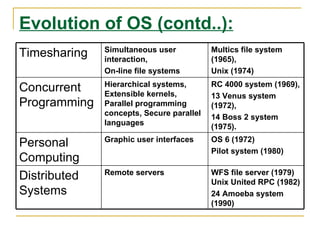
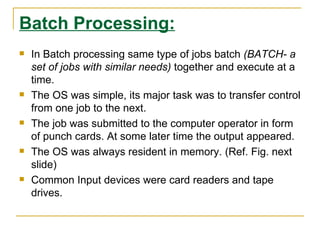
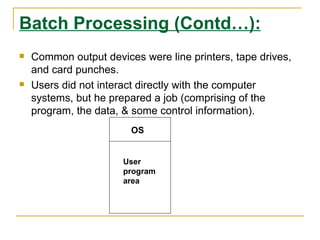
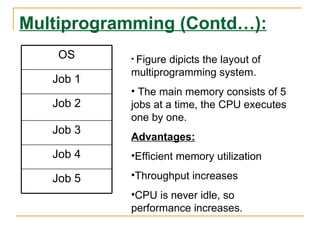
The document discusses an introduction to operating systems. It defines an operating system as software that enables computer programs to run by managing hardware resources. It describes the evolution of operating systems from batch processing to time-sharing systems. It outlines the main functions of operating systems like managing memory, controlling I/O devices, and facilitating file storage. It also differentiates between single-user and multi-user operating systems.