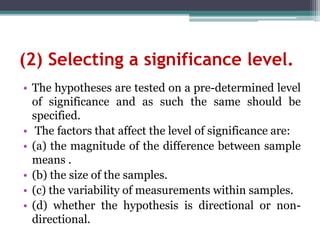
This document provides an overview of hypotheses testing in research. It defines a hypothesis as an explanation or proposition that can be tested scientifically. The main points covered are:
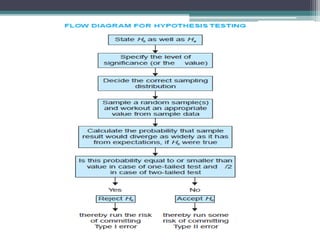
1. The general procedure for hypothesis testing involves making formal statements of the null and alternative hypotheses, selecting a significance level, choosing a statistical distribution, collecting a random sample, calculating probabilities, and comparing probabilities to determine whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
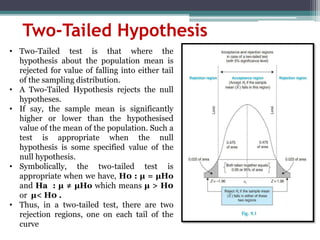
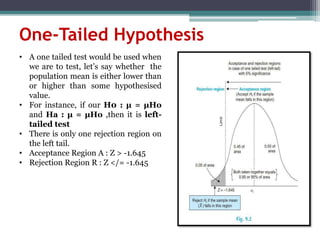
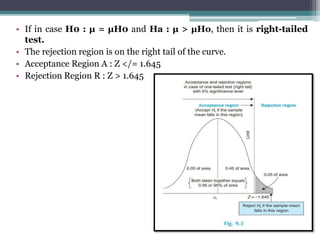
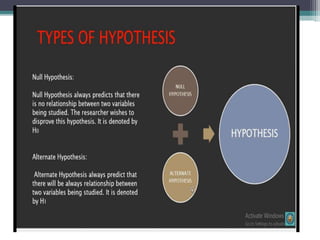
2. There are two types of hypotheses tests - one-tailed and two-tailed. A one-tailed test has one rejection region while a two-tailed test has two rejection regions, one in each tail.
3. Errors in hypothesis testing can occur when the null hypothesis







![[1] Making a Formal statement
• The step consists in making a formal statement
of the null hypothesis (H0 ) and also of the
alternative hypothesis (Ha ).
• This means that hypotheses should be clearly
stated, considering the nature of the research
problem .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic-hypothesistestingrms-220512050900-f9392d9d/85/TOPIC-HYPOTHESIS-TESTING-RMS-pptx-10-320.jpg)