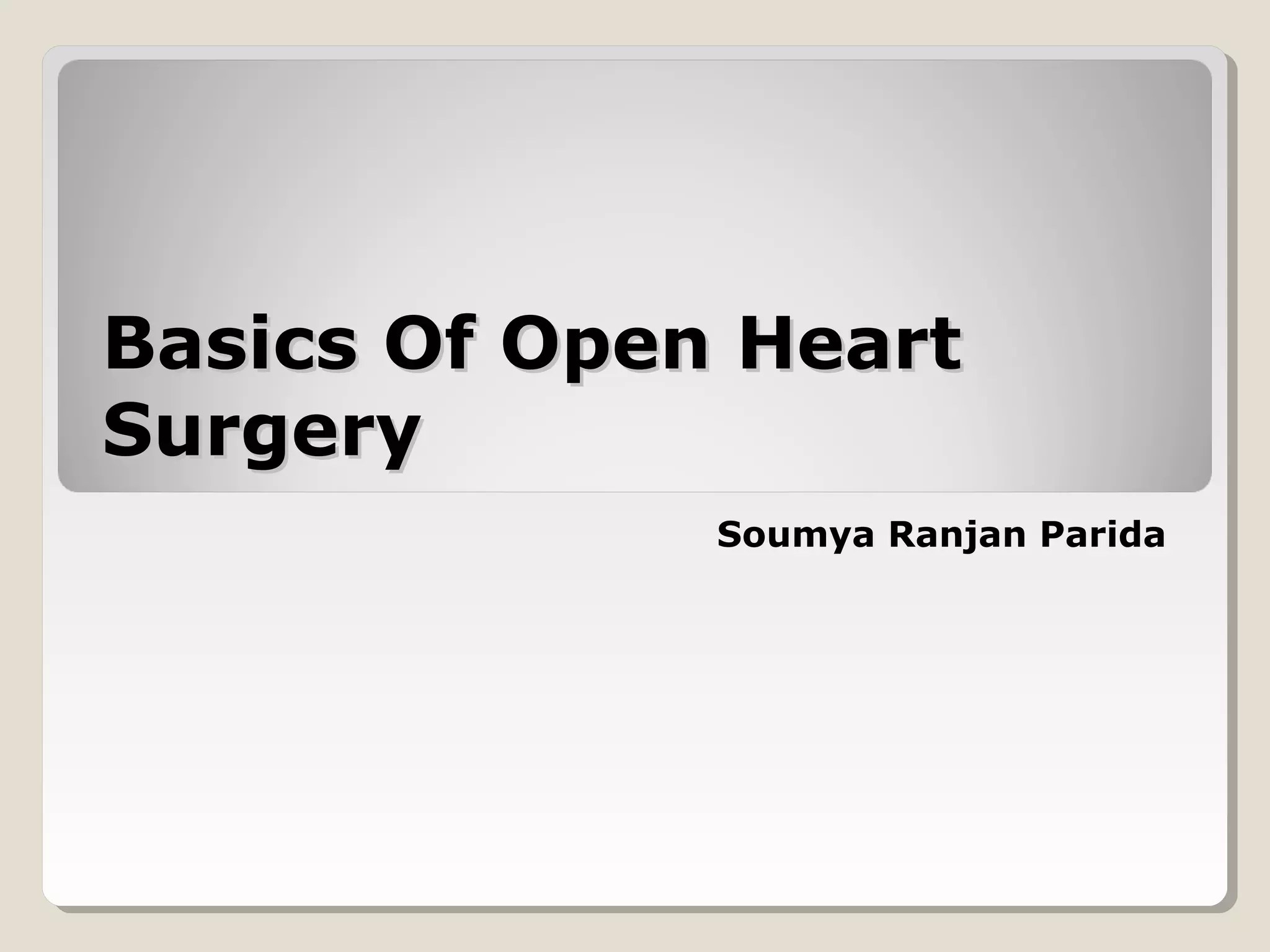
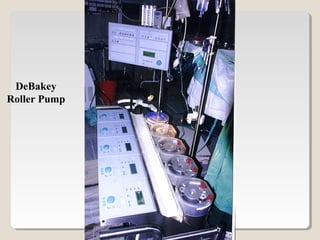
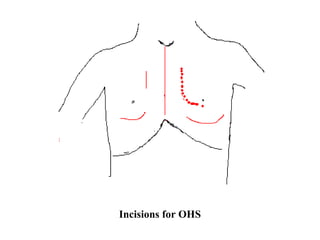
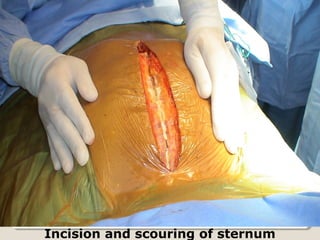
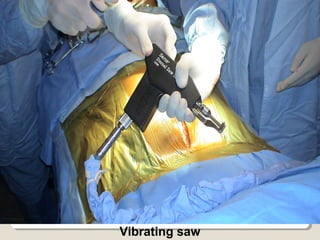
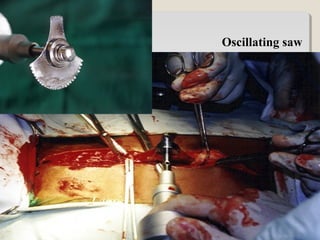
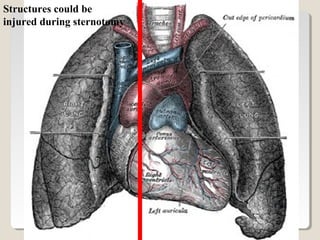
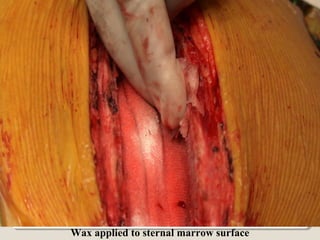
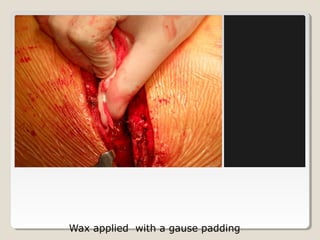
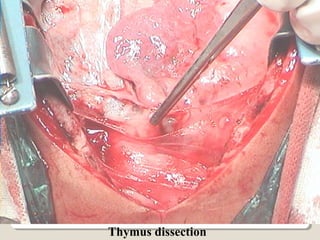
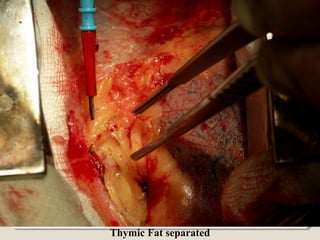
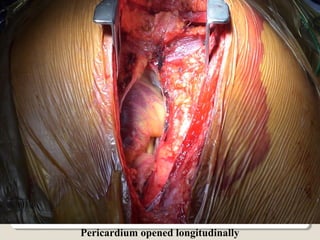
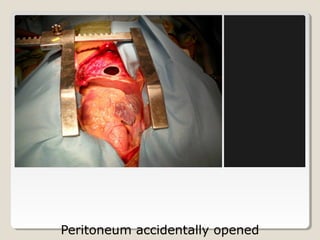
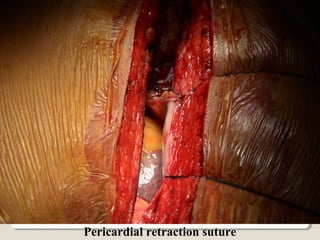
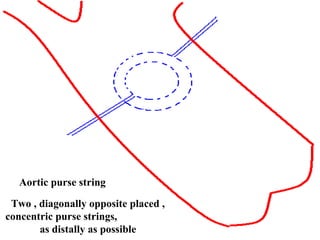
