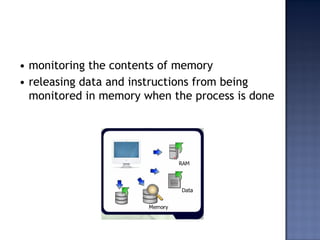
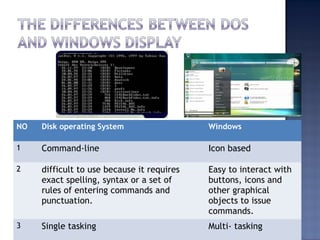
System software consists of programs that control computer operations and interface with users and hardware. There are two main types: operating systems and utility programs. Operating systems coordinate hardware, peripherals, memory, files and enable user communication. Examples include Windows, Mac OS X, Linux and Unix. Utility programs allow maintenance tasks like formatting. Operating systems manage data/programs, memory, devices, and provide user interfaces like graphical user interfaces (GUIs) that make software easier to use via menus, icons and buttons.