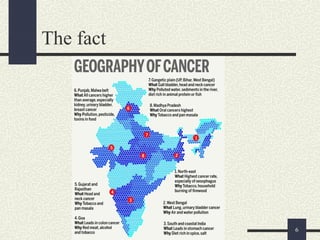
The presentation discusses cancer care in India, emphasizing the significance of early detection and prevention of various cancers, particularly breast and cervical cancers. It outlines the role of oncology nursing and highlights preventive measures, including lifestyle changes and early diagnostics. Additionally, it provides information on government schemes and assistance available for cancer patients in India.