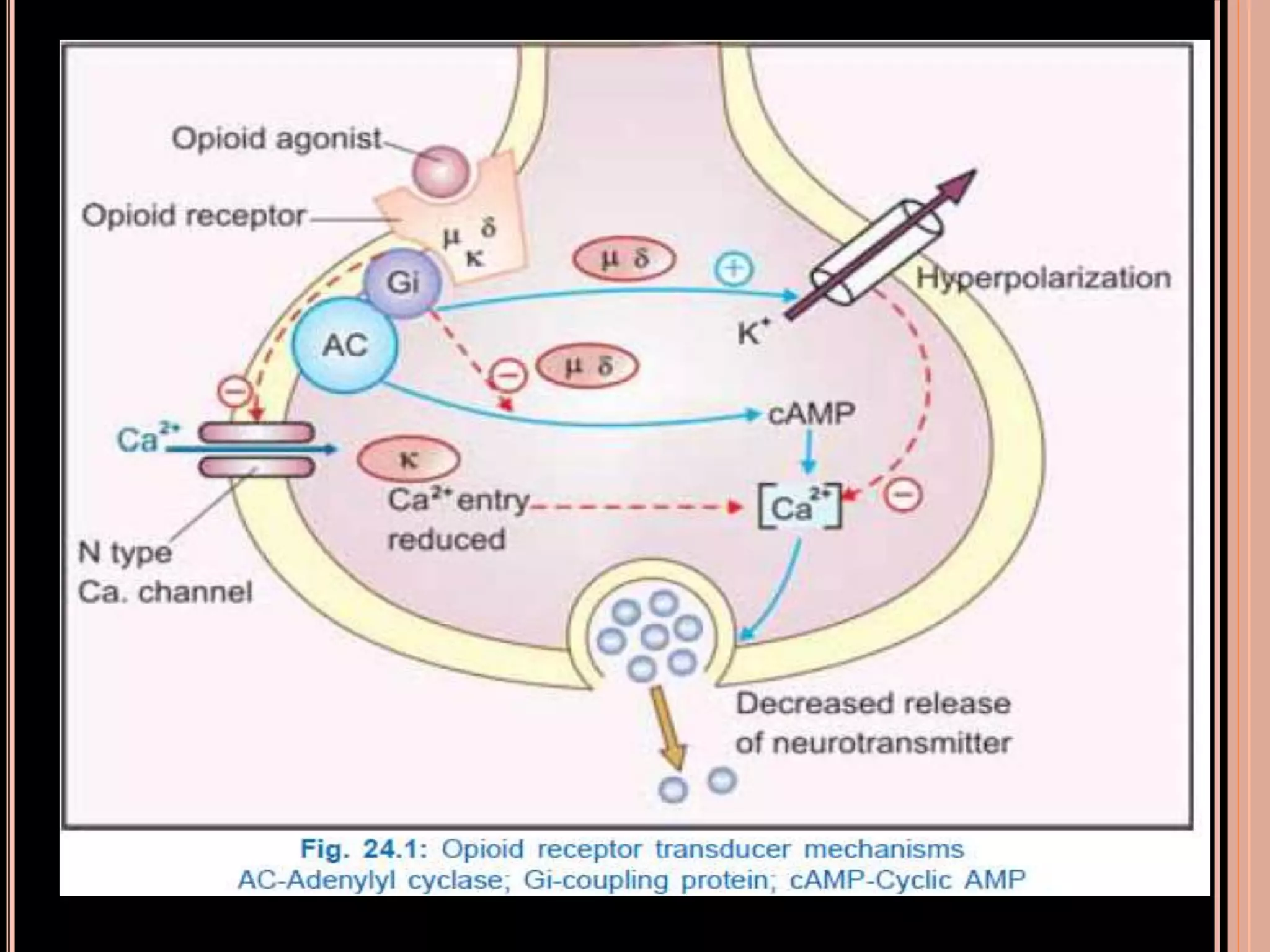
The document discusses opioid analgesics, which are derived from the opium seed and relieve deep seated pain without causing loss of consciousness. It describes the endogenous opioid peptides and their receptors in the brain and spinal cord that regulate pain responsiveness. It provides details on the classification, mechanisms of action, effects and therapeutic uses of various opioid analgesics, including morphine, codeine, heroin, pethidine, fentanyl, and tramadol. It also discusses the treatment of opioid dependence and the use of opioid antagonists like naloxone and naltrexone.