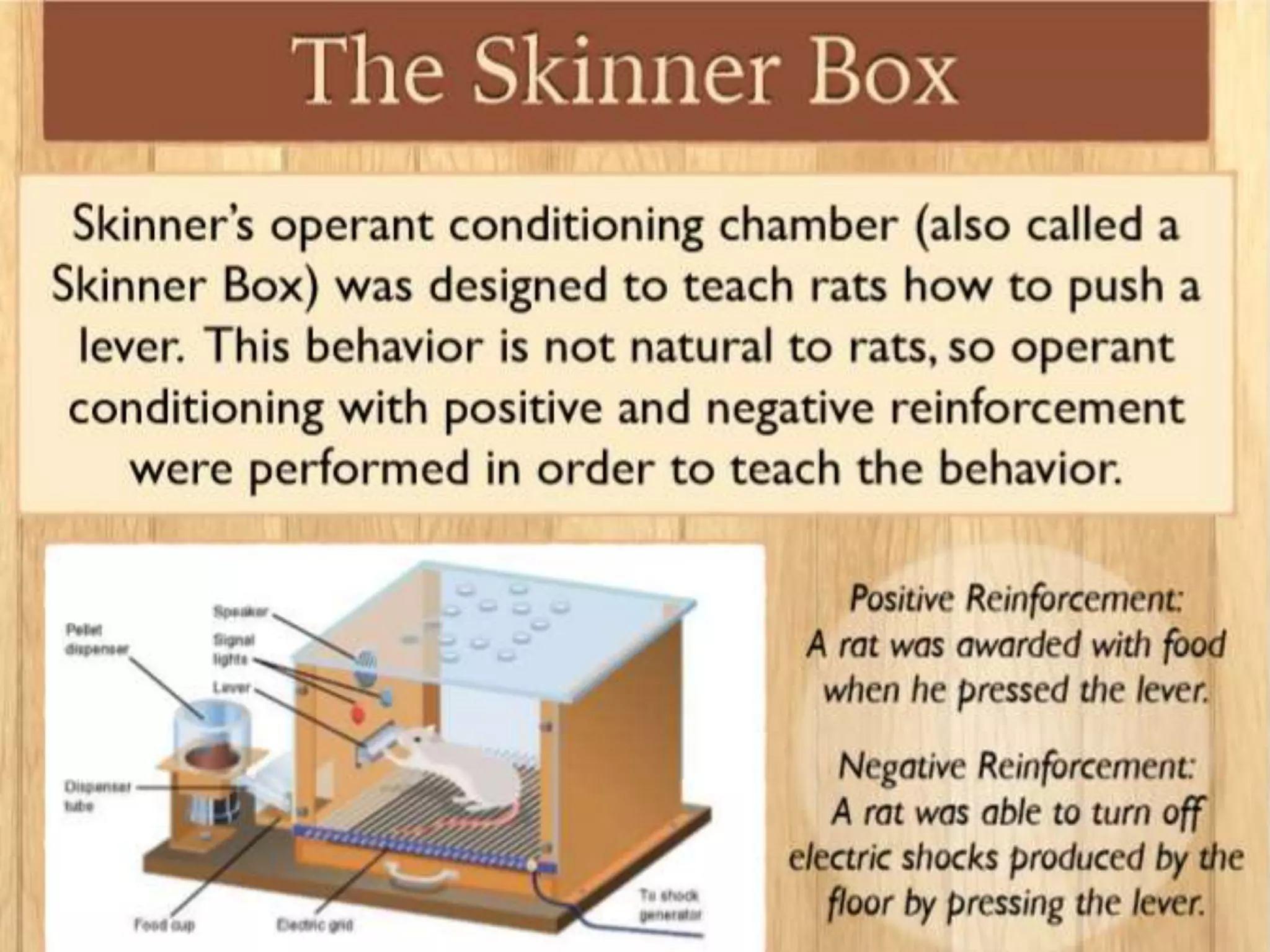
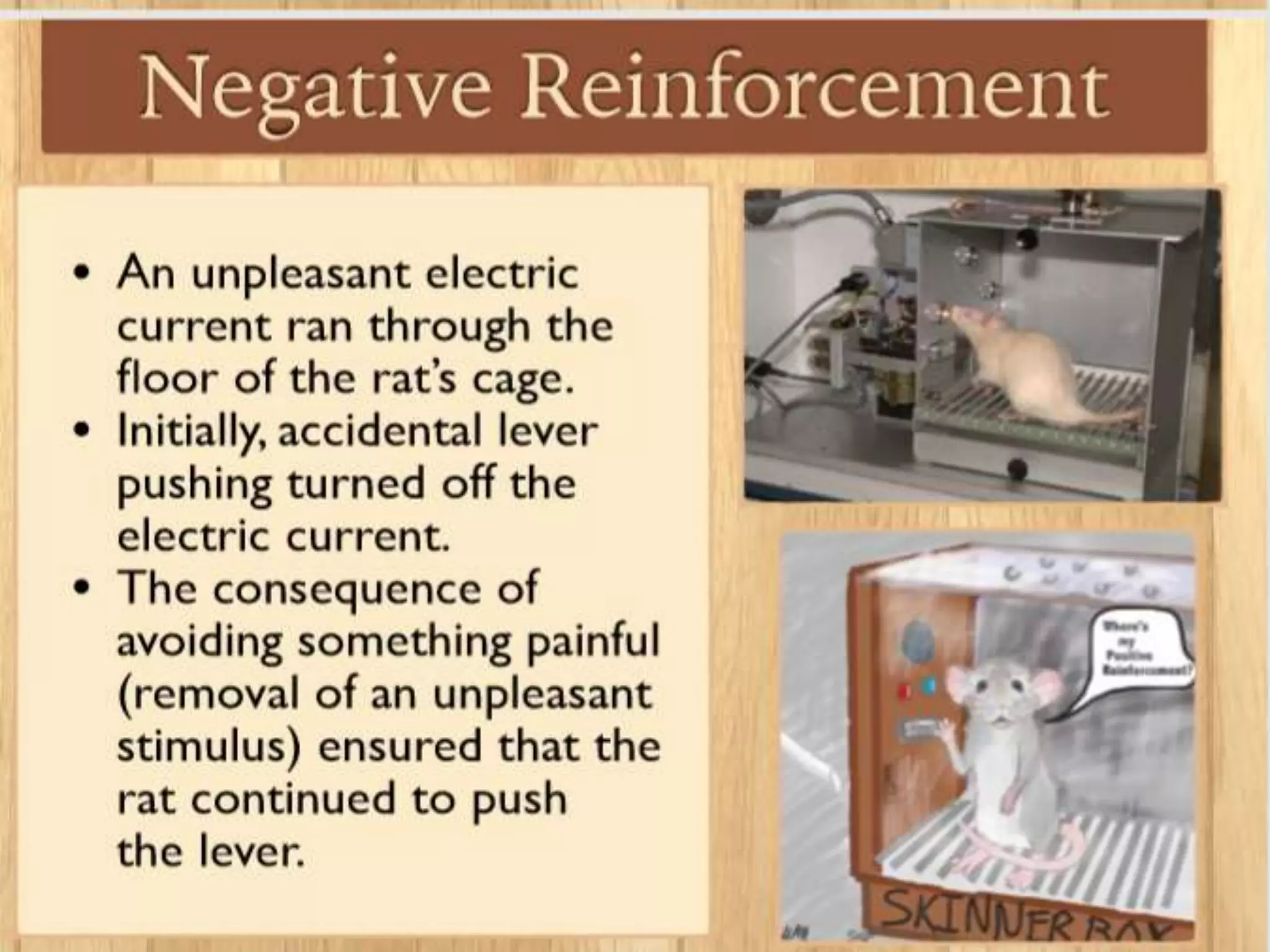
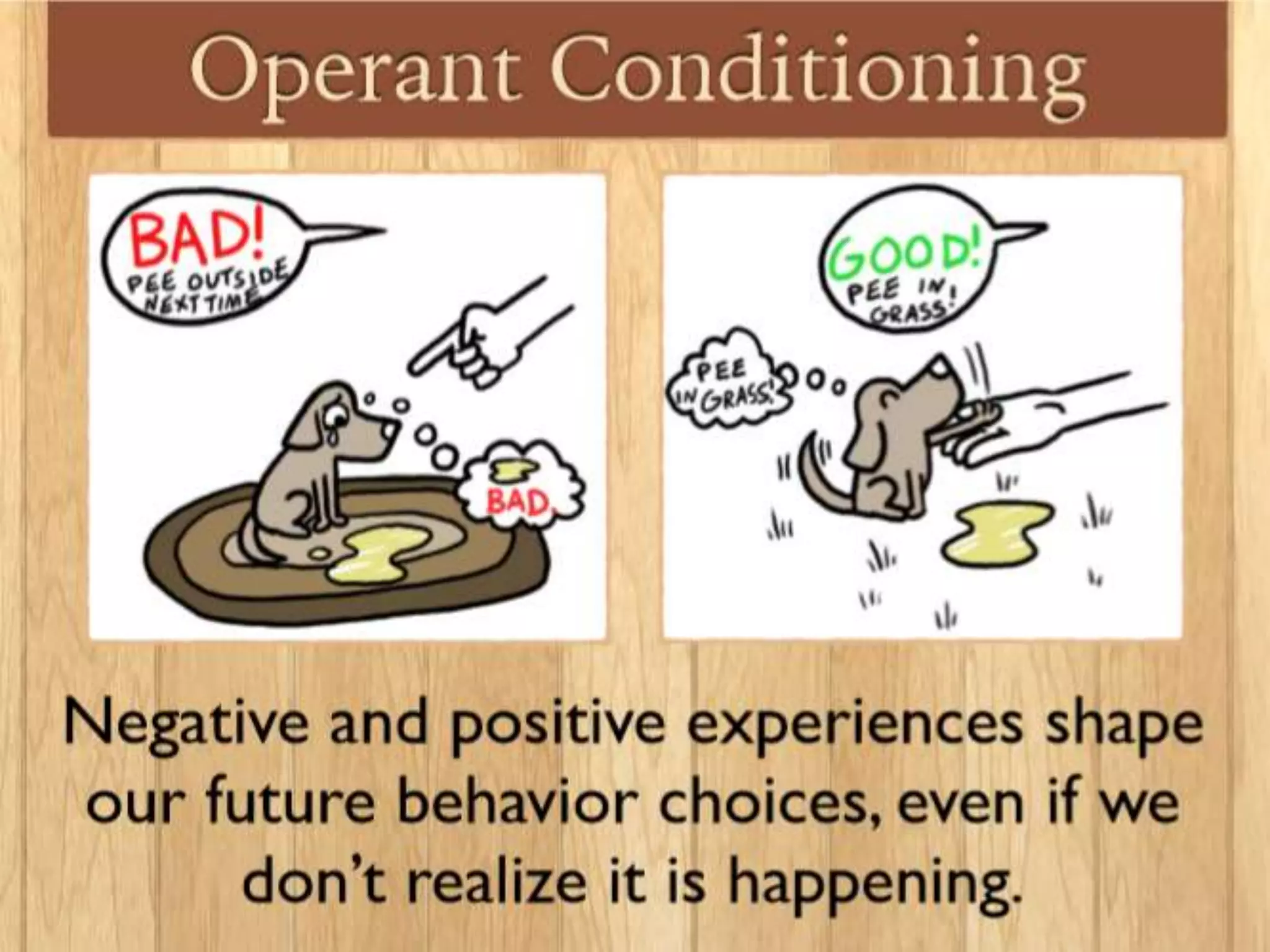
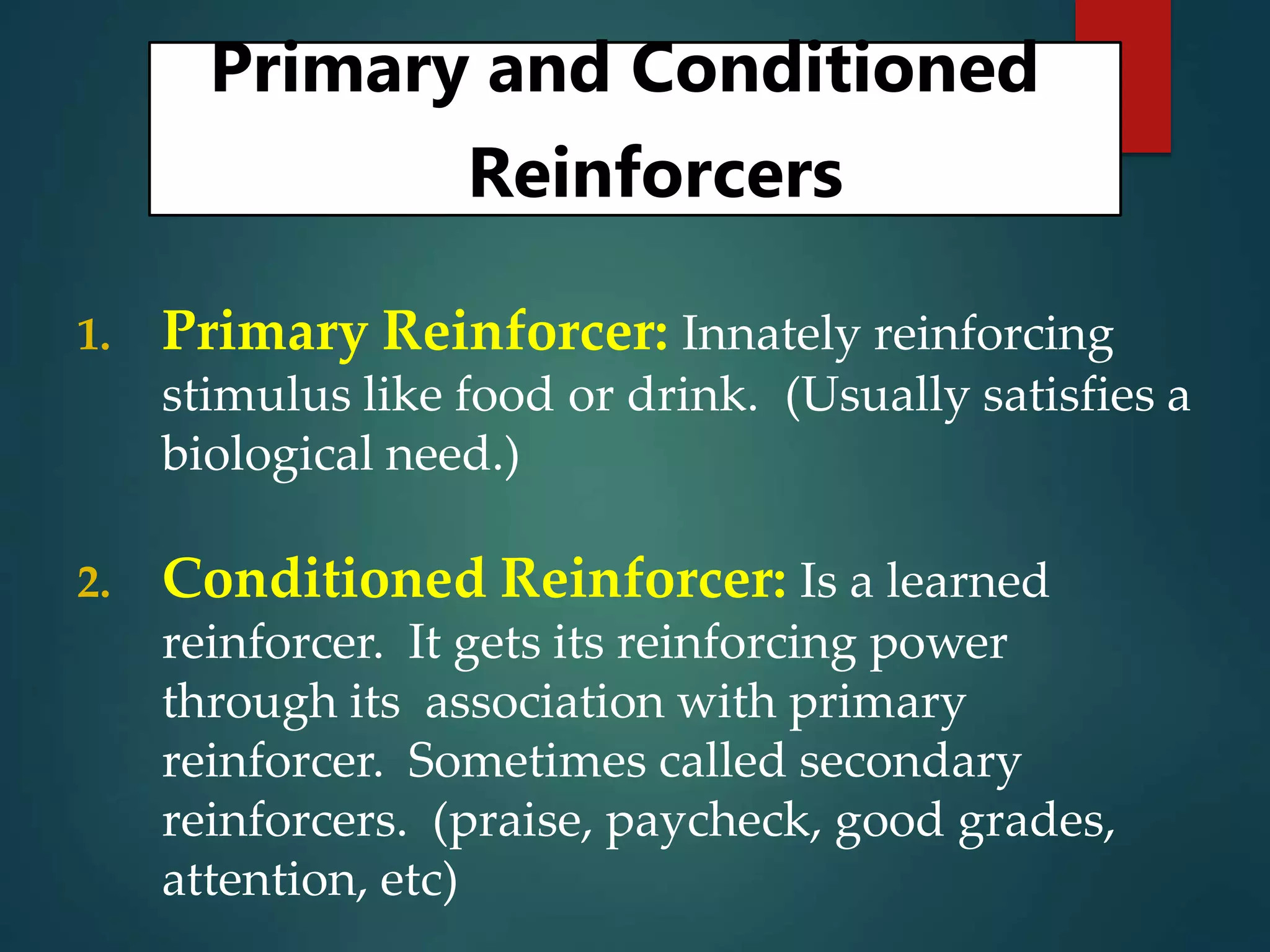
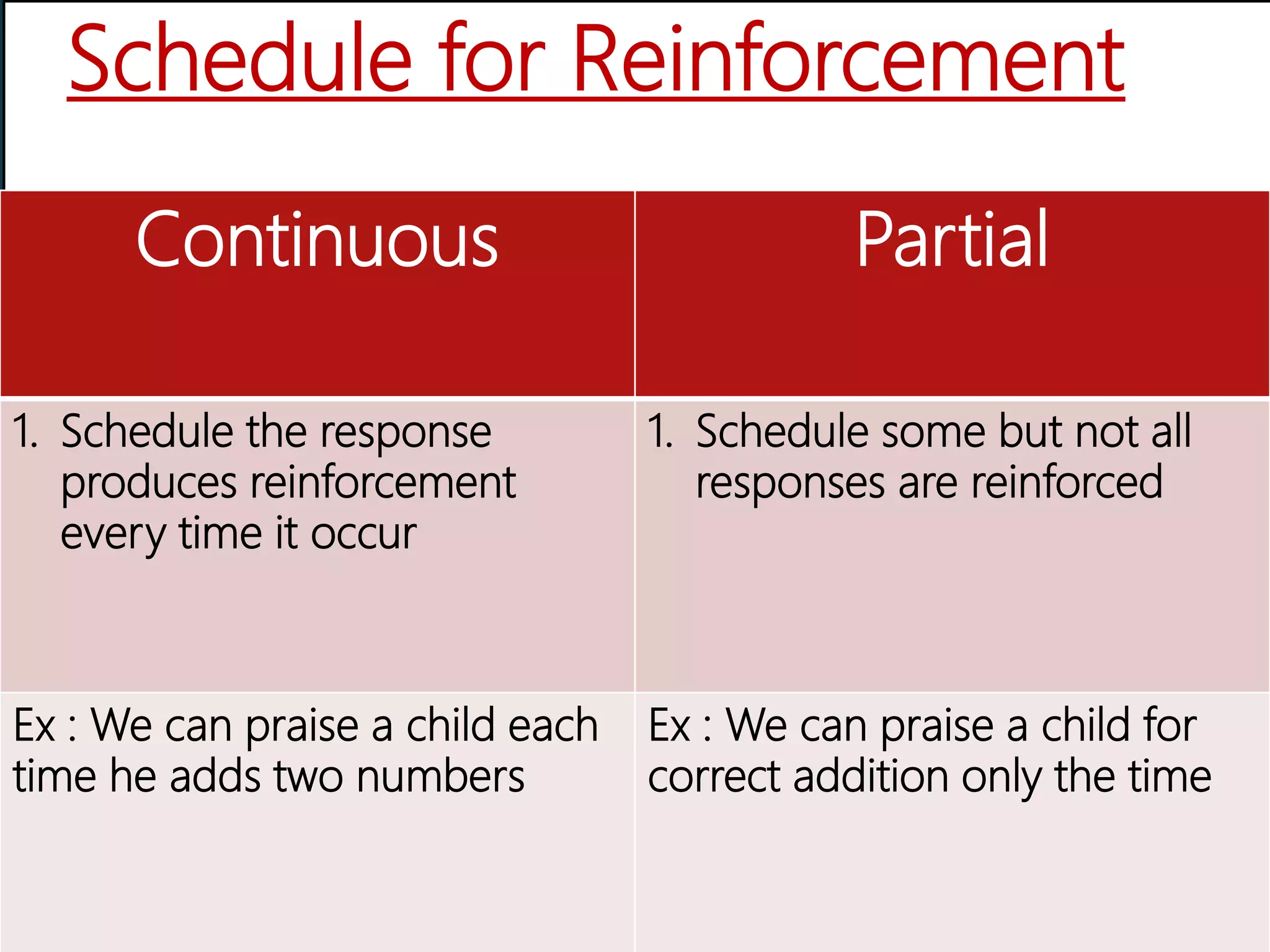
Operant conditioning is a theory of learning developed by B.F. Skinner that focuses on how voluntary behaviors are strengthened or weakened based on positive and negative consequences. Key aspects of operant conditioning include shaping behavior through reinforcement of closer approximations, extinction of behaviors when reinforcers are withheld, and spontaneous recovery of behaviors when removed from extinction. Reinforcers can be positive or negative and immediate or delayed. Different reinforcement schedules like fixed ratio and variable interval impact behaviors differently. While punishment can decrease behaviors, it has disadvantages and reinforcement is generally a better strategy for behavior change. Operant conditioning principles are applied in behavior modification programs and to enhance performance in sports, work, and other domains.