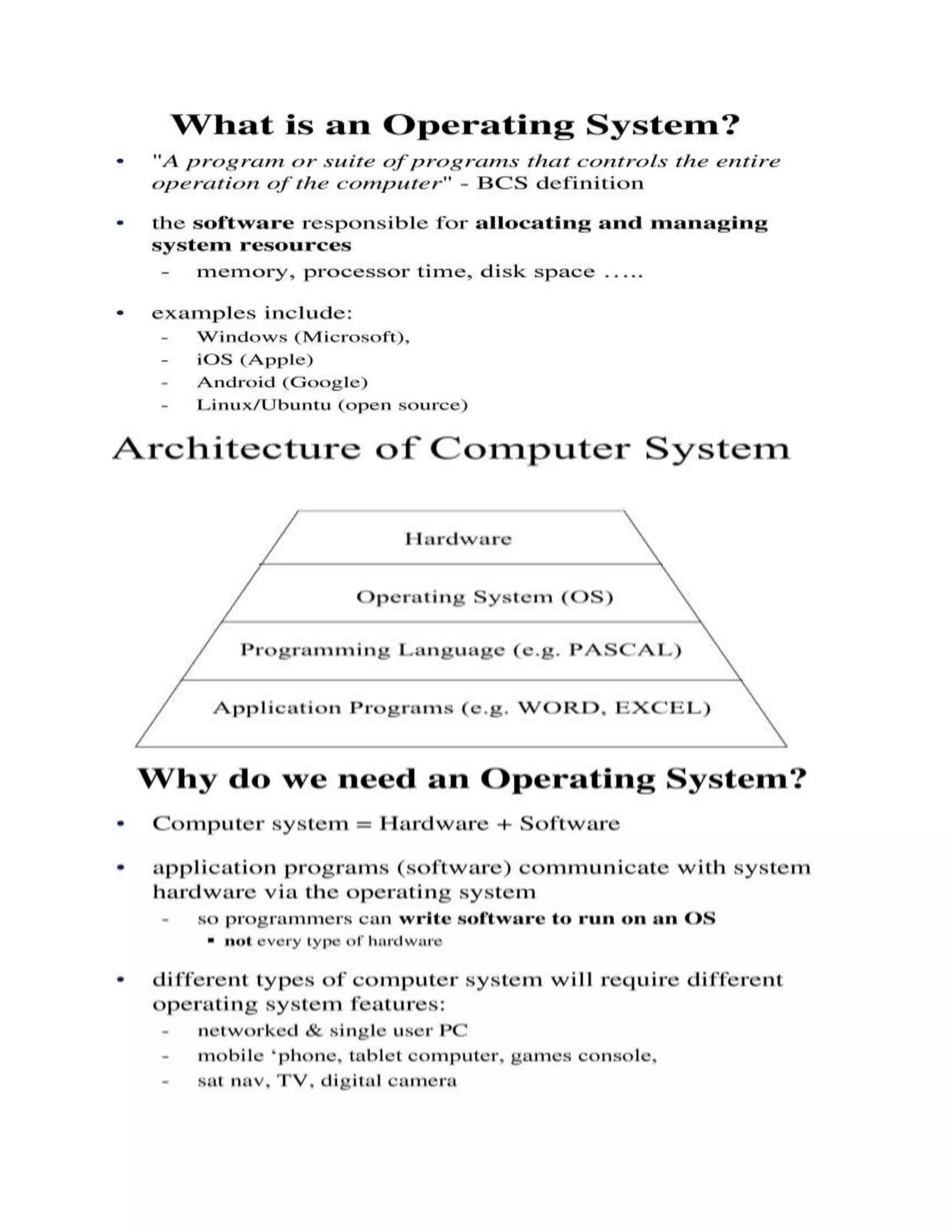
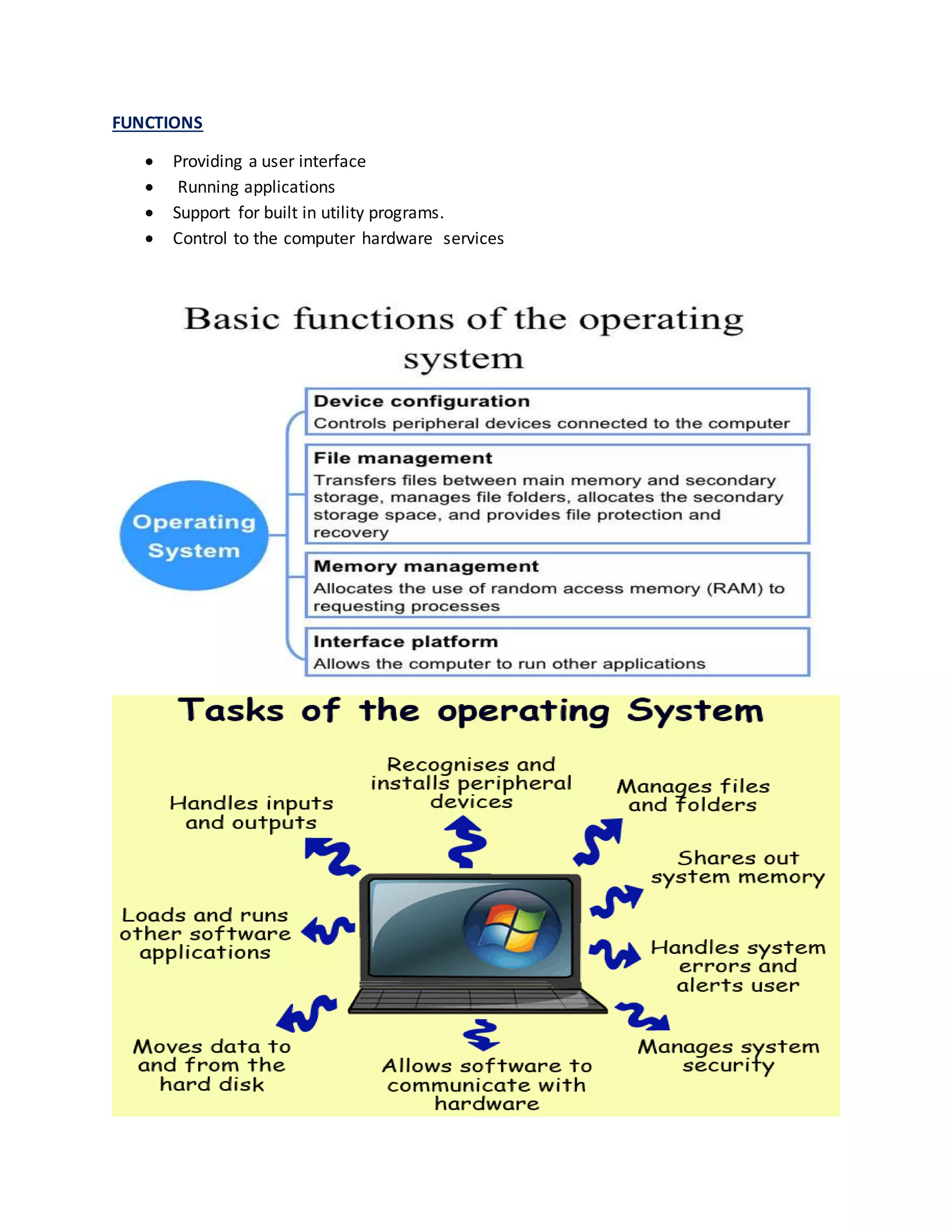
The operating system is a collection of software that manages computer hardware resources and allows application programs to function. It acts as an interface between the user and computer hardware, allocating resources like memory and controlling input/output. Common operating systems include Windows, Mac OS, Linux, and Android.