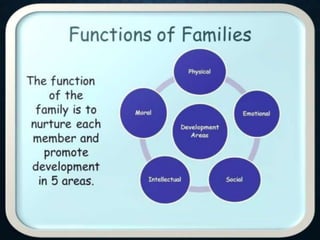
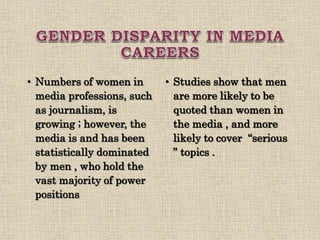
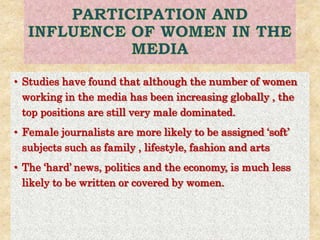
This document discusses gender identity and the factors that influence it. It explains that gender identity is a person's internal sense of their own gender, which may correspond with or differ from their sex assigned at birth. Gender identity is shaped by both biological factors like genes and hormones, as well as social and environmental influences from family, culture, and media. The roles of family, society, and media in socializing children and promoting gender stereotypes are also examined.