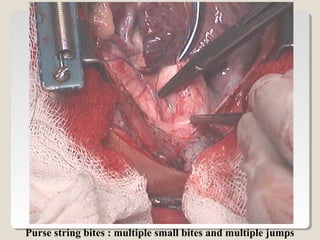
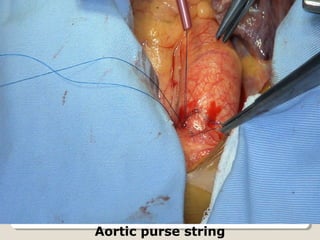
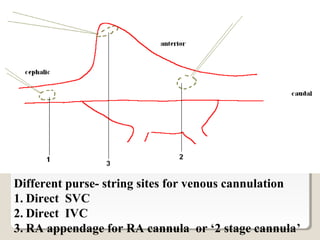
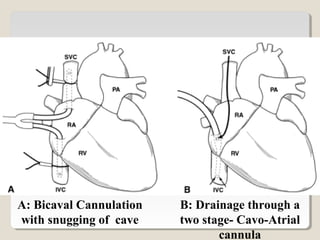
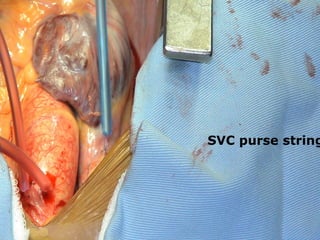
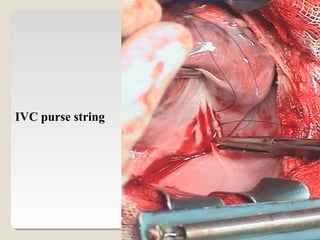
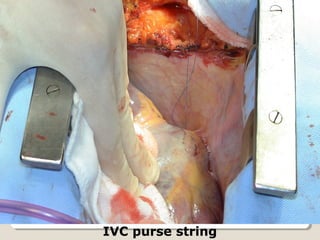
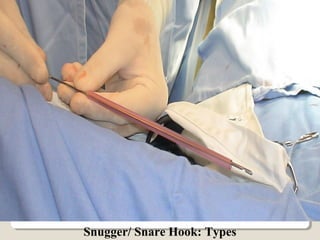
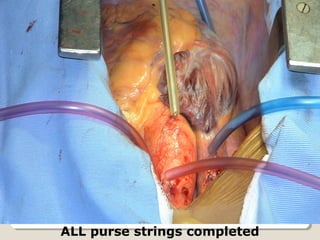
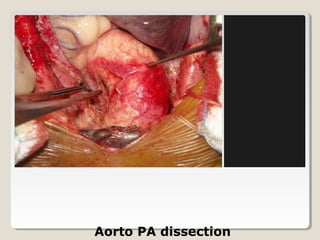
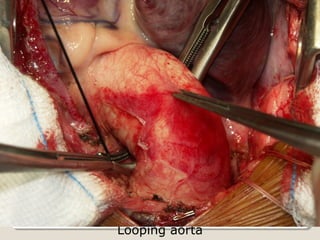
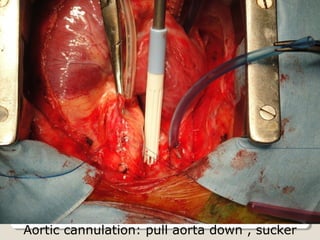
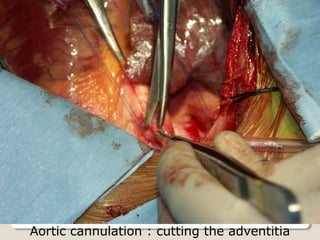
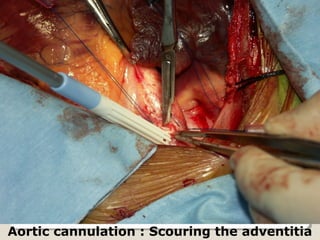
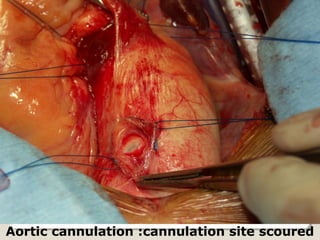
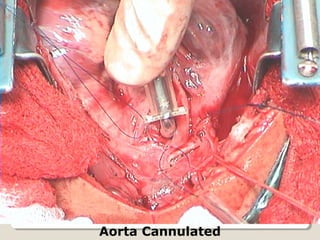
