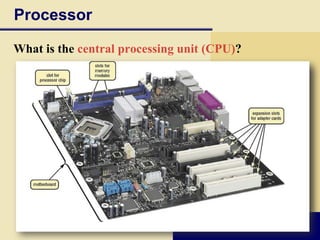
The document provides an overview of computers and their basic components, including input, output, processing, storage, and communications devices. It discusses the different types of hardware, software, and how computers are used in various contexts like education, business, healthcare, and more. The key aspects of computers, such as what they are, their basic functions and operations, components, and applications are summarized.