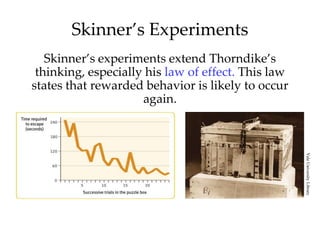
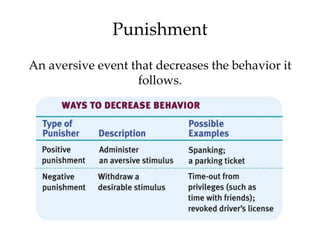
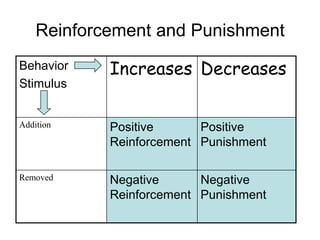
Skinner expanded on Thorndike's law of effect through experiments using operant chambers. He studied how behaviors are strengthened or weakened through reinforcement and punishment. Operant conditioning uses reinforcement to shape behaviors through successive approximations. Reinforcers can be primary, conditioned, immediate, or delayed. Reinforcement schedules include continuous, partial, fixed-ratio, variable-ratio, fixed-interval, and variable-interval. Punishment typically has negative side effects and provides no information to change behavior.