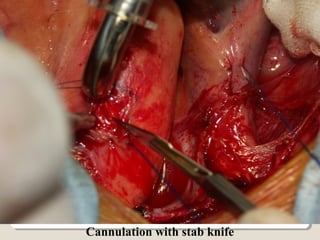
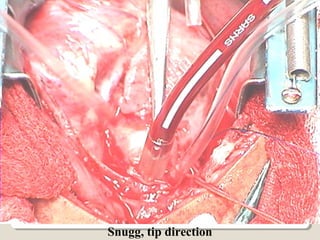
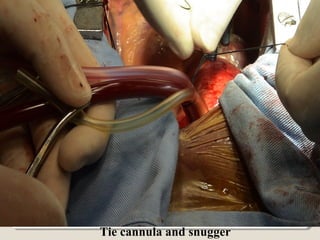
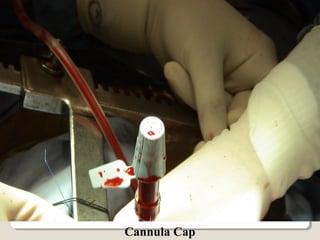
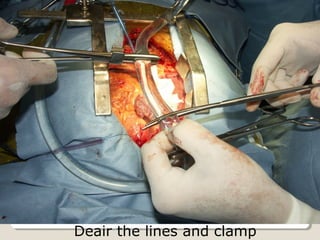
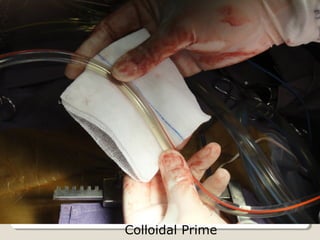
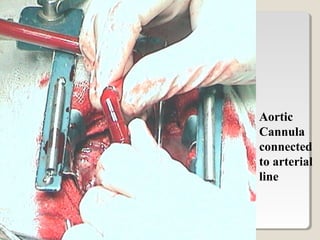
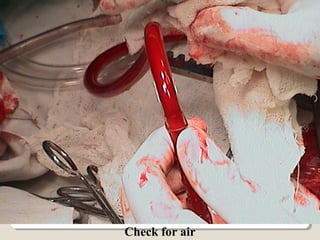
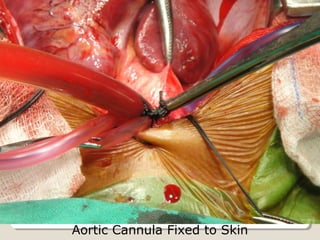
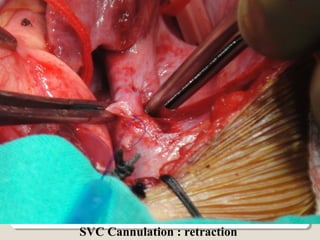
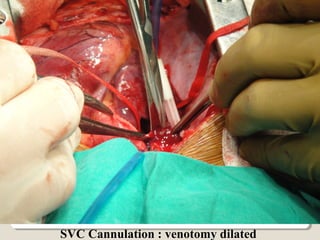
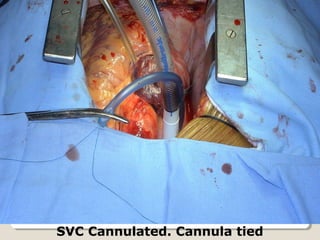
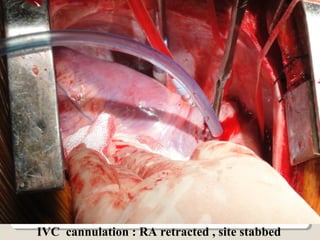
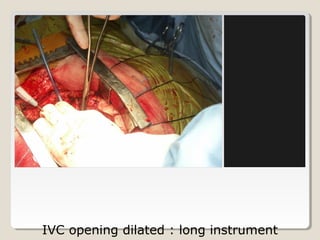
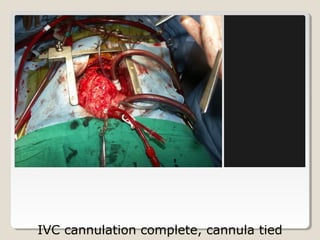
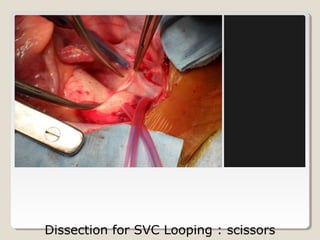
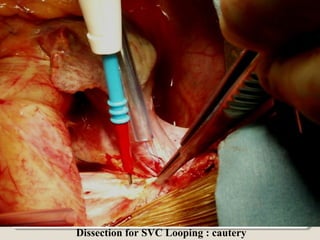
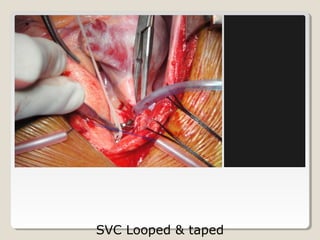
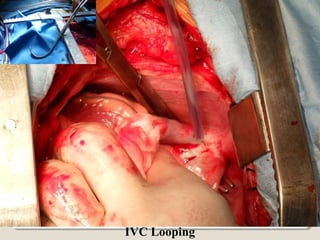
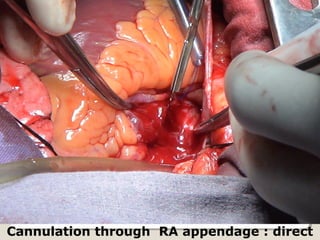
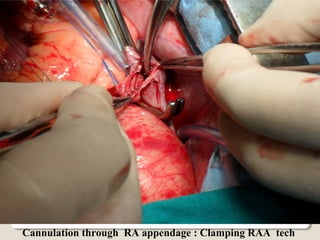
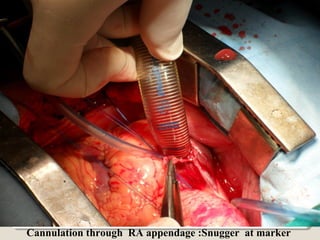
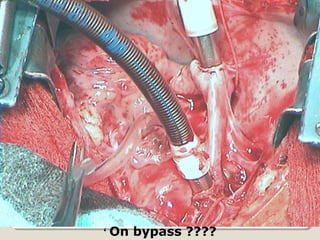
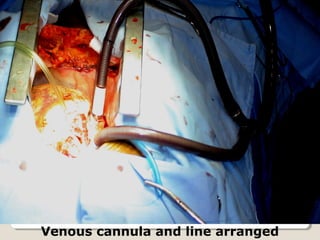
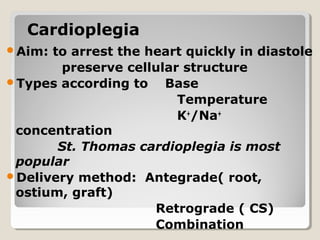
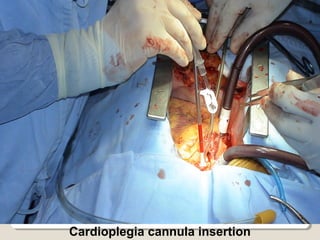
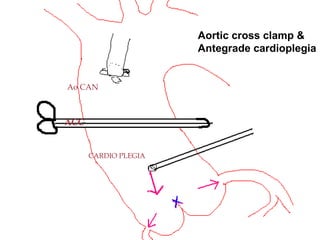
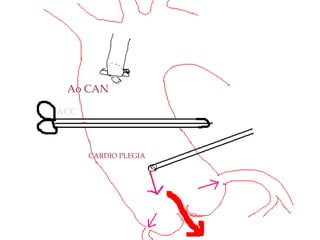
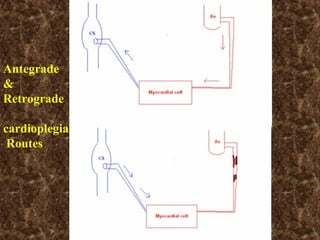
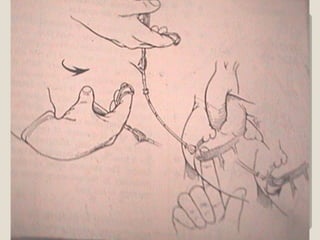
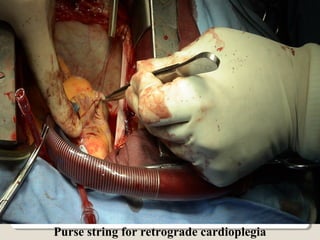
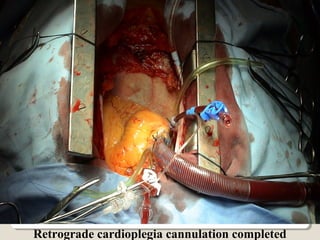
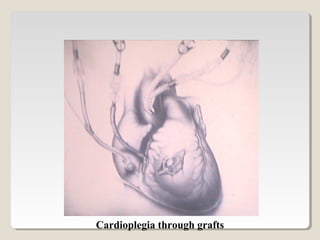
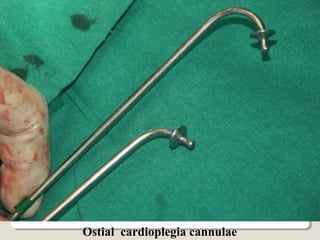
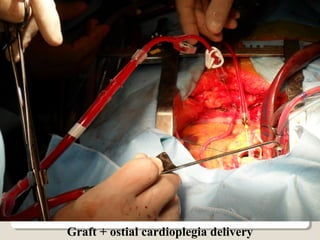
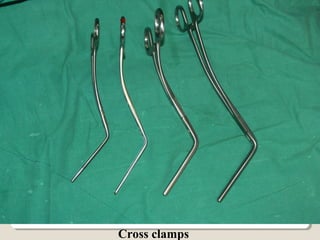
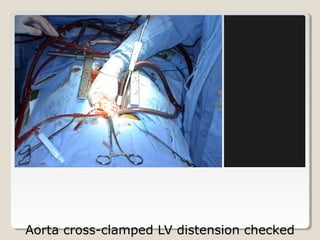
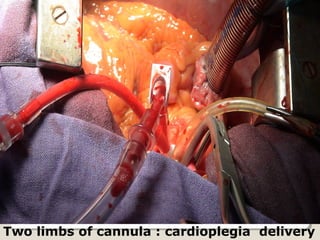
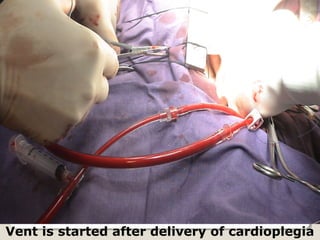
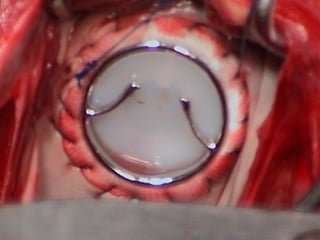
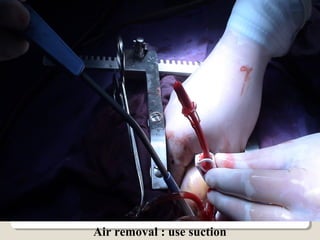
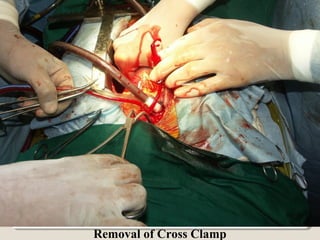
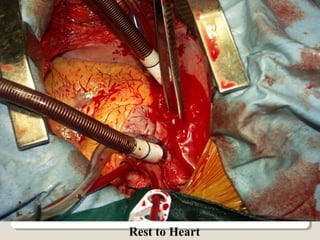
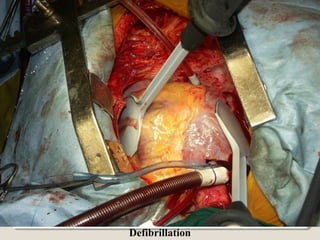
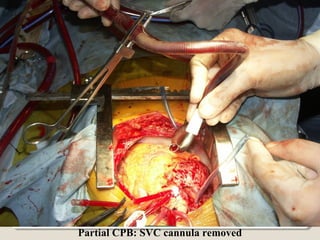
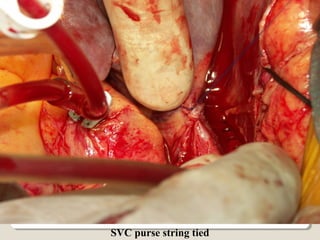
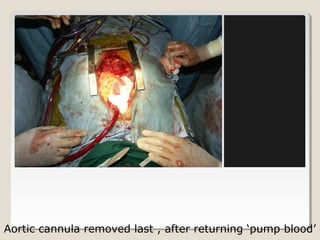
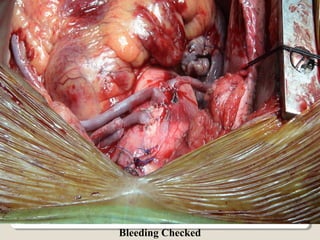
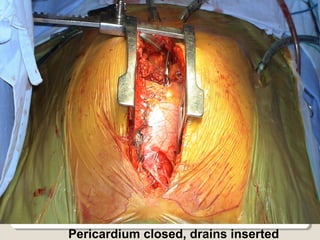
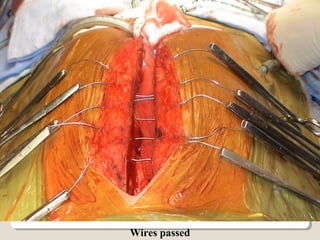
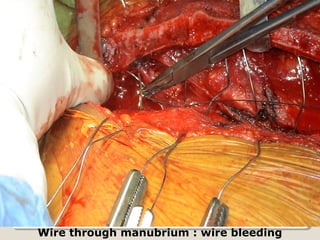
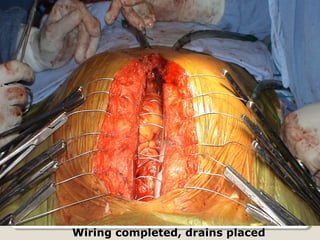
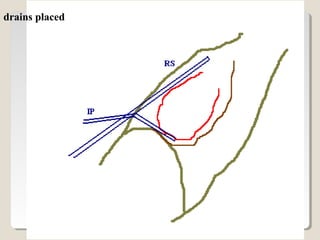
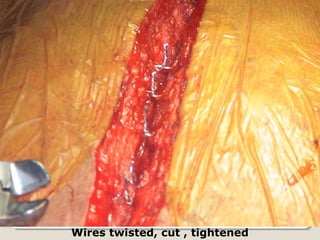
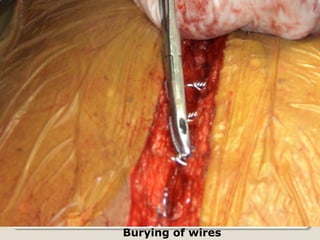
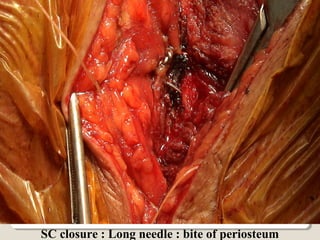
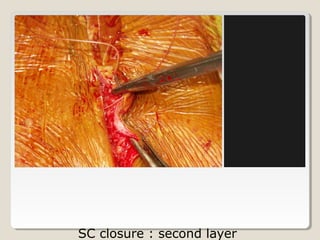
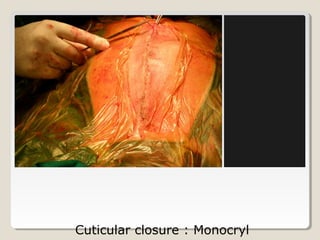
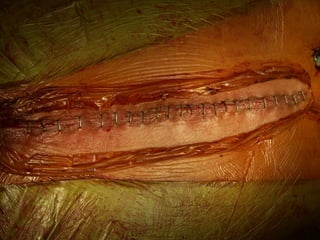
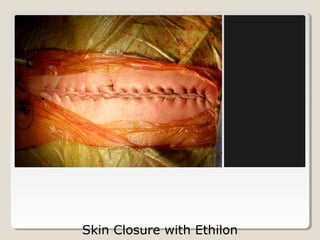
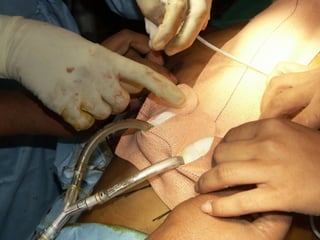
Open heart surgery requires that the heart be still, dry, and relaxed. The basic steps involve opening the chest, placing the patient on bypass to circulate their blood, cooling and stopping the heart, performing the intracardiac operation, closing the heart, and weaning the patient off bypass. Key parts of the procedure include cannulating major vessels like the aorta and vena cavas to connect the patient to the bypass machine, delivering cardioplegia to arrest the heart, performing the necessary incisions and repairs on the heart, and closing the chest. Developing techniques have allowed some operations to be done without placing the patient on bypass.